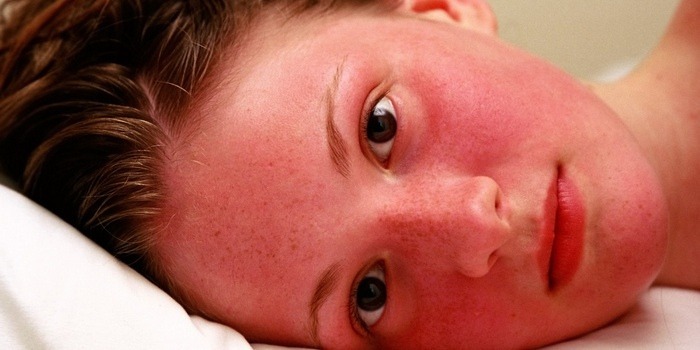
Treatment methods
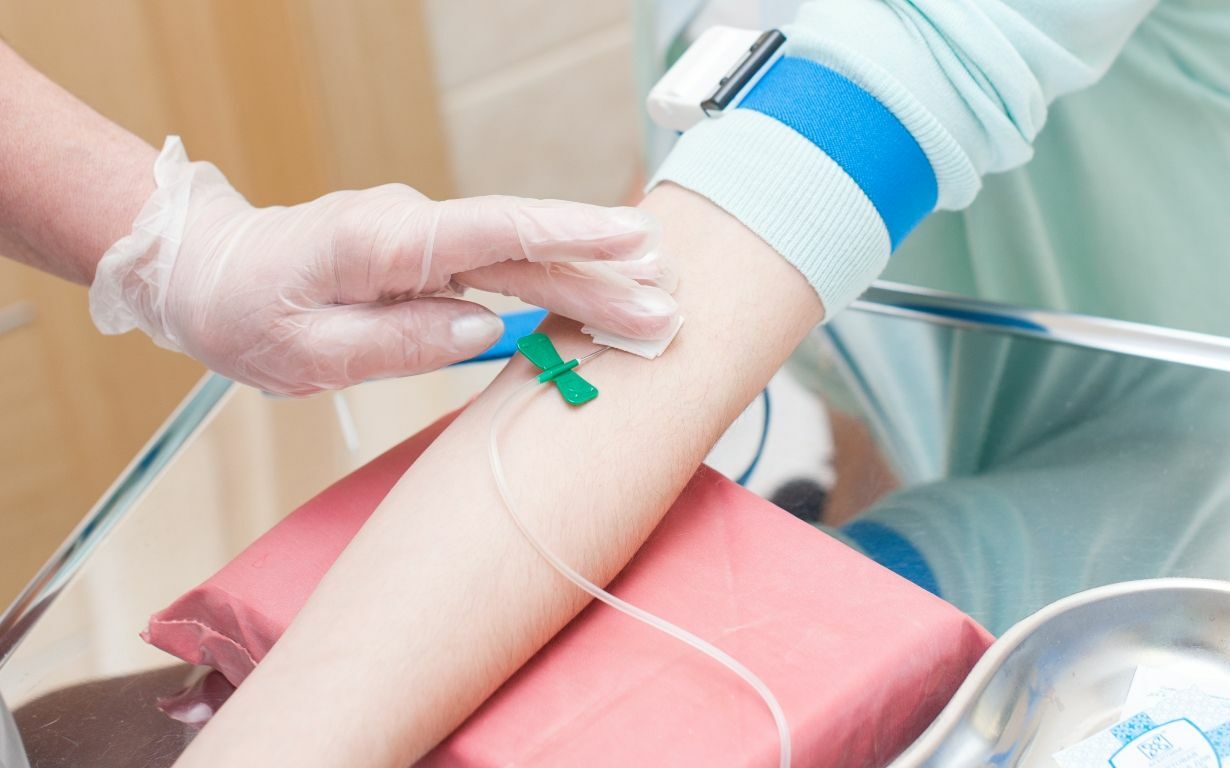
The procedure extracts excessive amounts of blood, resulting in a decrease in red blood cell levels and blood viscosity. This process helps prevent complications associated with excessive red mass.
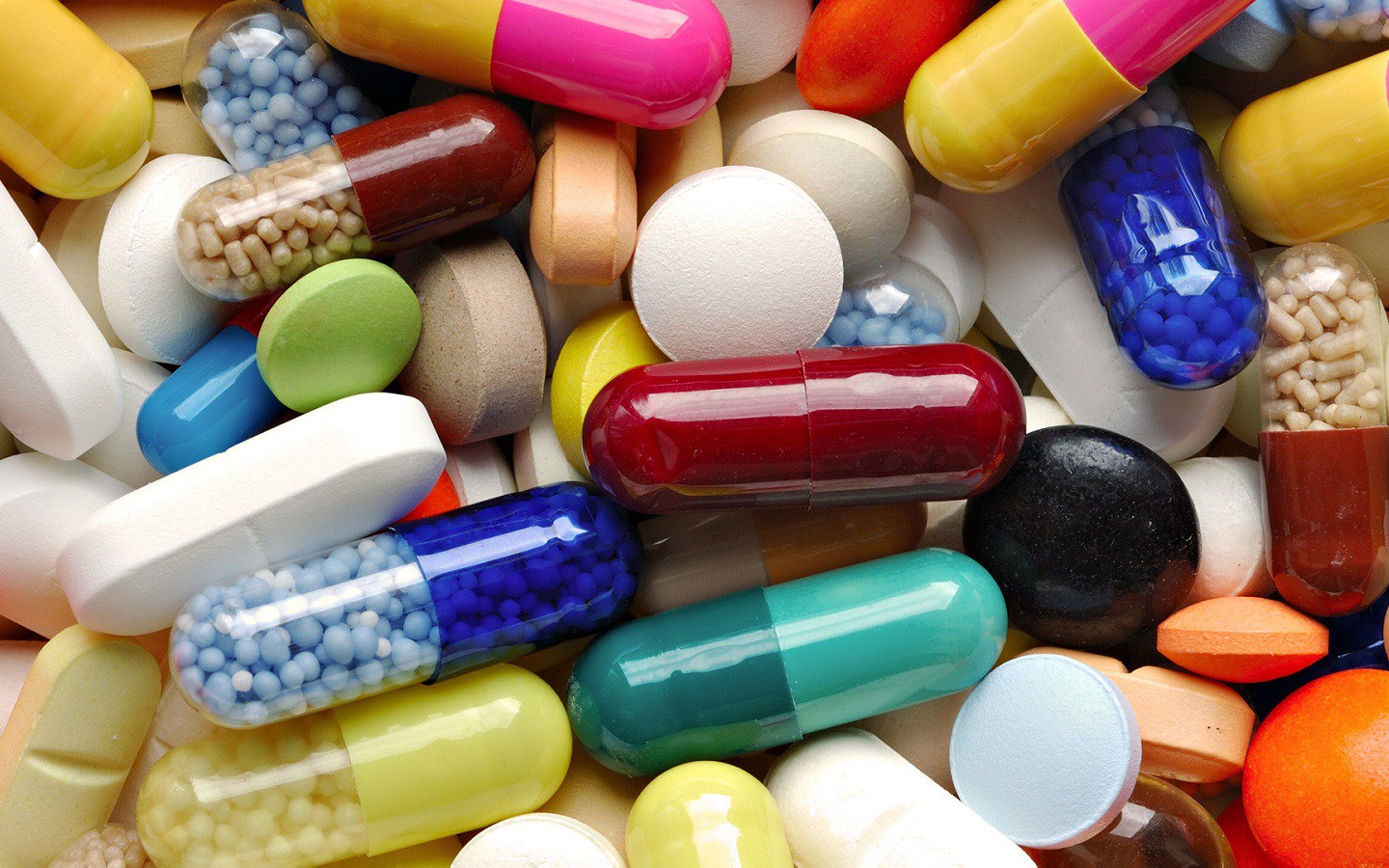

Specialists may prescribe blood thinning medications such as aspirin. They help prevent blood clots and improve circulation. Interferon drugs may be used to reduce red blood cell production.
An excessive number of red blood cells can increase the viscosity of the blood, making it harder to move through the blood vessels and raising blood pressure. This can cause headaches, especially in the morning or after physical activity.
An increased number of red blood cells can cause the spleen to enlarge, causing discomfort and pain in the upper abdominal area. In patients with this disease, hemoglobin and hematocrit (the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume) levels are significantly elevated, which can affect blood concentration and blood properties.
Increased blood viscosity makes it difficult for oxygen to reach the tissues, which can cause feelings of weakness and fatigue. The skin may take on a reddish hue due to an increase in red blood cells.
Premature or hypoxic neonates may develop transient polycythemia. In the primary condition, mutation of the JAK2 gene leads to excessive production of red blood cells.
A secondary condition develops when the excessive red blood cell count is due to some other disease or factor such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, cancer, kidney cysts, taking androgens, or even prolonged exposure to high altitudes.
Diagnosis at MDI Clinic
The physician begins gathering information about the patient’s medical and family history. This includes symptoms, duration of symptoms, risk factors and heredity. Physical examination may reveal signs such as reddened skin, enlarged spleen, and high blood pressure.
Blood tests assess hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, and red blood cell concentration. Elevated values may prompt the physician to suspect polycythemia.
Diagnosis of a secondary condition may require genetic testing to detect mutations in genes responsible for regulating red blood cell production, such as the JAK2 gene.
An enlarged spleen can be detected with an ultrasound scan. An electrocardiogram is performed to evaluate the heart and to detect signs of cardiac overload, which may be a consequence of the disease. Arterial gasometry assesses blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, which can be useful in assessing oxygen metabolism and the patient’s condition.
The best doctors in Israel
All doctorsPrice
How we are working
-
StepSubmitting an application

Simply leave a request or contact us at the numbers in the contact tab.
-
StepTalking to a counselor

You will be contacted by our consultant shortly after submitting your application. After the interview and review of the medical history, he will proceed to prepare a treatment program.
-
StepProgram preparation

Our specialists will draw up a personalized program, including a diagnosis and treatment schedule, the names and positions of the doctors, and the cost of treatment.
-
StepTravel arrangements

The coordinator will plan and organize the trip in every detail – from advice on preparing documents, to purchasing tickets, booking accommodation and even organizing excursions.
-
StepTreatment

Our staff will provide patient support throughout the diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation period.

Форма обратной связи
"*" indicates required fields