NEWS
 Hormone therapy for cancer in Turkey
Hormone therapy for cancer in Turkey
Hormone therapy is an important treatment for cancer, especially for breast cancer, prostate cancer, and other hormone-sensitive tumors. In Turkey, as in many other countries, innovative research and new approaches to hormone therapy are being developed, making the country a leading center for cancer treatment in the region.
One of the major benefits of hormone therapy is its ability to weaken or stop tumor growth by blocking the action of hormones that promote cancer. In Turkey, oncology specialists are actively applying this method based on advanced research and clinical experience.
One of the key applications of hormone therapy in Turkey is the treatment of breast cancer. This type of cancer often depends on estrogen for its growth, and hormone therapy aims to block the action of these hormones. Turkish oncologists use various drugs such as tamoxifen, letrozole and anastrozole to suppress the growth of cancer cells and improve the prognosis for patients.
Another important area of hormone therapy in Turkey is the treatment of prostate cancer. Hormonal therapy may be used as primary or adjuvant treatment, or in case of relapse. The use of andrgen deprivation and other hormonal agents can significantly slow disease progression and improve patients’ quality of life.
However, despite the effectiveness of hormone therapy, it can cause certain side effects such as hyperpigmentation, gynecomastia, hypertension and others. Therefore, doctors in Turkey carefully monitor patients and adjust the treatment regimen according to their individual needs.
Turkey is an important center for cancer treatment, including hormone therapy. With the constant introduction of the latest research and treatment methods, this country continues to improve cancer outcomes and provide high quality medical care to patients.
 Immunotherapy for cancer in Turkey
Immunotherapy for cancer in Turkey
Immunotherapy is one of the most innovative and promising methods of cancer treatment. This approach is based on using the immune system to fight cancer cells. Surgery and chemotherapy treatments destroy cancer cells directly. The immune method activates all the body’s forces against malignant neoplasms.
One of the most common approaches to immunotherapy is the use of drugs aimed at blocking proteins – checkpoint inhibitors – that suppress immune system activity. This promotes the effective attack of cancer cells.
CAR-T therapy involves modifying a patient’s T cells to enhance the attack of cancer cells. The modified T cells are returned to the patient’s body where they can fight cancer more effectively.
The technique also consists of developing and administering vaccines that stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Unlike chemotherapy, immunotherapy is generally characterized by fewer side effects because it aims to activate the immune system rather than directly damaging healthy tissue.
This method can lead to long-term cancer control, even after treatment has ended. This means that patients can have long periods of remission and improved quality of life.
Leading cancer centers in Turkey are equipped with modern equipment and have highly qualified medical staff capable of effectively applying immunotherapy methods.
Immunotherapy is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer, providing patients with more effective and less toxic treatments. In Turkey, this treatment method is widely available and continues to show outstanding results in the treatment of cancer.
 Radiation therapy in Turkey
Radiation therapy in Turkey
Radiation therapy is one of the main treatments for cancer and is used all over the world. In Turkey, radiation therapy occupies a significant place in the comprehensive treatment of cancer due to modern technology and high level of medical care.
Turkey introduces advanced techniques and uses modern medical equipment for radiation therapy. This includes linear gas pedals, cyberknife and other advanced systems that allow us to precisely and effectively irradiate tumors.
Medical centers in Turkey attract qualified oncologists and radiologists with extensive experience in radiation therapy. This ensures that patients receive quality and professional service.
Each patient is thoroughly examined and an individualized treatment plan is drawn up, taking into account the peculiarities of their disease and general state of health. This allows for optimal results and minimizes side effects.
Radiation therapy in Turkey is often used in combination with other treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and targeted therapy. This comprehensive approach increases the effectiveness of treatment and improves patient prognosis.
Medical centers in Turkey provide comfortable conditions of stay for patients and their attendants. This includes modern wards, quality food and friendly staff who provide patients with support and care throughout their treatment.
Radiation therapy in Turkey is an effective and safe method of cancer treatment, which provides patients with high quality medical care and comfortable conditions of stay. With state-of-the-art technology, highly qualified specialists and a comprehensive approach to treatment, radiation therapy in Turkey is becoming an increasingly popular choice for many patients.
 Target therapy in Turkey
Target therapy in Turkey
Targeted therapy is an innovative approach to cancer treatment based on identifying and blocking specific molecular targets within cancer cells. In Turkey, this technique is being actively introduced and successfully applied in the treatment of various types of cancer.
Turkey’s medical industry is renowned for its highly qualified specialists in oncology and genetics, who provide a high level of cancer diagnosis and treatment. Many medical centers in the country are equipped with advanced equipment and laboratories to perform molecular genetic analyses and identify mutations sensitive to targeted therapies.
One of the main advantages of targeted therapy is its personalized nature. In Turkey, each patient is given a thorough molecular genetic diagnosis to identify unique mutations in their cancer cells. Based on these data, an individualized therapy plan is developed, including the selection of the most effective medications.
Many medical centers in Turkey have access to the latest drugs. Targeted therapy is often used in combination with other treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. This enhances the effect of the treatment and increases the chances of a full recovery. In Turkey, doctors take a comprehensive approach to cancer treatment, incorporating various therapies to achieve the best results.
Medical institutions in Turkey are actively introducing innovative technologies and developing new drugs for targeted therapy. This includes developing more precise and effective molecular inhibitors, antibodies and other drugs aimed at blocking specific molecular pathways in cancer cells. Thanks to innovative technologies and drugs, Turkish doctors are able to offer patients modern and effective treatment methods.
 Bone marrow transplantation in Turkey
Bone marrow transplantation in Turkey
Bone marrow transplantation is one of the most complex and intensive procedures in oncology and hematology. Turkey, with its advanced medical infrastructure and highly trained specialists, offers a number of advantages for patients in need of this procedure.
Turkey is famous for its skilled specialists in oncology, hematology and transplantology. The country’s leading medical centers attract experienced physicians and researchers who specialize in bone marrow transplantation. This ensures that patients have access to high quality medical care and professional care at all stages of the procedure.
Medical facilities in Turkey are equipped with the advanced equipment and technology necessary for a successful bone marrow transplant. This includes specialized bone marrow transplant units, state-of-the-art operating suites, high-tech laboratories and intensive care units.
Doctors in Turkey take an individualized approach to each patient, taking into account their unique needs and disease patterns. Before undergoing a bone marrow transplant, each patient undergoes a comprehensive examination and health assessment to develop an optimal treatment plan.
Medical services in Turkey are often available at lower prices compared to other countries in Western Europe and North America, while not compromising on the quality and level of medical expertise. This makes Turkey an attractive destination for patients looking for high quality treatment at affordable prices.
Medical centers in Turkey are constantly introducing the latest innovative treatments in the field of bone marrow transplantation. This includes the use of new drugs, technologies, and transplant approaches that help improve patient outcomes and prognosis.
Medical facilities in Turkey strictly adhere to international safety and quality standards when performing bone marrow transplants. This includes following strict sterilization protocols, infection control, post-operative patient follow-up, and more.
 Chemotherapy in Turkey
Chemotherapy in Turkey
Turkey’s medical industry is known for its highly skilled oncologists and chemotherapy specialists. Physicians and medical staff receive extensive training and have years of experience working with chemotherapy patients. This ensures that patients receive the highest level of medical care and concern throughout their treatment.
Medical facilities in Turkey are equipped with modern equipment and the use of advanced technologies in the field of chemotherapy. This includes innovative intravenous drug infusion machines, precision drug dosing systems and real-time patient monitoring.
One of the main principles of chemotherapy in Turkey is an individual approach to each patient. Before treatment begins, a thorough assessment of your health status, type and stage of disease, and other factors that may affect the choice of the best chemotherapy regimen is performed. This allows the treatment to be tailored to each patient’s individual needs as much as possible and to achieve the best possible results.
Many medical centers in Turkey have access to the latest innovative drugs and participate in clinical trials to develop new chemotherapy methods and regimens. This allows patients to access advanced therapeutic options and participate in the advancement of medical science.
While the quality of medical care in Turkey remains high, the cost of chemotherapy is generally more affordable than in many other countries, making Turkey an attractive choice for patients looking for quality treatment at affordable prices.
The benefits of chemotherapy in Turkey include highly qualified specialists, state-of-the-art equipment and technology, personalized treatment, access to innovative drugs and clinical trials, patient comfort and support, and affordability of treatment. These factors make Turkey one of the leading medical destinations for chemotherapy and attract patients from all over the world.
 Kidney cancer treatment in Turkey
Kidney cancer treatment in Turkey
Renal oncology is a serious disease that requires ongoing research and the development of new treatment approaches. The latest research in this area represents the hope for more effective diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
One of the key areas of recent research is molecular classification of tumors. Scientists are studying the genetic and molecular characteristics of the disease to identify specific tumor subtypes that may affect prognosis and response to treatment. This allows you to personalize your treatment approach and improve outcomes for patients.
Immunotherapy has become one of the most promising areas. New research in immunotherapy includes the development of innovative drugs, such as proven point inhibitors and CAR-T cell inhibitors, that aim to activate the immune system to fight cancer cells. This opens up new possibilities for treating the disease, especially when traditional methods fail.
Metabolomics, which studies metabolic processes in the body, is an increasingly important area of research in cancer. Research in this area is helping to identify unique metabolic profiles of tumors that can be used to diagnose, assess prognosis, and develop new therapies.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in oncology research, including kidney cancer. Machine learning and data analytics algorithms are used to process large amounts of information, including medical educations, genomic data, and images to identify new patterns, predict prognosis, and optimize treatment strategies.
Clinical trials remain an important tool in the development of new methods for the diagnosis and treatment of renal cancer. Participating in clinical trials allows patients to gain access to cutting-edge treatments, as well as contribute to science and help other patients in the future.
 Throat cancer treatment in Turkey
Throat cancer treatment in Turkey
Throat cancer is a dangerous cancer that can have a serious impact on a patient’s quality of life. However, thanks to the constant advancement of medical science and technology, there are many modern treatments that can improve the prognosis of patients.
Modern methods of molecular genetic diagnostics can identify unique mutations and characteristics of cancer cells, which can help in individualizing the treatment approach and selecting the most effective drugs.
Pembrolizumab is an immunotherapy drug that blocks the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway, enhancing the body’s immune response to cancer cells. It has been approved to treat the disease when other treatments fail. Multiple clinical trials have shown its effectiveness in increasing survival and improving prognosis for patients.
Nivolumab is also a PD-1 inhibitor, which stimulates the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells. It has been approved for the treatment of various forms of cancer, including metastatic soluble keratinosis and low differentiation cancers. Nivolumab demonstrates a high level of efficacy and tolerability, making it an important drug in the treatment of this disease.
Cetuximab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks receptors for epidermal growth factor (EGFR), which prevents cancer cells from growing and developing. It is often used in combination with radiotherapy or chemotherapy to treat throat cancer. Many clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in improving survival and disease control.
In recently completed clinical trials, the use of Pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy was found to result in a significant increase in survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic type of disease
 Bladder cancer treatment in Turkey
Bladder cancer treatment in Turkey
Bladder oncology represents a significant medical problem worldwide. Despite existing treatments that include surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, new drugs and treatments promise to improve the prognosis and quality of life for patients with this disease.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in the treatment of the disease is the use of immunotherapy. Drugs such as inhibitors of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) activate the body’s immune system to better fight cancer cells. This treatment method has already shown significant results in treating patients with metastatic and recurrent types of disease, and research continues to expand its use.
Although chemotherapy is one of the standard treatments, recent research is focusing on developing more effective and less toxic drugs. For example, the use of combination chemotherapy regimens that include novel agents such as doxorubicin and navelbine can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
New research is also focusing on the development of combination therapies involving a mix of different therapeutic approaches. For example, combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy or targeted therapy may enhance treatment effects and improve outcomes for patients with bladder cancer.
In addition to new treatments, research is also focusing on prevention and early diagnosis of the disease. Advances in screening methods and more accurate diagnostic tests allow the disease to be detected earlier, when it is more amenable to successful treatment.
Overall, new drugs and treatments for bladder cancer offer new opportunities to improve patient outcomes and survival. Further research and advances in technology in this area could significantly improve the prognosis for patients suffering from this serious disease.
 Lip cancer treatment in Turkey
Lip cancer treatment in Turkey
Lip cancer, although rare compared to other cancers, is still a serious health threat, especially in individuals exposed to prolonged sun exposure and those who use tobacco and alcohol. Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, new research in this area promises to improve therapeutic outcomes and patient survival.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in the treatment of the disease in Turkey is the development of molecular diagnostics. New methods for analyzing genetic material are identifying specific mutations and molecular markers that can help individualize treatment and predict outcome.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an innovative educational technique that provides high quality, high resolution tissue images. In recent years, OCT has begun to play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and monitoring of the disease. This method allows visualization of structural changes in lip tissue with high clarity, making it a valuable tool for diagnosis and evaluation of treatment efficacy.
Recent research in immune genetics is helping to understand the role of the immune system in the development and progression of this disease. Analyzing genetic markers associated with immune response may help predict response to immunotherapy and identify patients who may benefit most from this treatment modality.
Nanotechnology represents a promising method for drug delivery and education in cancer cells. Nanoparticles can be used on cancer cells, increasing the effectiveness of the therapy and reducing toxicity to healthy tissues.
Advances in e-medicine are opening up new opportunities for real-time monitoring of lip cancer patients and remote consultations. This allows for better patient monitoring, reduced risk of complications, and improved patient outcomes.
Equally important is the research in the area of the disease. Programs to prevent this disease, which include promoting healthy lifestyles, regular dental checkups, and limiting tobacco and alcohol use, play a key role in reducing its prevalence.
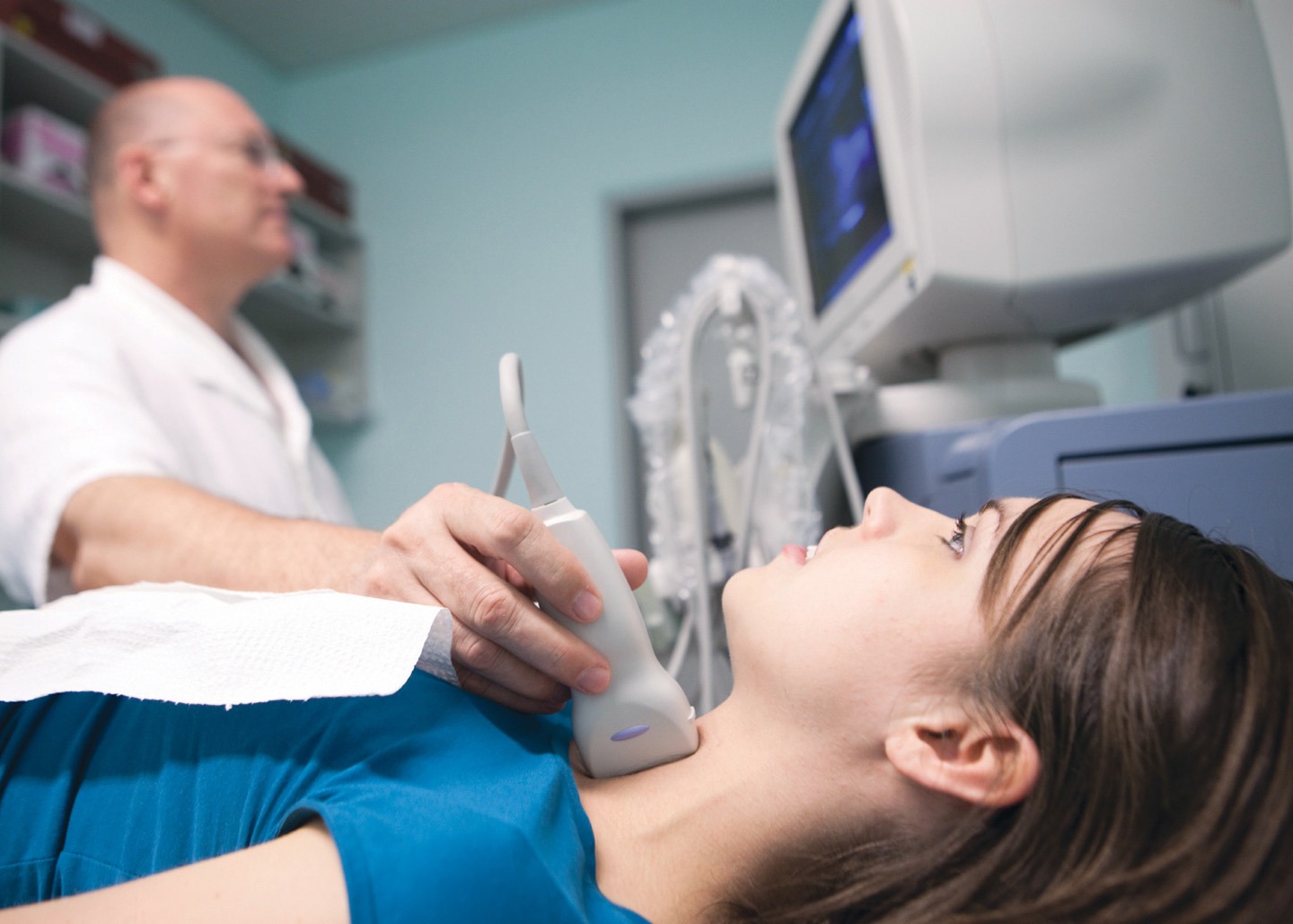 Thyroid cancer treatment in Turkey
Thyroid cancer treatment in Turkey
Thyroid oncology is ranked as the third most common of all malignancies in women. Despite the general trend of increasing numbers of cases, the latest research on these diseases offers promising prospects.
One of the most significant advances is the development of molecular diagnostics. New research is identifying molecular markers and genetic changes that may help in more accurately diagnosing disease subtypes, determining stage, and predicting treatment outcome.
Targeted therapy is becoming an increasingly important component of cancer treatment. Innovation in this field focuses on developing new drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells. This allows treatment to be individualized and more effective while reducing side effects.
Research in prognostic markers and predictive factors helps in determining the risk of recurrence and predicting survival in patients with cancer. This allows the selection of the most appropriate treatments and optimizes strategies for monitoring and following patients after therapy.
Most often, doctors resort to surgical removal of the tumor. New research aims to develop advanced surgical techniques, such as robotic surgery and minimally invasive procedures, that reduce the risk of complications and improve surgical outcomes.
Further research and clinical trials will help expand our understanding of the biology of this disease and develop even more effective treatments and prevention methods. Working in this area represents a key component in fighting cancer and improving the prognosis for patients.
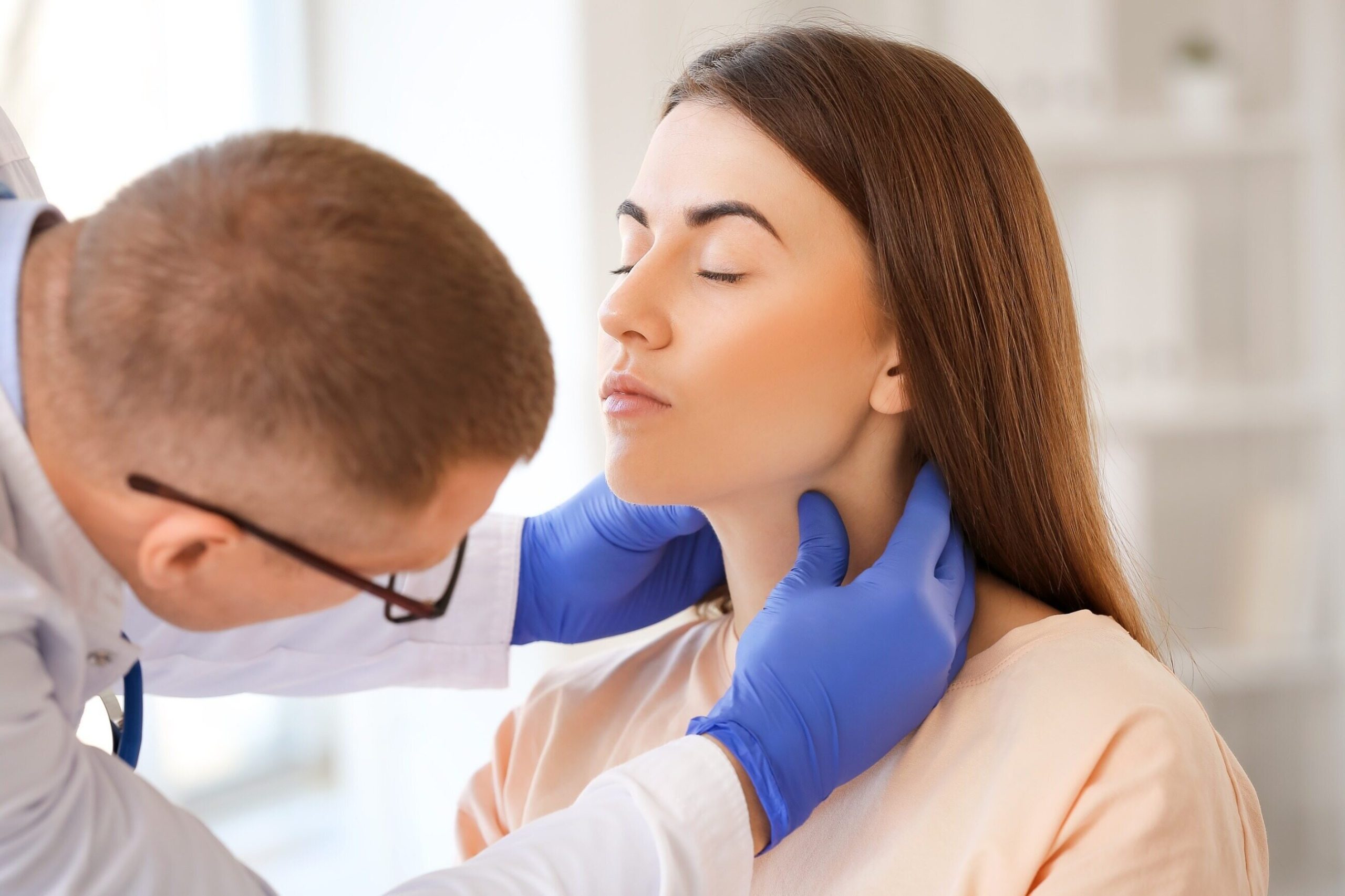 Vocal cord cancer treatment in Turkey
Vocal cord cancer treatment in Turkey
One of the key areas of research on vocal cord cancer is the study of its molecular and genetic basis. The latest research is identifying genetic mutations and changes that may play a role in the development of vocal cord cancer. This opens new perspectives for understanding the molecular mechanisms of the disease and developing individualized therapies based on the molecular characteristics of the tumor.
The newest research focuses on developing more accurate methods for genomic testing and molecular labeling of vocal cord cancer. This allows the unique molecular characteristics of each patient’s tumor to be identified, helping to select the most effective treatments and predict outcomes.
New research focuses on the tumor microenvironment and immune status of patients with vocal cord cancer. This allows us to understand the interaction between the tumor and the body’s immune system, and to develop immunotherapy strategies to enhance the immune response against cancer cells.
Participation in clinical trials and multicenter studies allows us to evaluate the effectiveness of new therapies and drugs in a large patient population. This facilitates the rapid introduction of advanced technologies and treatments into clinical practice.
New research is also focusing on the development of patient support and rehabilitation programs following treatment for vocal cord cancer. This includes developing resources for patients and their families, as well as physical and psychological rehabilitation programs to recover from treatment.
The research is also aimed at developing methods of vocal cord cancer prevention and early diagnosis of precancerous conditions. This allows tumors to be detected early, when they are more amenable to successful treatment, and steps can be taken to prevent the cancer from developing.
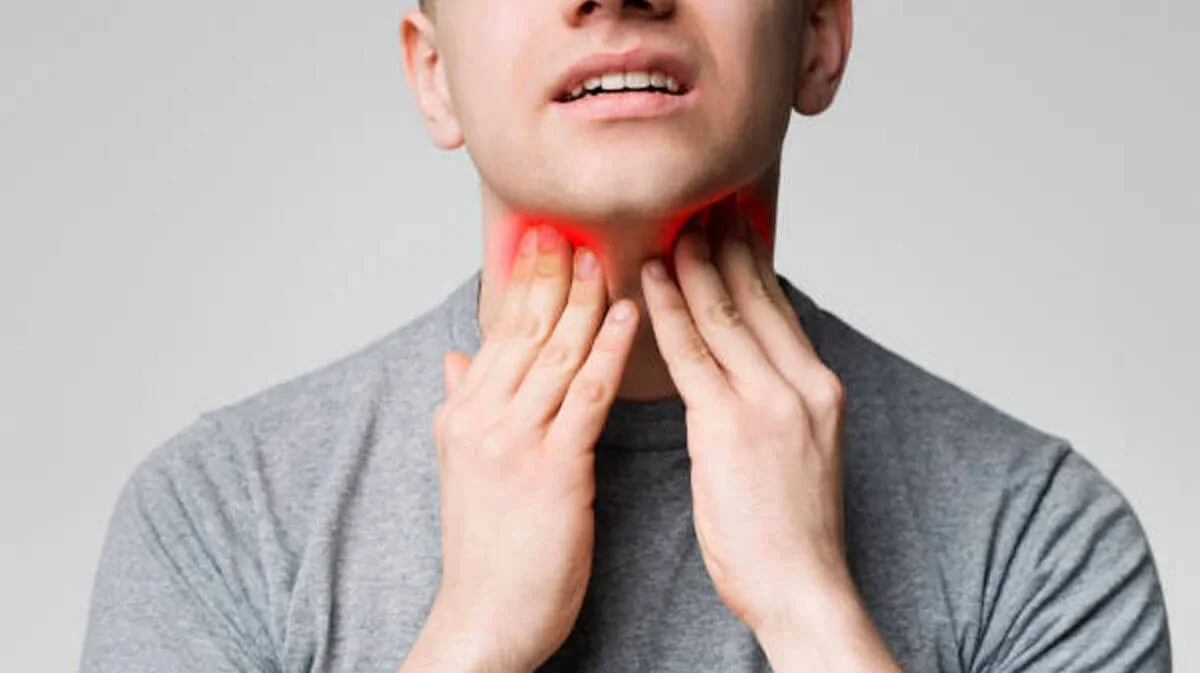 Treatment of tonsil cancer in Turkey
Treatment of tonsil cancer in Turkey
Oncology of the tonsils, although rare, is a serious disease that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Identifying tumors in this area of the throat and neck can be difficult because of their hidden location and nonspecific symptoms.
Immunotherapy is one of the most promising areas of cancer treatment. The method uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Drugs such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., antibodies to PD-1 or PD-L1) stimulate immune cell activation and enhance their anti-tumor effects. This improves treatment efficacy and prognosis for patients with tonsil cancer.
Targeted drugs are directed at specific molecular targets in cancer cells, allowing for more precise and effective targeting of the tumor. New targeted therapies include the use of inhibitors of tumor growth signaling pathways, monoclonal antibodies, and other innovative drugs that can block specific biochemical processes in cancer cells.
Targeted Radiation Therapy (SBRT): This is an advanced radiation therapy technique that delivers high doses of radiation directly to the tumor, minimizing the effects on surrounding healthy tissue. This may be particularly useful for patients with localized tonsil cancer in whom surgery is not possible or desirable.
With the development of minimally invasive and robotic surgical techniques, more precise and less invasive tonsil tumor removal has become possible. This reduces the risk of complications, shortens recovery time and improves patients’ quality of life after surgery.
New methods of analyzing the genome and molecular characteristics of tumors make it possible to determine the individual characteristics of cancer cells and select the most effective treatment methods for each patient. This includes the use of molecular markers to predict response to drug therapy and determine the potential for relapse.
Participation in clinical trials allows patients to access advanced treatments and experimental drugs that may be more effective and less toxic than standard methods. Clinical test tubes also contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies and to the overall effectiveness of treatments.
 Gastric cancer treatment in Turkey
Gastric cancer treatment in Turkey
Gastric cancer remains one of the most common and deadly cancers in the world. Despite significant improvements in diagnosis and treatment in recent decades, high mortality rates remain a challenge for the medical community. However, recent research in the field promises significant promise and breakthroughs that may change the treatment paradigm and improve patient survival.
One of the key areas of research into the disease is the study of its genetic basis. The latest research is identifying genetic mutations and changes that may play a role in the development of the disease. This opens new perspectives for understanding the molecular mechanisms of the disease and developing individualized therapies based on the molecular characteristics of the tumor.
Targeted therapies directed at specific molecular targets in cancer cells represent a promising approach in the treatment of gastric cancer. New research focuses on developing and testing new drugs that can inhibit tumor growth and development while improving treatment outcomes and patient survival.
Immunotherapy, which stimulates the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, also represents a promising avenue for treating the disease. The latest research is focused on developing new immunotherapeutic strategies, including the use of CAR-T cells, which may significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
One of the main goals of the new research is to develop effective methods for early diagnosis and screening of gastric cancer. This includes the use of new biomarkers, educational methods and technologies, such as the endoscopic research capsule, which allows tumors to be detected early when they are more amenable to successful treatment.
New research is also focusing on finding prognostic and predictive markers that can help determine disease prognosis and response to treatment in specific patients. This includes the study of genetic, epigenetic characteristics of tumors that may be associated with treatment outcomes and patient survival.
 Treatment of 12-digestive cancer in Turkey
Treatment of 12-digestive cancer in Turkey
One of the promising directions in the treatment of duodenal cancer is the use of targeted drugs. New research is focusing on developing drugs that target specific molecular targets such as growth factor receptors (e.g., EGFR), signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT/mTOR), and other cancer biomarkers, allowing for more precise and effective targeting of the tumor.
Immunotherapy is a promising avenue for the treatment of duodenal cancer. New research is focusing on developing immunotherapeutic strategies such as blocking immune checkpoints (e.g., PD-1, PD-L1), using CAR-T cells and tumor vaccines to activate the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
In-depth study of the genetic and molecular features of duodenal cancer is helping to identify novel biomarkers, prognostic factors, and targets for therapy. This allows for a personalized approach to each patient’s treatment and the development of individualized therapeutic regimens.
Conducting clinical trials of new drugs, therapy combinations, and innovative therapies plays an important role in developing and evaluating the efficacy of new therapeutic strategies in the treatment of duodenal cancer. Clinical trials help to test the safety and efficacy of new therapies and evaluate their potential in clinical practice.
New technologies and surgical treatment techniques such as minimally invasive procedures, robotic surgery and navigational intervention allow for more precise and effective tumor removal, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and reducing the risk of complications.
These latest research and innovations in the treatment of duodenal cancer offer new prospects for improving the prognosis and quality of life of patients suffering from this disease. The introduction of new treatments and therapeutic strategies into clinical practice can significantly improve the effectiveness of this type of cancer.
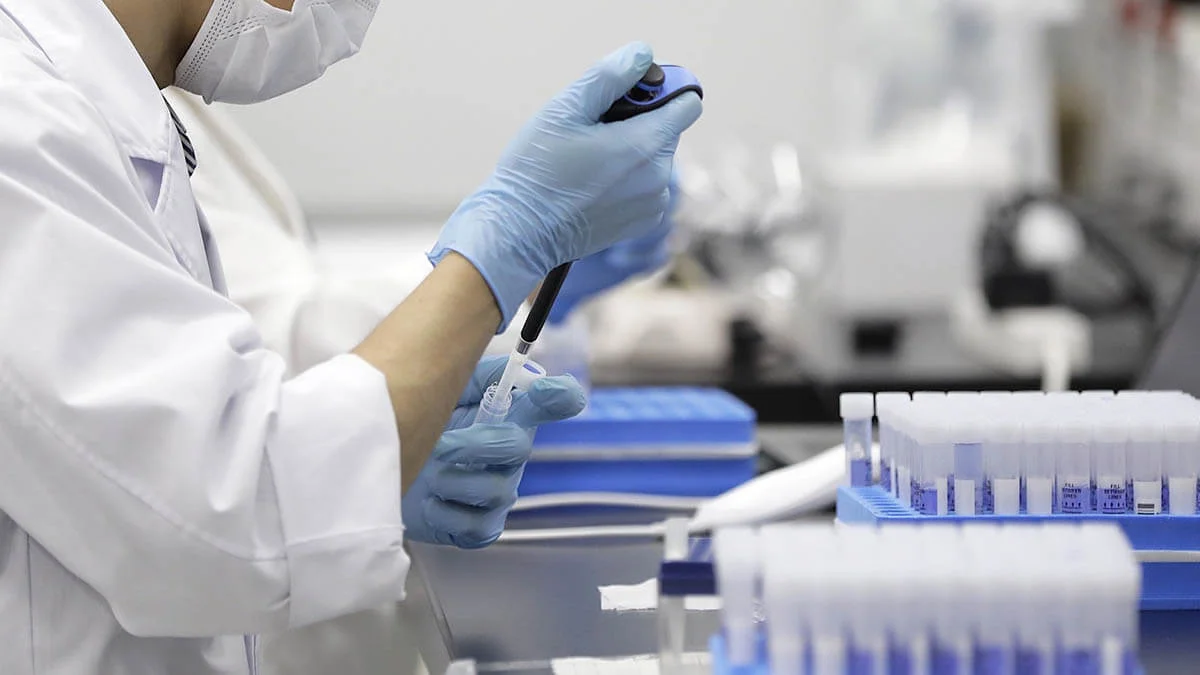 Diagnosis and new methods of cancer treatment in Turkey
Diagnosis and new methods of cancer treatment in Turkey
Research is also focusing on developing new methods for early diagnosis of cancer, which will allow tumors to be detected earlier when they are more amenable to successful treatment. This includes the development of biomarkers, the use of educational methods and the latest educational technologies such as endoscopic studies and educational capsules.
New research is focusing on developing integrative treatments that include a combination of different therapeutic approaches such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. This approach allows for the most effective and comprehensive treatment of the tumor, increasing the chances of complete cure or long-term remission.
The research aims to identify prognostic and predictive factors that will help predict a patient’s response to certain treatments. This includes studies of genetic mutations, tumor molecular signatures, immunological markers, and other biomarkers that may be associated with treatment outcomes and patient survival.
With the development of medical informatics and artificial intelligence, new opportunities are emerging for analyzing large amounts of data, processing medical images, and developing individualized therapeutic approaches based on personalized medicine.
The establishment of clinical registries and collaborative networks helps bring researchers, clinicians and patients together to share information, expertise and data to accelerate the development of new cancer diagnostics and treatments.
These cutting-edge studies represent an important step forward in the fight against cancer and offer new perspectives to improve patients’ prognosis and quality of life. Further development and implementation of these techniques and therapeutic strategies into clinical practice can significantly improve the effectiveness of any type of cancer.
 Meningioma treatment in Turkey
Meningioma treatment in Turkey
Meningioma diagnosis usually involves a number of different examination methods that help doctors accurately determine the presence of the tumor, its location, size, degree of malignancy, and potential complications.
The doctor conducts a detailed examination of the patient, finding out the presence of symptoms such as headaches, visual disturbances, seizures and changes in neurological status. It is also important to find out the patient’s medical and family history.
MRA can be used to assess the vessels passing through the tumor, which can be useful for surgical planning and determining the risk of bleeding.
Given that some neoplasms may be associated with hyperproduction of hormones such as prolactin, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), or others, it may be necessary to evaluate blood levels of these hormones.
One of the most promising approaches to treating the disease is the use of targeted therapy. Drugs aimed at inhibiting specific molecular targets, such as inhibitors of molecular growth pathways (e.g., mTOR, EGFR), may have an effective effect on meningioma growth and development. Some new drugs, such as everolimus and lapatinib, have already undergone clinical trials and have shown promising results in therapy.
One of the key areas of research on neoplasms is the study of their genetic basis. Researchers have identified a number of genetic mutations that may play a role in meningioma development, including mutations in the NF2, AKT1, SMO, and other genes. These studies are helping to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying tumor development and identify novel molecular targets that may be targets for targeted therapies.
Immunotherapy also represents an actively researched area in the treatment of oncology. The development of vaccines against meningioma antigens and the use of immune checkpoints to stimulate the body’s immune response may help to enhance the immune response to the tumor and improve treatment efficacy.
 Carcinoid treatment in Turkey
Carcinoid treatment in Turkey
Carcinoid tumors are a rare but serious type of cancer that manifests from neuroendocrine cells and can occur in various organs of the body, including the intestines, lungs, and pancreas. Although carcinoids can be slow-growing tumors, they can become aggressive and metastasize to other parts of the body.
With the advent of new innovative treatments, researchers and physicians around the world are striving to improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients with this type of cancer.
One of the most promising approaches in the treatment of carcinoids is the use of targeted therapy aimed at inhibiting specific molecular targets that play a key role in tumor development.
Immunotherapy is another innovative treatment for carcinoids. Immunotherapy approaches such as immune checkpoint blocking and CAR-T cell therapy are being actively studied to determine their efficacy against carcinoids. These techniques can help activate the body’s immune system to target tumor cells for targeted destruction, improving patient prognosis and survival.
Radiotherapy and surgical techniques also remain important components of carcinoid treatment. Modern radiotherapy technologies, such as intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and proton beam radiation therapy, allow for more precise targeting of beams to the tumor, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Surgical innovations such as minimally invasive procedures and robotic surgery can provide more effective and safer tumor removal.
The development of personalized medicine based on genetic and molecular characteristics of the tumor and the patient opens new possibilities for an individualized approach to carcinoid treatment. Clinical trials play a key role in testing new therapies and implementing them into practice, allowing for continuous improvement and better outcomes for carcinoid patients.
Drugs such as octreotide and lanreotide are analogs of somatostatin, which inhibits the release of hormones and neuropeptides involved in the regulation of tumor growth and development. Analogs are used to reduce symptoms of carcinoid syndrome, including hyperproduction of serotonin, histamine, and other biologically active substances.
Drugs such as sunitinib and everolimus inhibit tyrosine kinases, enzymes responsible for signaling pathways that regulate tumor growth and development. These drugs may be effective in treating some types of carcinoids, especially in the metastatic form of the disease.
 Why it is better to treat oncology in Turkey
Why it is better to treat oncology in Turkey
Turkey is known not only for its rich cultural heritage and beautiful scenery, but also for its top-notch medical industry, including cancer treatment. Modern technologies, qualified specialists and affordable prices make Turkey an attractive destination for patients in need of oncologic treatment.
Turkey has modern medical centers with advanced equipment for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Many clinics have the latest machines for radiation therapy, surgery and molecular genetic testing. This allows specialists to accurately and effectively diagnose and treat various forms of cancer.
Doctors in Turkey have a high level of professionalism and experience. Many of them have undergone training and internship abroad, have international certificates and participate in international conferences and research in the field of oncology. This allows them to utilize advanced treatment methods and provide patients with quality medical care.
One of the key benefits of oncology treatment in Turkey is affordability. The cost of medical services in Turkey is often lower than in developed Western countries, while the quality of care remains at a high level. This makes Turkey an attractive medical tourism destination for patients seeking quality treatment at affordable prices.
Medical centers in Turkey provide comprehensive treatment and support to patients at all stages of their battle with cancer. This includes specialist consultations, an individualized treatment plan, psychological support, rehabilitation and post-operative follow-up.
It is important to note that Turkey is constantly developing its medical infrastructure and improving the quality of its services. Medical centers strive to actively implement new technologies and treatment methods, follow the latest scientific research and cooperate with leading international medical institutions.
Various drugs are used in the treatment of cancer in Turkey, including chemotherapeutic, immunotherapeutic and targeted drugs. These drugs can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other treatments such as surgery and radiation therapy.
Turkey offers modern and innovative methods of oncology treatment, affordable prices and top-class medical care. Qualified specialists, advanced equipment and a comprehensive approach make Turkey one of the leaders in cancer treatment, attracting patients from all over the world.
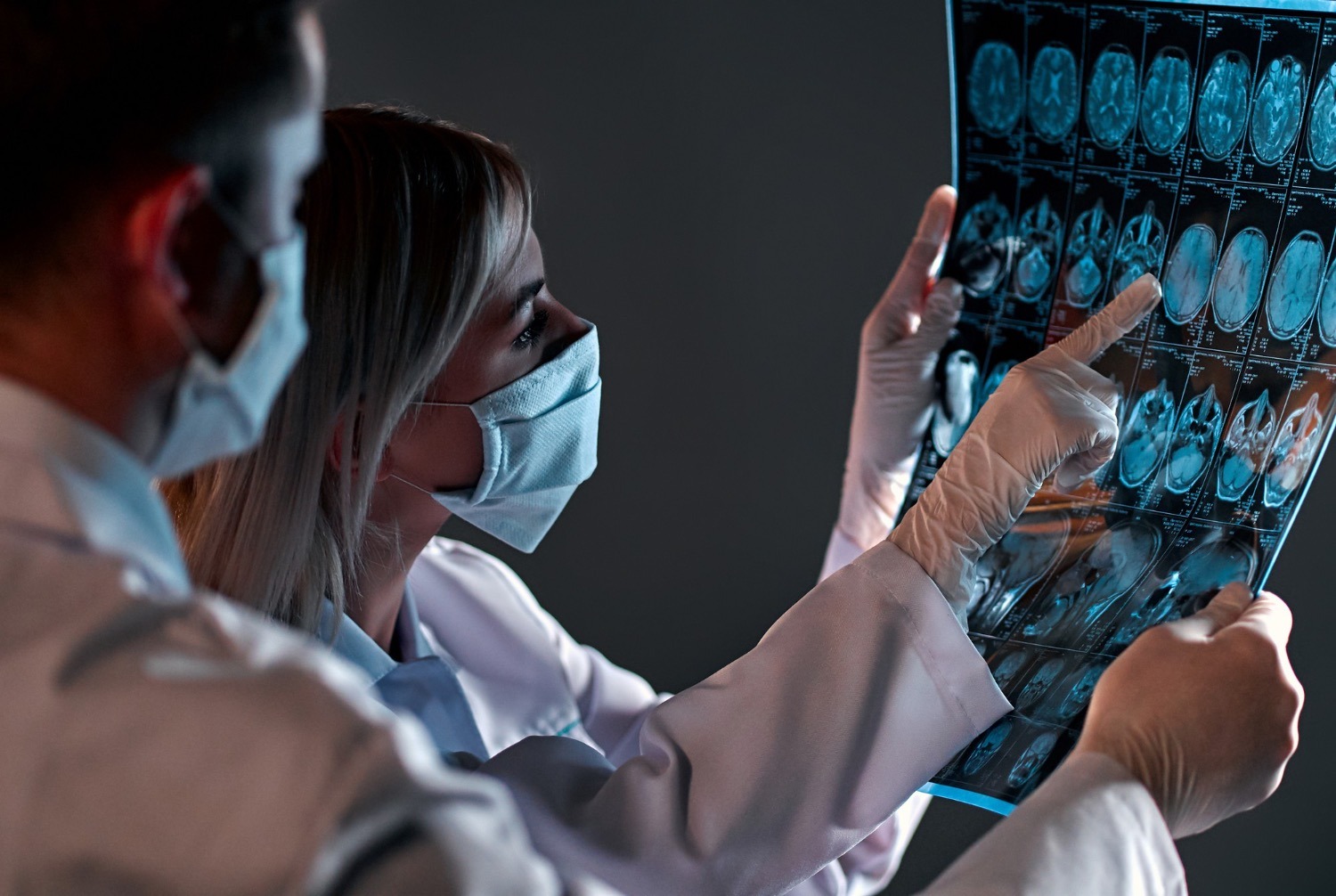 Brain cancer treatment in Turkey
Brain cancer treatment in Turkey
Brain oncology is a serious disease characterized by the development of malignant tumors in the brain tissue or its surrounding structures. This condition requires careful attention because of its potentially serious consequences and the complexity of therapy.
Viruses, infections – cytomegalovirus may also be linked to cancer development, but their role requires further research.
Prolonged exposure of the body to high doses of ionizing radiation, for example as part of treatment for other types of cancer, can increase the risk of developing the disease.
Persistent or worsening headaches, especially in the morning or with changes in body position, may be one of the early signs of the disease.
Problems with movement coordination, unsteadiness when walking, and other balance problems may indicate that certain areas are affected.
The doctor conducts a detailed examination of the patient and gathers information about symptoms, their duration and intensity, as well as medical and family history.
A study of the brain is done to detect the presence of cancer cells or metastases. This refers to the close proximity to the ventricles of the brain. Genetic tests identify inherited mutations that provoke the development of cancer.
A biopsy may be performed, where tissue samples are taken for further examination under a microscope to determine tumor type and stage.
Scientists are studying genetic mutations that may be linked to disease development – the RB1, NF1, PTEN and other genes. The identification of these mutations is helping to understand the biological processes underlying tumor development and to develop new therapies that target specific genetic alterations. Research is also being conducted to identify biomarkers that may help in the diagnosis and prognosis of brain cancer.
The use of nanotechnology allows the development of new drugs that bypass blood brain barriers and improve the effectiveness of therapy.
 Neuroblastoma treatment in Turkey
Neuroblastoma treatment in Turkey
Neuroblastoma is a rare but serious cancer that usually arises in early childhood from nerve tissue. In recent decades, significant progress has been made in the diagnosis and therapy of the disease, resulting in improved survival and prognosis for patients.
Diagnosis is a key step because it helps to determine the stage of the disease, select the best treatment method and assess prognosis.
The doctor performs a general examination of the patient, paying attention to the presence of tumors, enlarged lymph nodes and other symptoms. History taking includes information about symptoms, duration of illness, and the presence of relatives with similar conditions.
Taking a tissue sample for histologic examination is essential to confirm the diagnosis of neuroblastoma. A biopsy can determine the type of tumor, its maturity and other characteristics, which is important for choosing the best treatment method.
Blood tests can be performed to assess levels of certain tumor markers such as neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and catecholamines, which helps in diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
The disease may be genetic in nature, so genetic testing can be done to identify mutations associated with the disease. This helps determine if there is a hereditary component and provides information about the risk of the disease in other family members.
The disease can have varying degrees of maturity, which affects the choice of treatment and prognosis. For this purpose, a specific classification system such as the INSS or INRGSS system can be used to determine the stage of the disease.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is important to determine the extent of tumor spread and the presence of metastases. This helps doctors determine the stage of the disease and develop the most effective treatment plan. A variety of examination methods can be used for this purpose, including additional educational techniques such as radiography, ultrasonography and whole-body scans.
In order to choose the optimal treatment plan and minimize the risks associated with therapy, it is important to assess the functional status of the patient’s organs and body systems. This may include specialized tests and studies, such as assessing heart, liver, and kidney function.
Current methods for diagnosing neuroblastoma may also include molecular genetic analyses aimed at identifying specific genetic changes or mutations associated with tumor development. This allows you to more accurately characterize the tumor and choose the most effective treatment.
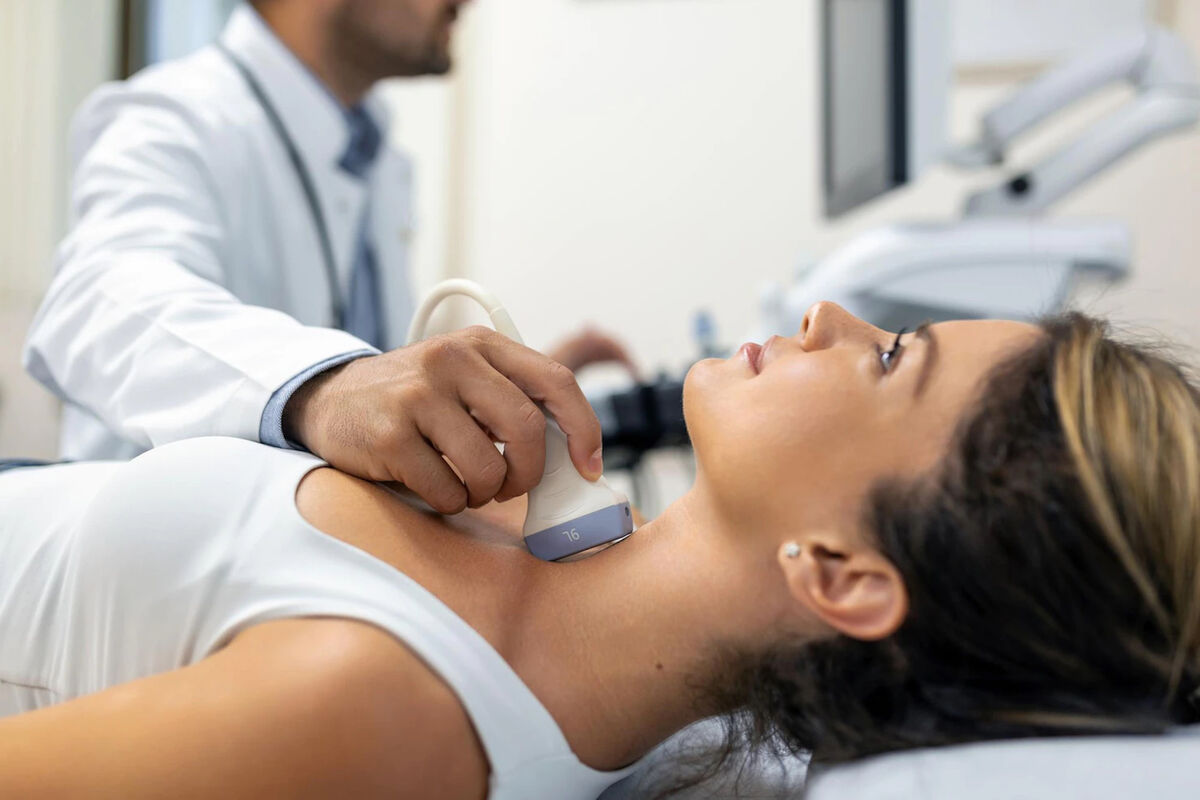 Lymphoma treatment in Turkey
Lymphoma treatment in Turkey
Lymphoma refers to one of the varieties of malignant neoplasms, the place of localization of which is the lymphatic system. The disease is divided into two varieties. An important step is to accurately determine the type of disease.
Chemotherapy is considered one of the mainstay therapies. Various chemotherapy protocols are used, including single or combination drugs. Chemotherapy regimens are tailored to the type of disease and the patients’ condition. Modern chemotherapy medications can enhance the effect and reduce the likelihood of negative side effects.
Immunotherapy is an innovative disease management technique that aims to stimulate immune forces to fight cancerous tissue. Monoclonal antibodies and checkpoint inhibitors, can be used as immunotherapy. This approach has become meaningful and has yielded positive results in controlling the disease in some patients.
Radiation therapy is used as a stand-alone option or combined with chemotherapy drugs to reduce the size of the tumor, destroy cancer cells, and prevent recurrence. Modern methods allow to direct the radiation beams as precisely as possible on the tumor without affecting the surrounding healthy tissues.
Bone marrow transplantation or stem cell transplantation is recommended for patients with recurrent form. Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to replace diseased or damaged bone marrow cells with healthy ones, which helps to restore the immune system and destroy cancer cells.
Treatment of the disease is becoming increasingly effective due to modern methods of diagnosis and therapy, as well as innovative approaches used in medical practice. Rapid advances in research and medical technology are opening up new perspectives in the treatment of this disease, which can improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients with the disease.
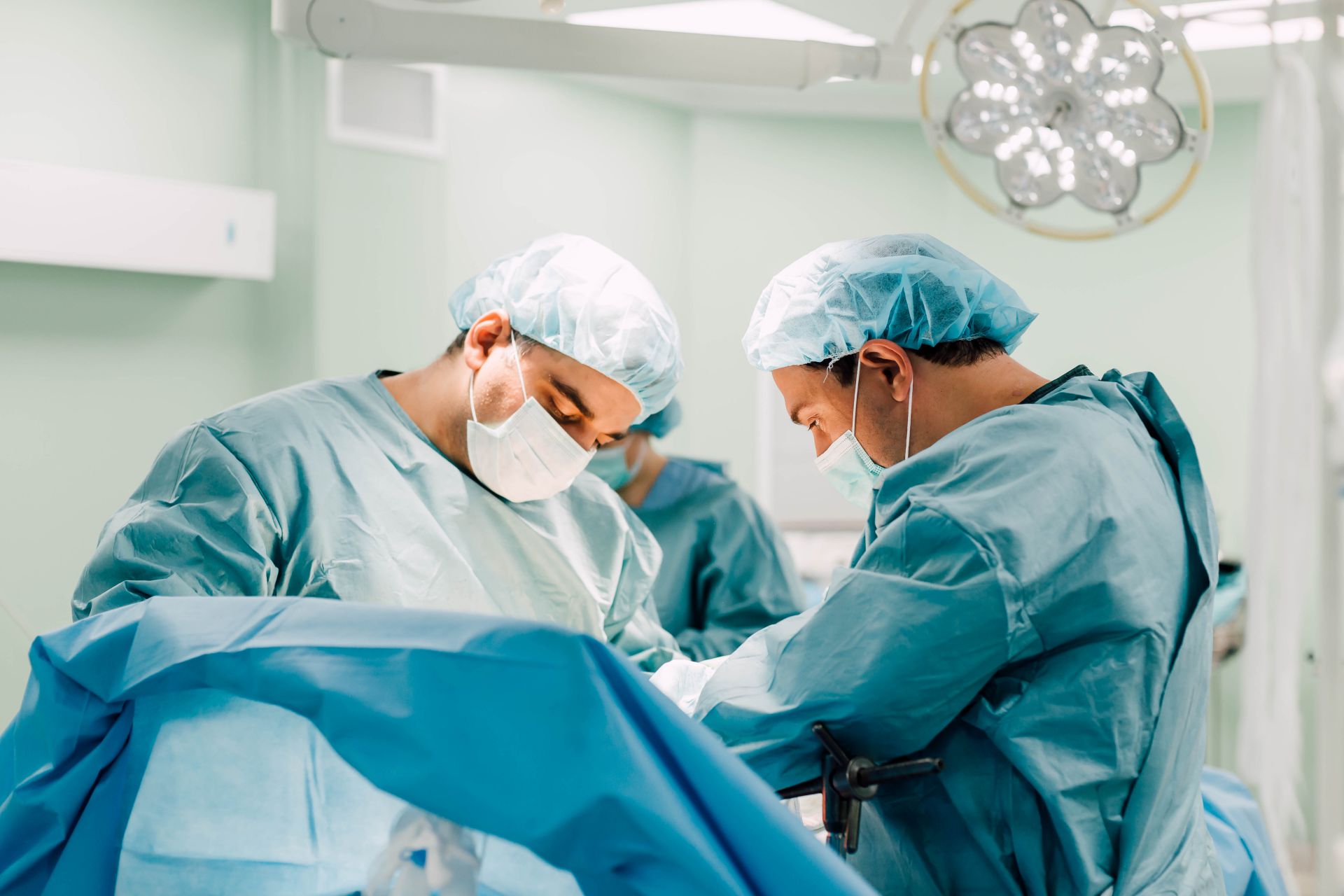 Rectal cancer treatment in Turkey
Rectal cancer treatment in Turkey
Turkey is known for its advanced medical facilities with state-of-the-art equipment and technology. Many of these institutions have international accreditation, such as the Joint Commission International (JCI) accreditation, which ensures that they meet high quality standards. As a result, patients have access to advanced methods of diagnosing and treating colorectal cancer.
Rectal cancer treatment in Turkey often involves a close-knit team of specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and gastroenterologists. This allows us to develop the best individualized treatment plan for each patient, taking into account the stage of the disease, general health condition and individual characteristics.
A doctor may begin the diagnosis of colorectal cancer with a general physical exam and history taking to identify symptoms and risk factors for the disease.
Some specific blood tests may be performed to assess liver and other organ function and to detect cancer markers that may indicate the presence of a tumor.
Rectal examination allows the doctor to evaluate the condition of the rectum and detect the presence of any abnormalities such as tumors or polyps. Most often, doctors order a colonoscopy, a procedure in which a flexible tube with a camera (colonoscope) is inserted into the rectum and allows the doctor to visually inspect the entire large intestine area. During a colonoscopy, tissue samples may be taken for biopsy.
Surgery is the primary treatment for rectal cancer, especially in the early stages of the disease. In Turkey, surgeons in Turkey specialize in performing surgical procedures using advanced techniques and technology. This includes resection of the rectum, laparoscopic and robotic surgery, and anastomosis (connecting the two ends of the colon after tumor removal). These techniques provide less traumatic surgery, quicker recovery, and improved patient outcomes.
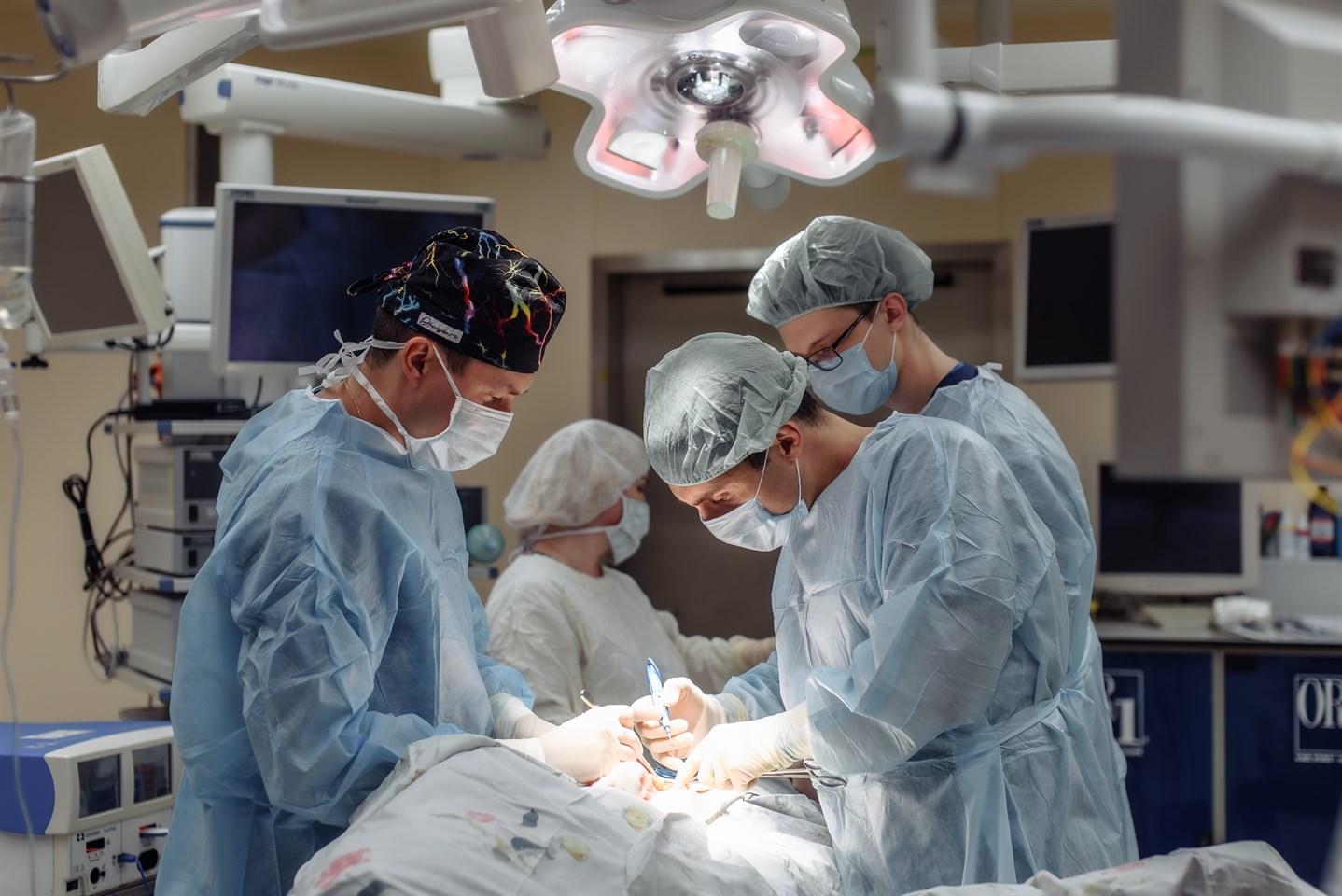 Gallbladder cancer treatment in Turkey
Gallbladder cancer treatment in Turkey
Diagnosis of gallbladder oncology plays a key role in determining the stage of the disease and choosing the best treatment plan. Computed tomography allows obtaining detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding tissues, determining the size of the tumor and assessing the degree of spread of the process.
MRI provides higher resolution and provides more detailed information about the structure and characteristics of the tumor. Ultrasound evaluates the structure of the gallbladder and detects neoplasm or other changes. Taking a tissue sample for histologic examination is very important to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of cancer.
The most utilized technique for gallbladder oncology remains surgery. Depending on the localization of the tumors, surgical interventions consist of partial or complete removal of the gallbladder, as well as the surrounding affected tissues and lymph nodes.
Patients with advanced stage are additionally prescribed chemotherapy or radiotherapy. In this way the remaining cancer cells are destroyed and recurrence is prevented.
Turkey actively participates in clinical trials and introduces the latest technologies and techniques for the treatment of gallbladder oncology. This includes utilizing innovative surgical techniques, developing new drugs for chemotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies, and exploring promising radiation therapy and immunotherapy.
Many medical centers in Turkey are equipped with advanced equipment and technology, which ensures a high level of diagnosis and treatment. Turkey uses advanced surgical techniques including resection of the gallbladder and surrounding tissues, laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Turkish medical centers provide modern complementary therapies to help prevent recurrence and improve prognosis.
Each patient receives individualized treatment that takes into account their health condition, stage of disease and other factors to promote optimal outcomes and improve quality of life.
 Melanoma treatment in Turkey
Melanoma treatment in Turkey
Melanoma treatment in Turkish medical centers often involves a multidisciplinary team of specialists, including oncologists, dermatologists, and radiologists. This is to develop the best individualized treatment plan for each patient, taking into account the stage and individual characteristics.
Surgery is often scheduled very often, especially early stage surgery. The techniques – lymphadenectomy, cryosurgery, marginal resection, etc. show excellent effect. They also have reconstructive surgery skills that can help restore aesthetics and tissue function after tumor removal.
Turkey actively participates in international clinical trials on melanoma and implements the latest developments in this field. Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate new therapeutic options. This applies to immunotherapy, targeted therapies and combination approaches. These studies contribute to innovative methods and drug development with improved patient outcomes and prognosis.
The country has an extensive network of clinics and centers specializing in the treatment of melanoma. Patients can be served by highly trained professionals with the most innovative treatments regardless of their location in the country. Consultations with leading melanoma experts are also available to get a second opinion and develop the most effective treatment plan.
Melanoma treatment in Turkish medical centers is an innovative and multidisciplinary approach based on advanced diagnostic and treatment methods, cooperation between doctors of different specialties and patient support at all stages of treatment. The combination of a high level of medical expertise, accessibility of services and psychological support makes the country an attractive destination for melanoma treatment, providing patients with optimal outcomes and care.
 Esophageal cancer treatment in Turkey
Esophageal cancer treatment in Turkey
Diagnosis of esophageal oncology plays a key role in determining the stage of the disease in order to develop an individualized therapy plan. Turkish medical institutions use the best techniques to accurately determine the nature and spread of the tumor.
Endoscopy is the primary method for imaging the esophagus and detecting tumors. The doctor may use a flexible endoscopic tube with a video camera to examine the inside walls of the esophagus and take biopsy samples for further analysis.
Samples of esophageal tissue taken during endoscopy are biopsied to determine if cancer cells are present. Biopsy is the key method for confirming the diagnosis of esophageal cancer.
Computed tomography provides detailed images of the esophagus and surrounding tissues, which can determine the size and stage of the tumor, as well as identify possible metastases.
MRI can be used to obtain more detailed information about the structure and distribution of the tumor in the esophagus. Endoscopic ultrasound imaging combines endoscopy with ultrasound scanning for a more accurate picture.
The doctors are engaged in international clinical research and put the latest advances into practice. Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate the latest techniques. This applies to immunotherapy, molecularly targeted therapies, and combination approaches to improve patient outcomes.
Open resection involves accessing the esophagus through an incision in the patients abdomen. The surgeon removes part or all of the neoplasm, as well as surrounding healthy tissue. After the tumors are excised, the esophagus is reconstructed using remnants of the esophagus or other tissues (such as intestine).
Laparoscopic intervention occurs through small incisions in the abdomen and special instruments inserted through these incisions. Laparoscopic or robotic surgery promotes quick recovery and reduces the risk of complications after surgery.
Sometimes surrounding lymph nodes are removed to prevent the spread of cancerous tissue. The surgeon removes lymph nodes that may have been infected by the cancer to prevent recurrence and metastasis.
 Treatment of adenocarcinoma in Turkey
Treatment of adenocarcinoma in Turkey
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumor that develops from the glandular cells that make up the epithelium of various organs. It can affect various parts of the body, including the lungs, prostate, stomach, intestines, and other organs. Treatment for adenocarcinoma requires a comprehensive approach and individualized planning, making it important to choose the right medical direction. Turkey, with its modern medical infrastructure and advanced treatment methods, is becoming an increasingly popular choice for patients facing this type of cancer.
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for adenocarcinoma, especially in the early stages of the disease. In Turkey, surgeons specialize in minimally invasive methods of surgical intervention, which allow to preserve the functionality of organs as much as possible and reduce the risk of complications.
For patients who require additional treatment after surgery or in advanced stages of the disease, Turkey offers modern radiotherapy and chemotherapy. These methods can be used as stand-alone treatments or in combination to improve outcomes.
In recent years, innovative treatments for the disease, including immunotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies, have been actively developed in Turkey. These approaches allow for more precise and effective tumor control, minimizing side effects and improving patient survival prognosis.
Turkey actively participates in international clinical trials and conducts its own research to develop new treatments for the disease. This includes research into new drugs, therapies, and genetic and immunotherapy research. Scientists and doctors in Turkey are constantly striving to find innovative and effective treatments to improve the prognosis for patients.
There is also a focus on psychological and emotional support for oncology patients. Many health centers offer support and counseling programs and palliative care services that are designed to improve patients’ quality of life during and after treatment.
 Glioma treatment in Turkey
Glioma treatment in Turkey
A glioma is a tumor that develops from glia cells, the main support and protection of nerve tissue in the brain and spinal cord. This is a serious disease that requires comprehensive and qualified treatment. In recent decades, Turkey has become a popular destination for medical tourism, including glioma treatment. The combination of high level of medical services, modern technologies and affordable prices makes Turkey an attractive destination for patients from all over the world in need of quality glioma treatment.
Turkey has an extensive network of modern medical facilities equipped with advanced equipment and operating to the highest standards. Many of them are Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited, which confirms that they meet international quality standards. Doctors and medical staff in Turkey often have international experience and a high level of professionalism.
Turkey utilizes the most advanced methods of diagnosing and treating glioma. This includes computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET scans) and other advanced educational techniques. In addition, doctors specialize in surgical tumor removal, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, offering patients a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Glioma treatment in Turkey is often available at lower prices compared to other countries, while maintaining high quality medical services. This makes Turkey an attractive option for patients who need quality treatment at an affordable price.
In Turkey, surgeons specializing in neurosurgery perform glioma surgery using advanced techniques and technologies such as navigational neurosurgery and intraoperative MRI.
The main goal of surgery is to maximize tumor resection with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue, which helps to reduce the risk of recurrence and improve survival prognosis.
The country utilizes the latest chemotherapy protocols, including the use of the latest drugs and drug combinations that can help destroy cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
These treatments are often combined to achieve the best results in treating the disease. A comprehensive approach, advanced technologies and highly qualified medical staff make Turkey an attractive destination for patients seeking treatment for this complex cancer.
 Liver oncology treatment in Turkey
Liver oncology treatment in Turkey
Liver oncology is a serious medical problem that requires a comprehensive and multilevel approach to diagnosis and treatment. In recent decades, considerable efforts have been directed towards the development of new methods and technologies to combat tumor diseases of this organ. Turkey, like many other countries, has advanced research and development in the treatment of liver oncology.
Accurate diagnosis of the disease is critical to the successful treatment of liver cancer. This includes an extensive list of investigations such as CT and MRI scans, ultrasound, positron emission tomography, biopsies and laboratory tests.
Many clinics and medical centers in Turkey have advanced equipment and highly qualified medical staff, which allows you to conduct all necessary examinations at the highest level.
One of the main methods of treatment for liver oncology is surgery. This may include tumor removal (liver resection), liver transplantation, radical treatment of metastases, and other procedures. The leading surgical centers in Turkey perform complex surgeries to a high standard, making them among the leading centers in the surgical treatment of liver oncology.
Often, treatment for liver cancer involves a combination of different methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and others. This multimodal approach achieves the best results and increases the chances of survival.
In some cases, especially in cases of extensive liver damage or in the presence of cirrhosis, liver transplantation may be recommended. This is a radical method of treatment in which the patient is transplanted with a new organ from a donor.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used to reduce tumor size before surgery, to destroy residual tumor cells after surgery, or as stand-alone treatments when surgery is not possible.
New therapies such as immunotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies represent promising approaches to the treatment of liver oncology. They are based on using the immune system or molecular mechanisms to fight the tumor.
 Kidney oncology treatment in Turkey
Kidney oncology treatment in Turkey
Renal oncology is a serious disease that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. In Turkey, a country with a developed medical infrastructure and advanced treatment methods, the diagnosis and therapy of renal oncology is based on modern technology and a multidisciplinary approach.
Immunotherapy is becoming an increasingly widely used therapy for the disease. This approach is based on stimulating immune forces against cancer cells. Immunotherapy may include the use of immune protein blockers, such as PD-1 and CTLA-4, which promote the activation of immune cells to destroy the tumor.
Molecularly targeted therapy is based on the use of drugs that directly target the molecular mechanisms of tumor growth and development. Molecularly targeted therapy is often used for metastatic cancer that is not amenable to surgical treatment.
In some cases, a combination treatment consisting of several techniques at the same time may be required. This multimodal approach may increase efficacy and improve the course of the disease.
After completion of active treatment, patients undergo regular medical monitoring and follow-up to detect recurrences and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. This is important for timely detection of possible recurrences or complications and prescription of further treatment, if necessary.
Minimally invasive surgery, such as laparoscopy or radiofrequency ablation, may also be used to remove the tumor. These options are less invasive and may be preferable for some patients.
Turkish medical centers participate in various studies aimed at developing the latest techniques for diagnosing and treating the disease. This allows us to introduce the latest technologies and approaches into clinical practice and provide patients with access to cutting-edge treatments.
 Leukemia treatment in Turkey
Leukemia treatment in Turkey
Leukemia, or blood cancer, is a serious disease of the hematopoietic system that requires complex and long-term treatment. In Turkey, there are a number of features that define the approach to leukemia treatment and provide a high level of care for patients.
Leading medical institutions in Turkey practice a multifaceted approach to leukemia treatment that includes a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplantation and the latest immunotherapy techniques. This approach allows for a more effective fight against tumor cells, improves the prognosis of the disease and increases patient survival.
There are a number of specialized medical centers in Turkey that specialize in the treatment of cancer. These centers are equipped with advanced medical equipment and have highly trained professionals.
Turkey is actively pursuing innovative treatments for the disease, including the latest chemotherapy drugs, molecularly targeted therapy, immunotherapy and other advanced therapies.
Bone marrow transplantation is one of the key treatments for the disease when other methods are not effective enough.
High-quality bone marrow transplants are performed in Turkey using advanced techniques and technologies, resulting in high survival rates and successful treatment outcomes.
Each patient receives an individualized treatment approach that takes into account their unique characteristics, the type and stage of their disease, and the presence of comorbidities.
In addition to medical treatment, psychological support and help in dealing with the emotional stress associated with the disease and its treatment is provided in Turkey.
After completing active treatment, leukemia patients are provided with a monitoring and follow-up system that includes regular medical check-ups and examinations to monitor their health and detect possible relapses of the disease.
Healthcare providers strive to integrate optimal standards of care for patients, including excellence in clinical practice, adherence to treatment and monitoring protocols, and ethical and professional standards in patient care.
 Treatment of sarcoma in Turkey
Treatment of sarcoma in Turkey
Sarcomas are classified as rare malignant tumors that appear in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system – bones, muscles, tendons, and connective tissues.
Diagnosis is the most complex process, which includes various methods of examination and research to accurately determine the presence of a tumor, its type, stage of development and spread, as well as assess the general condition of the patient.
The physician interviews the patient to gather a medical history, including complaints, symptoms, their duration and nature. Allows imaging of internal organs and tissues to detect the tumor process, assess the size of the tumor and the presence of metastases.
A biopsy is a mandatory diagnostic step in which a sample of tumor tissue is taken for careful examination under a microscope. The analysis allows you to accurately determine the type of disease, its histological structure, as well as assess the degree of malignancy of the tumor.
The obtained material is subjected to histological examination, which determines the type of tumor and its degree of malignancy. The assay can determine the expression of various protein markers, which helps to clarify the diagnosis and select the optimal treatment strategy.
Some types of disease may have certain genetic mutations or changes that may be important for disease prognosis and treatment selection. Genetic and molecular biological studies can help identify these changes and determine their clinical significance.
Once the diagnosis is established, the extent of tumor spread (metastasis) is assessed, including examination of lymph nodes, organs and body systems.
Leading medical centers in Turkey have extensive experience in dealing with sarcomas and have highly qualified specialists in oncology, surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and other related fields. This ensures that patients have access to the highest level of medical care and ensures that the quality of treatment is of the highest standard.
 Ear cancer treatment in Turkey
Ear cancer treatment in Turkey
Turkish medical institutions are constantly introducing new technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of ear cancer. This includes the use of high-precision educational systems such as robotic surgery and navigational guidance for radiosurgical procedures. Such innovations improve the accuracy and efficiency of procedures, reducing recovery time and the risk of complications.
Surgical removal of the tumor is a commonly used method of treating the disease, especially in the early stages of the disease. Surgeons can perform tumor removal while preserving as much as possible the functional and cosmetic aspects of the organ.
For some forms of the disease, specific drugs are available that aim to inhibit certain molecular targets in cancer cells, which can lead to their destruction.
Medical centers in Turkey apply integrated, which includes not only medical and surgical treatment, but also rehabilitation. Patients receive comprehensive follow-up and support to regain function and quality of life after treatment.
Korean medical centers place great emphasis on psychological support for patients with ear cancer. This includes counseling by psychologists and psychotherapists, support groups for patients and their families, and information resources about the disease and how to cope with it.
After completing active treatment, many patients require rehabilitation to regain functions such as hearing, speech, and chewing. Rehabilitation measures may include audiologic treatment, speech therapy, physical therapy, and psychological support.
For advanced stage patients who cannot be completely cured, palliative treatment is provided to relieve symptoms of pain, improve quality of life and alleviate suffering.
Each patient with cancer requires an individualized approach to treatment, and a treatment plan is tailored to their unique characteristics and needs. It is important that treatment is supervised by qualified specialists in oncology and ear disease to achieve the best results and improve the prognosis of the disease.
 Tongue cancer treatment in Turkey
Tongue cancer treatment in Turkey
Tongue oncology treatment is a complex and multifaceted process that requires an individualized approach depending on the type of tumor, its stage, the patient’s overall condition, and other factors.
Immunotherapy in Turkey is becoming an increasingly popular treatment for cancer. It stimulates the immune system against cancer cells. The doctor may prescribe immunotherapy drugs as a stand-alone method or with other techniques.
Surgery can range from partial removal of part of the tongue (glossectomy) to radical resection of the tongue if the tumor has spread. Surgery may also include removal of lymph nodes in the neck area to prevent the spread of cancer cells.
Chemotherapy can be used alone or supplement surgery, radiation therapy. The drugs destroy cancer cells in the tumor and prevent their recurrence.
Patients with the disease and their loved ones may face many questions. Education and support is provided to help patients and their families understand the disease, its treatment, expectations and how to cope with the consequences.
Group education and support sessions, online resources, and individual counseling by psychologists and social workers can help patients and their loved ones cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of the disease.
For patients with advanced tongue cancer or inoperable tumors, it is important to provide palliative care to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and maintain comfort.
The palliative team – doctors, nurses, social workers, psychologists and other professionals work to provide comprehensive support and care.
After tongue cancer treatment, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
 Prostate cancer treatment in Turkey
Prostate cancer treatment in Turkey
In Turkey, prostate cancer treatment is carried out using advanced methods and technologies, providing a high level of medical care.
Modern surgical treatments for prostate cancer, including robotic prostatectomy, are available in Turkey. Robotic systems allow surgeons to perform surgeries with high precision and less impact on surrounding tissues, which promotes faster recovery and reduces the risk of complications.
Turkish clinics offer state-of-the-art equipment for radiation therapy, including high-tech linear gas pedals, which ensure that the beams are precisely directed at the tumor and minimize the impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
Advanced chemotherapy and hormone therapy drugs are also available, which can be used to treat the disease in combination with other treatments or as stand-alone therapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the tumor.
Brachytherapy is a technique in which sources of radioactive radiation (seeds) are injected directly into or near the tumor. It may be recommended as one treatment or in combination with other treatments.
Proton beam therapy uses protons to treat the disease. The technique is highly precise and has the ability to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Interventional radiology is a field using imaging (such as x-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging) to perform minimally invasive procedures. Interventional radiology may be used to manage symptoms, control tumor growth, or perform ablation (destruction) of tumor tissue.
Turkey remains one of the leading medical destinations in the world, offering patients access to advanced treatments and innovative technologies. The combination of highly professional medical staff, modern medical facilities and advanced treatment methods makes Turkey an attractive destination for patients in need of treatment for a dangerous disease.
 Pancreatic cancer treatment in Turkey
Pancreatic cancer treatment in Turkey
Pancreatic oncology is a serious disease that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment. Turkey has a well-developed healthcare system that provides patients with access to advanced oncology diagnosis and treatment.
The initial diagnosis of pancreatic cancer involves a number of examinations and tests such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and biopsy. Turkish medical centers are equipped with modern equipment and highly qualified staff, which provides accurate diagnosis and allows to determine the stage of the disease.
One of the main treatments for pancreatic cancer is surgery. Advanced surgical technologies and techniques are available in Turkey, including robotic surgery and minimally invasive procedures. This allows surgeons to effectively remove the tumor while preserving surrounding healthy tissues and organs.
Radiation and chemotherapy are often used in combination with surgical treatment to destroy residual cancer cells or when surgery cannot be performed. Turkish clinics use advanced radiotherapy and chemotherapy, ensuring maximum treatment effectiveness with minimal side effects.
Current treatments for pancreatic cancer include immunotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies. These innovative approaches target cancer cells more precisely and effectively, minimizing side effects and improving treatment outcomes.
Treatment of the disease in Turkey is based on an individual approach to each patient. Doctors develop personalized treatment plans, taking into account the specifics of the disease, the patient’s overall condition and their needs. After treatment, quality rehabilitation support is also provided to help the patient recover from surgeries and procedures.
Turkey actively participates in international clinical research and development in the field of oncology. This allows the latest technologies and treatments to be introduced, ensuring that patients have access to cutting-edge innovations.
 Treatment of tubulopathy in Korea
Treatment of tubulopathy in Korea
Tubulopathies are a group of genetic diseases associated with impaired renal tubule function. These conditions can lead to various metabolic disorders, as well as kidney dysfunction and other serious complications.
The first step in treatment is to accurately diagnose and identify the genetic basis of the disease. Genetic counseling allows families to understand the risk of passing on genetic abnormalities to future generations. Modern diagnostic techniques such as genome sequencing and molecular genetic tests can identify the specific mutation underlying the disease.
Treatment is usually aimed at reducing the symptoms and complications associated with impaired renal tubule function. This may include taking medications to correct electrolyte balance, controlling blood pressure, and maintaining optimal hydration.
An important aspect of treatment is to maintain kidney function at an optimal level. This may include taking medications to protect kidney tissue, controlling protein excretion in the urine, and regular monitoring of kidney function.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in normalizing the condition. Dietary recommendations may include limiting the intake of certain foods such as sodium, potassium, or phosphorus, depending on the nature of the metabolic disorder.
One of the key aspects of treatment is the correction of electrolyte balance disorders. Depending on the specific type of disease, different approaches to regulating the levels of sodium, potassium, magnesium, and other electrolytes in the body may be needed.
Because the disease can lead to progressive renal failure, the primary goal of treatment is to preserve kidney function. This may include the use of medications to control blood pressure, reduce proteinuria, and reduce the burden on the kidneys.
In cases of severe kidney failure, kidney transplantation may be considered as a treatment option. This restores normal kidney function and improves the patient’s quality of life.
Research in this area is ongoing and new treatments and therapies are constantly being developed. This includes the development of new drugs, gene therapy, stem cell technology and other innovative approaches.
 Hemodialysis in Korea
Hemodialysis in Korea
Hemodialysis is a life-saving procedure that helps patients with chronic kidney failure to stay alive and improve their quality of life. As a leading country in medical technology and innovation, hemodialysis procedures are performed at the highest level in South Korea, giving patients access to advanced treatments and quality care.
In Korea, hemodialysis is performed using advanced medical technology and equipment. Many hemodialysis centers are equipped with state-of-the-art dialysis machines that provide precise regulation of procedure parameters, as well as monitoring and control of all aspects of the process.
Each patient undergoing hemodialysis receives an individualized treatment approach that takes into account their specific health condition, stage of kidney failure, and other medical indicators. This ensures that the procedure is carried out in the most effective and safe manner.
The medical professionals working in hemodialysis centers in Korea are highly qualified and experienced. Doctors, nurses and other medical staff are specially trained and educated to provide patients with the highest level of care and safety during the procedure.
Hemodialysis centers in Korea provide a comfortable environment for patients undergoing the procedure. The modern facilities are equipped with comfortable chairs or beds, televisions, free Wi-Fi and other amenities to make patients feel more comfortable and relaxed during a long hemodialysis procedure.
In addition to the hemodialysis procedure itself, patients at hemodialysis centers in Korea receive comprehensive medical care. This includes regular health monitoring, blood pressure monitoring, medication management and other medical services to keep the patient in optimal health.
Korean medical institutions are actively introducing innovative hemodialysis treatments such as oncotic therapy, the use of new types of dialysis membranes and pharmaceuticals aimed at improving the procedure’s effectiveness and reducing its side effects.
South Korea is actively conducting research and development in hemodialysis to improve technology and treatment techniques. Researchers and specialists across the country are working to develop new materials for dialysis membranes, improve filtration and monitoring systems, and develop new methods for disinfecting and sterilizing equipment.
Korea provides high quality education and training for professionals working in the hemodialysis field. Medical universities and colleges offer specialized training and apprenticeship programs for doctors, nurses and other health care professionals to ensure a high level of skill and professionalism in the field.
 Treatment of glomerulonephritis in Korea
Treatment of glomerulonephritis in Korea
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidney tubules. Because of it, kidney function is impaired and chronic renal failure develops.
Initially, it is very important to determine the cause of the disease. This includes infection (e.g., after a streptococcal infection), autoimmune disease (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), or other factors. Treatment is aimed at controlling the underlying process causing inflammation in the kidney tubules.
Glucocorticosteroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response that contributes to damage to the kidney tubules. This can help slow the progression of the disease and preserve kidney function.
In cases where the disease is due to an immune response, immunosuppressive drugs may be used. They help suppress the activity of the immune system and prevent further damage to the kidney tubules.
Maintaining normal blood pressure plays an important role in regulating the patient’s condition. The use of antihypertensive drugs, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin II receptor blockers (BRA II), reduces pressure in the renal capillaries and prevents further kidney damage.
An important aspect of treating the disease is proper nutrition. Patients are advised to limit protein, salt and fat intake and avoid foods rich in potassium and phosphorus. This helps to reduce the strain on the kidneys and reduce the risk of complications.
In cases where the disease leads to severe chronic kidney failure, a kidney transplant may be a necessary treatment option. This restores normal kidney function and improves the patient’s quality of life.
New treatments, such as monoclonal antibody therapy or the use of biomaterials to regenerate kidney tissue, are being investigated to improve disease outcomes and prevent disease progression.
Regular monitoring of kidney function, including urine and blood tests and blood pressure measurements, helps identify and control complications of the disease, such as protein in the urine, anemia, or hypertension.
Patients with glomerulonephritis are advised to avoid nephrotoxic medications and to follow their physician’s recommendations regarding the administration of any medications.
 Treatment of nephropathy in Korea
Treatment of nephropathy in Korea
Nephropathies, or kidney diseases, are a serious medical problem requiring comprehensive and effective treatment. In South Korea, as in many other developed countries, there is considerable research and development in the treatment of nephropathies. Thanks to advanced technology and medical discoveries, Korean specialists are actively pursuing innovative approaches to treat this type of disease.
In Korea, nephropathies are treated using an integrated approach that includes drug therapy, dietary recommendations, physical therapy and surgery if necessary. Each patient receives an individualized treatment plan that takes into account the specifics of his or her condition and the severity of the disease.
Korea is renowned for its advanced medical technology, which includes the use of robotic systems for surgery, the use of molecular genetics for diagnosis and treatment, and the extensive use of innovative education and rehabilitation techniques.
Special attention is paid to the prevention of nephropathies in Korea. This includes early identification of risk factors such as arterial hypertension, diabetes, obesity and others and taking steps to control them. Educational programs and prevention campaigns are regularly conducted to maintain a healthy lifestyle and to seek timely medical attention when symptoms appear.
Korean researchers are actively working to develop new drugs and therapeutic techniques for the treatment of nephropathies. This includes the use of molecularly targeted drugs, immunotherapy and other innovative approaches to improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
Korean specialists are actively collaborating with medical institutions and research centers around the world to share experiences and transfer best practices in the treatment of nephropathies. This contributes to improving the quality of medical care and developing new treatment methods.
Treatment of nephropathies in Korea is based on advanced technology, integrated approach and active implementation of innovative methods. By doing so, patients have access to effective and high quality care that improves their health outcomes and quality of life.
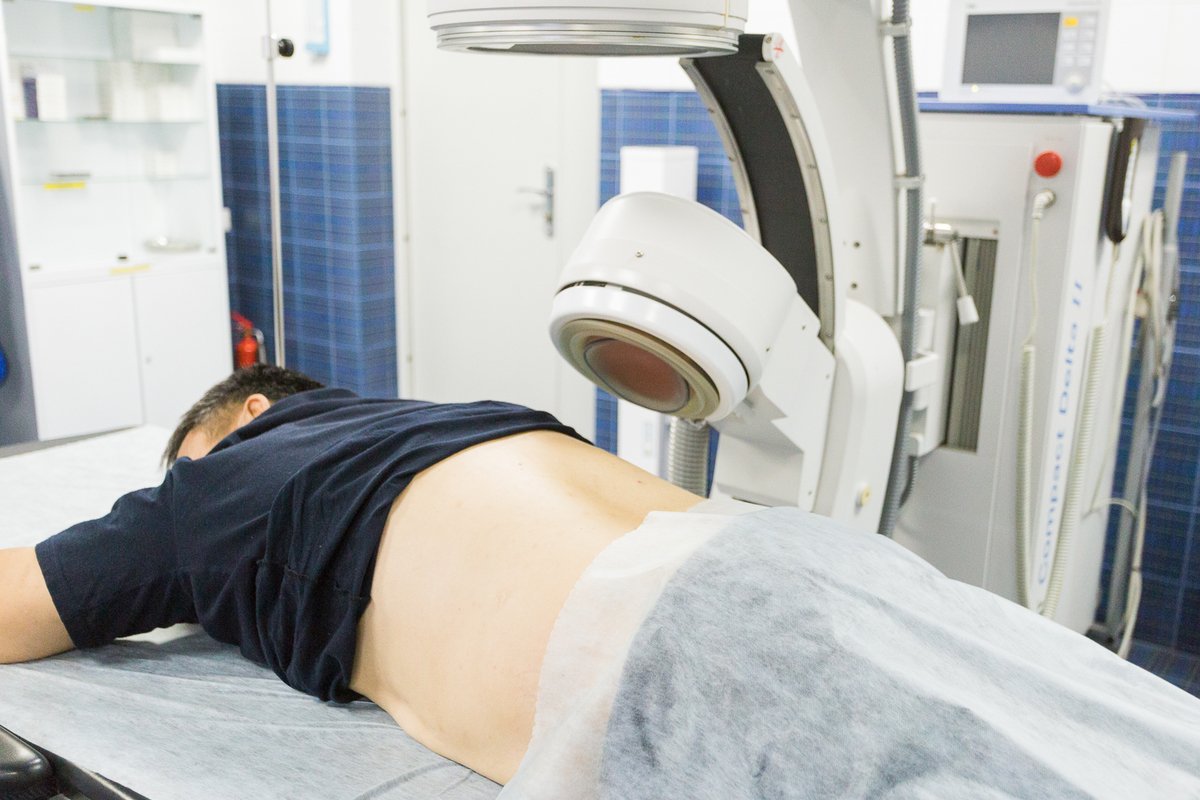 Treatment of urolithiasis in Korea
Treatment of urolithiasis in Korea
Urolithiasis is a common disease of the urinary tract, characterized by the appearance of concretions in organs such as the kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra. This condition leads to disease, discomfort, infections and other consequences. However, modern medicine offers various treatment strategies for urolithiasis that can significantly improve the condition of patients.
One of the main aspects of preventing and treating urolithiasis is maintaining adequate fluid levels in the body. Drinking water regularly helps dilute urine and prevent concretions.
Avoiding foods rich in oxalate, calcium can be an effective way to prevent recurrences. The doctor can proceed to an individualized diet, taking into account the composition of concretions and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
The use of medication methods are very effective. For example, medications based on alpha-blockers or citrates may help in providing relief to the patient.
To control pain symptoms that often accompany urolithiasis, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are used.
Shockwave lithotripsy refers to non-invasive procedures characterized by the operation of shock waves. This allows you to break the pebbles into smaller pieces.
Sometimes surgery may be required to remove the stones. Procedures such as urethroscopy, cystoscopy, laparoscopy or open surgery can show excellent effects.
After good treatment, it is important to take steps to prevent recurrences. This may include following a healthy lifestyle, eating a healthy diet, drinking fluids regularly, and regular checkups with your doctor.
Your doctor may prescribe medications such as thiazide diuretics to change the composition of your urine and prevent stones from forming. Patients should have regular follow-up and monitoring to determine the status and effectiveness of treatment. This will help prevent recurrences or events from occurring early on and take the necessary steps.
New technologies and treatments, such as laser therapy or endoscopic stone removal, continue to be available and offer new options for treating the disease.
 Nephroptosis treatment in Korea
Nephroptosis treatment in Korea
Nephroptosis, or renal ptosis, is a condition in which the kidney drops below its normal state due to loss of support from surrounding tissues and ligaments. This condition can lead to various symptoms such as lower back pain, urinary disturbances, and even damage to kidney tissue.
In surgery, a laparoscopic technique is often used to fix a mobile kidney. This restores it to its normal position and prevents it from sinking again.
Retroperitoneoscopic fixation: This method also allows surgeons to fix the kidney using retroperitoneal access, allowing for a minimally invasive approach and rapid patient recovery after surgery.
Some research is focused on developing biomaterials that can be used to create new structures to fix the kidney and restore it to normal.
Gene therapy: experimental studies are also exploring the use of gene therapy to target the ligaments and tissues that support the kidney, which may help prevent nephroptosis.
For patients at an increased risk of developing nephroptosis, such as women in pregnancy, it is important to have regular checkups and consultations with your doctor for early detection and prevention of this condition.
Regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding unnecessary stress on the kidneys can help prevent nephroptosis and improve your overall health.
Regular check-ups and follow-up with your doctor will help you monitor your kidney health and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. In case of any changes or symptoms, it is recommended to contact a physician for further consultation and adjustment of therapy.
For some patients, the disease can be a source of stress and anxiety. Psychological support and counseling can help patients cope with the emotional difficulties associated with diagnosis and treatment and improve their quality of life.
Research into the treatment of the disease is ongoing, and new methods and technologies are constantly being developed. This opens up new perspectives for improving treatment outcomes, shortening the rehabilitation period and improving the quality of life of patients.
In conclusion, treatment of the disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes conservative methods, surgery, rehabilitation and follow-up. Early medical attention, timely diagnosis and proper treatment are critical to the successful management of this condition. Further research and innovation will help improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients with nephroptosis.
 Treatment of dacryoadenitis in Korea
Treatment of dacryoadenitis in Korea
Dacryoadenitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal gland that can cause pain and discomfort in the eyelid and eyeball area. This condition usually occurs due to infection or blockage of the gland’s outlet duct. Treatment of the condition is aimed at eliminating inflammation, relieving painful symptoms, and preventing recurrence.
The main goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation in the area of the lacrimal gland. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as antibiotics or steroids may be recommended for topical application to the eyelid area or as systemic therapy, depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of infection.
Heat compresses can help improve blood circulation and relieve congestion in the lacrimal gland’s outflow ducts. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of the disease. It is recommended to apply heat compresses several times a day for 10-15 minutes each time.
Massage of the lacrimal gland can help open its exit ducts and improve tear outflow. This can be helpful in cases where the disease is associated with blockage of the excretory ducts. Massage should be done gently and as recommended by your doctor to avoid damaging the gland or aggravating inflammation.
If the disease is caused by a bacterial infection, systemic or topical antibiotics may be required. The choice of drug depends on the sensitivity to antibiotics of the infectious agent. A course of antibiotics usually lasts for a few days to a week, depending on the severity of the infection.
In recurrent or chronic forms, surgical intervention may be required. This may include flushing the lacrimal gland’s exit ducts, draining abscesses, or removing cysts. Surgical treatment is usually considered when conservative methods fail.
Despite significant advances in the treatment of dacryoadenitis, there is still a need for further research to develop more effective treatments and prevention methods. This includes researching new antibiotics, developing innovative surgical techniques, and understanding the underlying mechanisms of this disease.
 Episcleritis treatment in Korea
Episcleritis treatment in Korea
Episcleritis, an inflammatory disease of the episclera (the thin transparent membrane covering the sclera of the eye), can cause discomfort and visual problems. Episcleritis treatment is becoming more and more effective due to ongoing scientific and medical advances.
Episcleritis is characterized by inflammation of the episclera, which lies beneath the conjunctiva and over the sclera. This condition often manifests as soreness, redness of the eye, and a sense of irritation. Episcleritis can be acute or chronic and can occur independently or be associated with other systemic diseases.
In mild cases, the use of anti-inflammatory eye drops is acceptable. This applies to drops with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial action. In Korea, these drops are often developed with the latest scientific advances and are widely available in pharmacies.
Sometimes steroid medications may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation. However, their use requires strict supervision by a physician due to potential side effects.
It is worth noting the use of laser therapy. It aims to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. This technique is often used in advanced medical centers in Korea.
Immunosuppressants are used when the disease is due to immune disorders, immunosuppressants may be used to reduce immune system activity and prevent inflammation.
Surgery is performed when the disease becomes chronic and does not respond to other treatments. Recent research suggests that ultraviolet (UV) radiation may be effective in treating some forms of the disease. Korea has developed specialized ultraviolet therapy protocols that are used in clinics to manage this condition.
The use of anti-inflammatory injections, when the disease is accompanied by severe inflammation, injections of anti-inflammatory drugs into the area of inflammation may be used to control the condition more quickly and effectively.
Doctors in Korea usually take an individualized approach to treating each patient, taking into account the characteristics and severity of the condition. A combination of different treatments is often used to achieve optimal results.
 Cataract treatment in Korea
Cataract treatment in Korea
A cataract is an eye condition that causes gradual loss of vision due to clouding of the normally clear lens inside the eye. It is a common condition, especially among older adults, and it can significantly affect quality of life. However, modern medicine offers various treatments that can help patients.
As we age, the lens of the eye can lose its clarity due to protein buildup. Some people may be more predisposed to developing the disease due to genetics. Diabetes mellitus can increase the risk of developing the disease.
Symptoms may gradually worsen over time and include:
- loss of visual clarity;
- difficulty perceiving color and contrast;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- the appearance of “misting” in front of the eyes;
- the perception of double vision in one eye.
Treatment of the disease usually involves surgical intervention. The most innovative treatment is surgical intervention to replace the clouded lens with an artificial lens. This procedure is usually performed in a way that uses ultrasound waves to soften and remove the clouded lens and then replace it with artificial lenses.
There are several types of artificial lens that are used in lens replacement during surgery. Some can also correct farsightedness or nearsightedness, allowing the patient to see better without wearing glasses.
Surgery is the most common and effective way to treat the disease. In the procedure, the surgeon removes the clouded lens and replaces it with an artificial intraocular lens.
Cataracts are serious eye diseases that result in vision loss, but modern treatments, especially surgery, offer effective ways to restore vision and improve patients’ quality of life. If you have signs of cataracts or a change in the quality of your vision, it is important to see your doctor for diagnosis and to determine the best treatment method.
 Treatment of ocular atrophy in Korea
Treatment of ocular atrophy in Korea
Ocular nerve atrophy is a serious complication that can lead to vision loss and reduced quality of life for the patient. This condition reduces the reduction in size and functional activity of the oculomotor nerve, which in turn can be caused by various factors such as trauma, inflammation, compression or blood supply disorders.
Ocular nerve atrophy can have many causes, including trauma, infection, tumor, vascular infarction or atherosclerosis, and neurological diseases such as sclerosis. Regardless of the cause, the process of developing atrophy is associated with a decrease in the number of axons (nerve fibers) and degeneration of nerve cells.
The underlying cause may be some other disease or condition, such as an infection or tumor, that requires your own treatment. Therefore, the first step in helping the disease is to identify and treat the underlying cause.
Patients with this condition may benefit from the use of rehabilitation measures such as physical therapy, orthotic devices, or educational and rehabilitation programs to help restore or improve visual function.
Some complexes for developing methods aimed at stimulating nerve cell growth and survival using growth factors or cell transplantation. These techniques may contribute to the success of a personalized approach to oculomotor nerve disease in the future.
Some of the most advanced research efforts include the use of gene therapy and stem cell technologies to regenerate nerve tissue. Gene therapy can be aimed at repairing damaged genes or stimulating nerve cell growth, while stem cells can be used to generate new neurons. These methods are still in the research phase, but promise to be powerful tools in the fight against the disease.
Also, studies have shown that electrical nerve stimulation can improve ocular nerve health and visual performance in some patients with atrophy. This opens up new perspectives for the development of devices and methods aimed at improving visual function.
 Treatment of polycystic ovaries in Korea
Treatment of polycystic ovaries in Korea
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a common endocrine disorder characterized by the presence of multiple small cystic masses on the ovaries. It can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, hormonal disorders and other health problems in women. In Korea, as in other developed countries, medical science is constantly improving, and gynecology specialists offer advanced methods of treating the disease.
Modern drugs are widely used in Korea to treat polycystic ovaries. Doctors may prescribe hormonal medications to normalize the menstrual cycle and improve reproductive health.
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can be used to treat the disease. With laparoscopy, doctors can remove cysts on the ovaries and restore normal ovarian anatomy and function, which can help improve reproductive health.
Some clinics in Korea offer innovative treatments for this condition. This may include the use of newer technologies such as focused ultrasound, radiofrequency ablation, or genetic therapies that aim to normalize ovarian function and improve reproductive health.
One of the key principles is an individualized approach to each patient. Doctors carefully analyze medical history, perform a comprehensive examination and determine the best treatment plan, taking into account the specifics of each particular situation.
Korea practices an integrated approach to treating the disease, which includes not only drug and surgical therapy, but also complementary methods such as acupuncture, phytotherapy, and other alternative methods. This approach is aimed at providing a complex effect on the body, improving the general condition of the patient.
Leading medical centers in Korea are actively involved in research and clinical trials of new treatments. This allows the introduction of innovative technologies and techniques in practice, as well as the continuous improvement of existing approaches to the treatment of this disease.
Korean doctors adhere to the modern principles of medicine, which means that the entire treatment process is focused on the needs and desires of the patient. Doctors strive to establish a trusting relationship with patients, listen carefully to their concerns and preferences, and then develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account all aspects of their health and life.
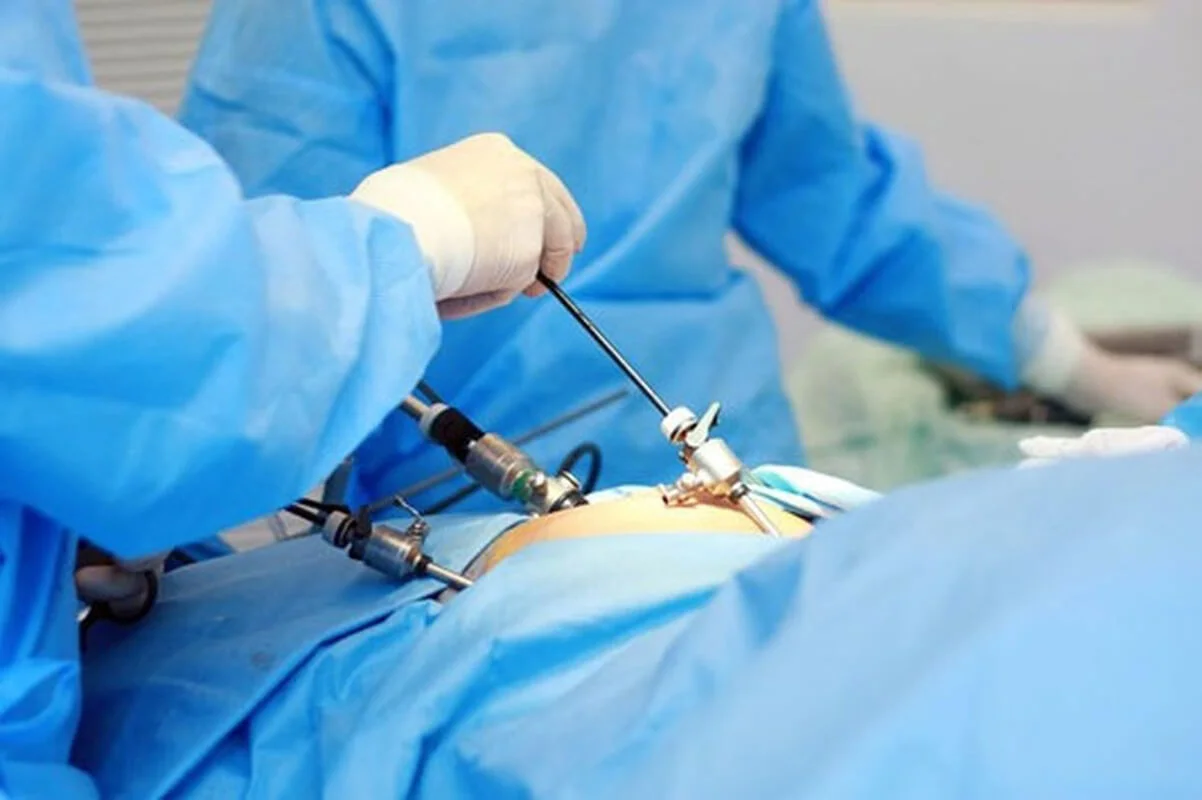 Uterine myoma treatment in Korea
Uterine myoma treatment in Korea
Uterine myoma, one of the most common gynecologic diseases among women of reproductive age, requires competent and effective treatment to improve quality of life and preserve reproductive health. Modern medicine offers a wide range of uterine myoma treatment methods, including both conservative and surgical approaches.
Using hormonal medications, such as hormonal contraceptives or progesterone, can help control myoma symptoms such as bleeding and pain.
Excess estrogen, the hormone responsible for endometrial growth, can contribute to myoma development. Imbalance between estrogen and progesterone levels may also play a role in this process.
Uterine myoma most often develops in women between the ages of 30 and 40. After menopause, the risk of developing myoma decreases. Pregnancy can stimulate myoma growth due to changes in hormones and blood flow in the uterus.
For small and asymptomatic myomas, surveillance may be recommended as a primary approach. This is suitable for women who do not have severe symptoms or reproductive health problems.
Hormonal medications such as hormonal contraceptives, progesterone and others can be used to reduce myoma symptoms such as bleeding and pain. These drugs block the production of estrogen, which can lead to a reduction in myoma size. They are commonly used in the preoperative period to reduce the size of myoma before surgery.
Myomectomy – surgical removal of myoma with preservation of the uterus. This method is often used in women who want to preserve fertility. Complete removal of the uterus. This method may be necessary in cases of severe myoma symptoms, large tumor size, or if other complications are present.
Laparoscopic myomectomy and hysterectomy are minimally invasive surgical techniques that may be preferred by some patients. They have less trauma, faster recovery and fewer complications after surgery.
Focused ultrasound is a procedure in which ultrasound waves are focused on the myoma, heating and destroying its tissue. This method can be effective in reducing myoma symptoms without surgery.
Radiofrequency ablation is a technique that uses radiofrequency waves to heat and destroy myoma tissue. It can also be used to treat myoma symptoms without surgery.
 Vulvitis treatment in Korea
Vulvitis treatment in Korea
Vulvitis, an inflammation of the vulva, is a common condition that can cause discomfort and discomfort in women. This condition requires timely treatment to prevent complications and restore the health of the vulva.
Causes can include infections, allergies, injuries, hormonal changes and stress. Each cause has its own characteristic signs and treatment options.
A feature of vulvitis is its symptomatology, which may include itching, irritation, redness and swelling in the vulvar area, as well as discharge, pain and discomfort during urination or sexual intercourse. These symptoms can be quite uncomfortable and can greatly affect a woman’s quality of life.
One of the first steps in treating the disease is practicing good hygiene. This includes regular gentle cleansing of the vulva using neutral soap and warm water, avoiding harsh detergents and synthetic underwear, and keeping the vulvar area dry after washing.
Anti-inflammatory creams and ointments are often used to relieve inflammation and discomfort in the vulvar area. These medications may contain steroids, antibiotics, antiseptics, or other active ingredients that help reduce inflammation and symptoms.
In cases where the disease is caused by a bacterial infection, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics to kill pathogens. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics, so it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and complete the full course of treatment.
If the condition is caused by a fungal infection, your doctor may recommend the use of antifungal medications in the form of creams, ointments, or oral medications. These remedies help to kill the fungus and reduce the symptoms of the disease.
To prevent worsening of the disease, it is important to avoid contact with potential irritants such as harsh detergents, synthetic underwear, strong scented hygiene products and chemicals.
For severe discomfort and pain in the vulvar area, warm compresses or baths with soothing herbs and plants such as chamomile or lavender may help. These treatments help relieve tension and reduce discomfort.
Once treatment is complete, it is important to take steps to prevent recurrence of the disease. This may include practicing good hygiene, avoiding potential irritants, and strengthening the immune system.
 Adnexitis treatment in Korea
Adnexitis treatment in Korea
Adnexitis, inflammation of the uterine appendages, is a serious condition that requires competent and timely treatment to prevent complications and preserve a woman’s reproductive health. Korea, with its advanced technology and high level of medical care, offers innovative approaches and effective treatments for adnexitis that make this country one of the leaders in women’s health.
In Korea, the treatment of adnexitis is based on an integrated approach that includes both medication and minimally invasive surgical procedures. Doctors conduct a thorough diagnosis and develop an individualized treatment plan for each patient, taking into account their clinical features and the severity of the disease.
Korean surgeons are skilled in advanced techniques of minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopy and robotic surgery. These techniques allow surgeries to be performed with minimal traumatic effects on patients, speeding recovery and shortening hospital stays.
Modern medications, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and drugs to improve the immune system, play an important role in the treatment of adnexitis. Doctors adjust dosing regimens and choose the most effective drugs, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
Once active treatment has been completed, it is important to ensure that the patient is continuously monitored and supported through the recovery process. Doctors conduct regular check-ups and examinations for timely detection of possible complications and prevention of their development.
Antibiotics play a key role in the treatment of adnexitis. Since inflammation is usually caused by a bacterial infection, the use of antibiotics helps to kill the pathogens and stop the inflammatory process from progressing. Modern antibiotics with high efficacy and safety are widely used in Korea.
In some cases, robotic surgery is used to treat adnexitis in Korea. This method allows surgeons to perform operations using a special surgical robot that is controlled by a doctor using a computer system. Robotic surgery provides more precise and less invasive interventions, which reduces the risk of complications and speeds patient recovery.
Korea is actively involved in research and development of new treatments for adnexitis. Leading medical centers of the country provide training and internships for medical specialists from different countries, exchange of experience and knowledge, which contributes to the development of global medicine.
 Salpingitis treatment in Korea
Salpingitis treatment in Korea
Salpingitis, an inflammation of the Fallopian tubes, is a serious condition that can lead to a variety of complications, including infertility and chronic lower abdominal pain. This condition requires immediate and adequate treatment to prevent its spread and minimize negative effects.
One of the main treatments for salpingitis is antibiotic therapy. Since inflammation is usually caused by a bacterial infection, the use of antibiotics helps to kill pathogens and prevent the spread of inflammation. Doctors usually choose a wide range of antibiotics to ensure effective treatment.
Laparoscopic surgery has become the treatment of choice for salpingitis due to its minimal invasiveness and high efficacy. In this method, instruments and an optical device are inserted through small incisions in the abdominal wall to examine and treat the Fallopian tubes. The laparoscopic method can remove pustules, clear the tubes of infection and restore their function.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are also used to relieve the inflammation and pain of salpingitis. These medications help to reduce inflammation and discomfort and improve the overall condition of the patient.
In acute salpingitis, therapy may be required to compensate for fluid loss and maintain hemodynamic stability. This may include intravenous fluids, electrolytes, and antibiotics to fight infection and maintain optimal hydration.
After the main course of treatment, it is important to carry out rehabilitation and recovery procedures that will help the patient to return to normal life more quickly. This may include physiotherapy, advice on lifestyle changes including stopping smoking and eating a healthy diet, and psychological support.
With the constant development of medical technology and treatment methods, doctors are constantly looking for new, more effective approaches to treating salpingitis. This may include the use of new antibiotics, biologic drugs, immunotherapy and other innovative techniques.
After treatment is complete, it is important to have regular medical checkups and examinations to monitor your health and prevent recurrence. It is also important to practice good personal hygiene and use contraceptive methods to prevent re-infection.
After successfully completing treatment for salpingitis, it is important to take steps to prevent recurrence. This includes practicing good personal hygiene, avoiding unacceptable sexual behavior, regular medical checkups, and using birth control if necessary.
 Endometritis treatment in Korea
Endometritis treatment in Korea
Endometritis, an inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus, is a serious disease that requires timely and adequate treatment to prevent complications and preserve a woman’s reproductive health.
One of the main treatments for endometritis is antibiotic therapy. Since inflammation is usually caused by a bacterial infection, the use of antibiotics helps to kill the pathogens and stop the inflammatory process from progressing. Antibiotic treatment is usually prescribed after the results of bacteriologic analysis of uterine mucosal smears.
Anti-inflammatory medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used to relieve the inflammation and pain of endometritis. These medications help reduce inflammation and discomfort, as well as lower body temperature.
In some cases, especially complicated endometritis with abscesses or other changes in the structure of the uterus, surgical intervention may be necessary. Laparoscopic surgery has become the treatment of choice as it is less traumatic, shortens the rehabilitation period and achieves good results.
In acute endometritis, infusion therapy may be required to maintain hemodynamic stability and compensate for fluid loss. Intravenous fluids, electrolytes, and antibiotics help fight infection and improve the patient’s overall condition.
After the completion of active treatment, it is important to perform physical therapy and rehabilitation procedures that will help restore the functional state of the uterus and accelerate the healing process. This may include physical therapy, therapeutic massage and exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
After completing an active course of treatment, it is important to take steps to prevent recurrence of endometritis. This may include supportive antibiotic therapy, regular medical check-ups and examinations to monitor your health.
Treatment of endometritis is a complex process that requires an individualized approach and a combination of different methods depending on the characteristics and severity of the disease. Modern treatments provide an effective and safe solution to endometritis, helping patients recover faster and avoid complications. It is important to see an experienced professional to diagnose and prescribe the best treatment for each case.
 Endocervicitis treatment in Korea
Endocervicitis treatment in Korea
Endocervicitis is inflammation of the endocervical canal, an area of the cervix caused by infection or other inflammatory processes. This is a common condition that requires timely and adequate treatment to prevent complications and preserve a woman’s health.
One of the main treatments for the disease is antibiotic therapy. Since inflammation is often caused by infection, the use of antibiotics helps to kill pathogens and stop the inflammatory process from progressing. Antibiotic treatment is usually chosen based on the sensitivity of the pathogen to the drugs, and broad-spectrum antibiotics are often preferred.
In addition to antibiotics, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs is also important in treating the disease. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain, inflammation, and discomfort in the cervical area. These medications can be taken orally or used topically as vaginal suppositories or creams.
To more effectively affect the focus of inflammation in the cervical region, local treatment methods are often used. This may include the use of vaginal suppositories or creams containing antibiotics or anti-inflammatory substances. These methods provide direct exposure to the affected tissues and can speed up the healing process.
In some cases, especially in the chronic course of the disease, the use of immunomodulators may be recommended. These drugs help to strengthen the body’s immune system, increase its resistance to infection and speed up the healing process.
Laser therapy is becoming an increasingly popular method of treating the condition. Laser treatment can precisely destroy the affected tissue, reducing inflammation and stimulating the healing process. This method is highly effective and minimally invasive, making it the method of choice for many patients.
In severe cases where conservative treatment fails to improve the condition, surgical intervention may be required. Surgery may involve removal of the affected areas of the endocervical canal or even partial removal of the cervix (conization). These methods are used in extreme cases and require serious discussion between doctor and patient.
After the main course of treatment, some patients may require physical therapy procedures to speed recovery and strengthen tissues. Physical therapy can include various modalities such as ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation and therapeutic massage to help improve circulation, reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Endocervicitis can have a significant impact on the patient’s emotional state due to pain, discomfort and anxiety regarding health. Therefore, it is important to provide the patient with psychological support and counseling to help them cope with the emotional difficulties associated with the disease and increase their psychological resilience during the treatment process.
 Bartholinitis treatment in Korea
Bartholinitis treatment in Korea
Bartholinitis is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and even complications if not treated promptly and adequately. South Korea, as well as other countries, pay special attention to this condition and utilize advanced treatment methods focused on maximizing patient comfort and quick recovery.
Surgical treatment includes a variety of techniques to help manage inflammation and prevent recurrence. In one of the procedures, a new drainage channel is created to facilitate the outflow of secretions. This method eliminates the problem and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Botulinum toxin injections into the gland are sometimes used. This method can block the gland and prevent cyst formation. The use of botulinum toxin can also help reduce pain and inflammation.
In recent years, the use of laser therapy to treat the disease has been expanding in Korea. Laser removal of glandular cysts can be a less invasive and more effective treatment option than surgical methods. This allows for a shorter recovery period and reduces the risk of complications after the procedure.
In addition to surgical methods, doctors in Korea often recommend a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce inflammation and pain of the condition. This allows you to manage your symptoms faster and prevent complications.
South Korea has an integrated approach to treating the disease, which includes not only drug and surgical therapy, but also related methods such as physical therapy, psychological support, and recommendations for lifestyle changes. This allows not only to quickly get rid of inflammation, but also to prevent recurrences and improve the quality of life of patients.
 Retinal detachment treatment in Korea
Retinal detachment treatment in Korea
Retinal detachment is considered a serious disease that leads to loss of vision if not treated in a timely manner. It occurs when the retina distorts its normal position in the back of the eye. This condition requires medical intervention to prevent adverse effects of visual function.
Several factors can cause the disease, including injury, diabetes, high blood pressure, glaucoma, age-related changes and hereditary factors.
The main symptoms include the presence of flashes of light, flies in front of the eyes, the feeling of a “curtain”, blackouts. If these symptoms occur, especially if they occur suddenly or intensify, consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary.
The surgical method involves sewing a silicone belt (bandage) around the eyeballs. Such a belt reduces retinal stretching and prevents further development of the disease.
Another procedure involves inserting a gas bubble into the eye to fix the retina in the correct position. In this way, the contact between the retina and the vasculature of the eye can be improved.
Targeted laser treatment of the damaged areas help stimulate the formation of scar tissue that anchors the retina.
Laser photocoagulation is used to treat the original causes of the disease. The procedure aims to destroy abnormal capillaries and strengthen the vascular wall, which can help prevent further retinal detachment.
In some cases, injections of medication inside the eye may be used to reduce inflammation, stimulate tissue regeneration, or reduce the risk of new blood vessel formation, which may be helpful in treating some types of disease.
After surgical procedures, doctors often prescribe eye drops. It is recommended to limit physical activity and visit an ophthalmologist regularly to monitor the condition of the eyes.
The psychological aspects of the disease should not be underestimated. For some patients, the disease is accompanied by a difficult experience, causing anxiety and depression. Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals can be an important component of overall treatment and recovery.
Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment make it possible to achieve good results and prevent deterioration of visual functions in patients. However, it is important to remember that the success of treatment depends on the timeliness of seeking help and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations both during and after treatment.
 Keratoconus treatment in Korea
Keratoconus treatment in Korea
Keratoconus is a progressive corneal disease characterized by gradual thinning and bulging of the corneal layer, distorting vision and impairing the patient’s quality of life. Treating this condition is a key focus of modern ophthalmology, and South Korea stands out for its innovative methods and technology in this field.
Corneal transplantation remains the primary treatment modality for the disease when corneal thickness becomes critically insufficient to maintain the structural integrity of the eye. However, in recent years, new corneal transplantation techniques such as DMEK and DSAEK have been developed in Korea, which minimize the risk of rejection and improve the prognosis of postoperative outcome.
Along with the traditional methods of corneal transplantation, non-transplantation correction methods are being actively developed in Korea. One such method is the intravitreal collimation lens (ICL), which is an implantable lens that corrects vision inside the eye. This method is particularly effective in patients with early stages of the disease and avoids the need for corneal transplantation.
South Korean ophthalmologists are actively using advanced technology to diagnose and treat the disease. One such technique is corneal topography, which allows for an accurate assessment of the shape and thickness of the cornea. In this way, the best treatment method can be selected. It is also worth noting the widespread use of refractive surgery techniques such as LASIK (laser epithelial keratectomy), which can be effective in correcting vision in patients in the initial stages of the disease.
Korean ophthalmology centers are actively involved in clinical research and development of the latest techniques to treat the disease. This allows patients to have access to the latest innovations and technologies that can improve treatment outcomes and increase the effectiveness of procedures.
Modern diagnostic techniques allow us to evaluate the individual characteristics of each case, including the degree of progression, corneal thickness, associated complications, and overall visual health. Based on these findings, ophthalmologists develop the best treatment plan, which may include surgical techniques, contact lens vision correction, or refractive surgery.
 Astigmatism treatment in Korea
Astigmatism treatment in Korea
Astigmatism is a common eye condition characterized by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens of the eye. This condition distorts vision and makes the image fuzzy. Although it cannot be categorized as a dangerous disease, it can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life, especially when performing tasks that require good vision. In Korea, treatment is carried out at a high level using advanced medical methods and technologies, as well as taking into account the individual needs of each patient.
Laser vision correction, such as LASIK or PRK, is one of the most common treatments in Korea. These procedures reshape the cornea of the eye with precision, leading to improved vision.
If laser correction is not possible, implantation of special intraocular lenses is possible. They help correct the correct focus of the retina, which improves vision.
Korea utilizes laser technology to provide more accurate and safer surgical procedures to correct the condition. This reduces the risk of complications and improves the effectiveness of treatment.
Doctors in Korea offer a personalized approach to treating the disease, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. This includes a detailed preliminary examination, assessing the degree of astigmatism and developing the best treatment plan to achieve the best results.
Korean ophthalmologists are highly qualified and experienced in the treatment of astigmatism, which enables them to achieve high results and improve patients’ vision.
Clinics in Korea are equipped with advanced medical technology and laser equipment to ensure accurate and effective surgical procedures to correct astigmatism.
Patients seeking astigmatism treatment in Korea can expect a high level of medical care, including individualized attention, professional counseling, and patient care.
 Blepharospasm treatment in Korea
Blepharospasm treatment in Korea
Blepharospasm is characterized by involuntary spasmodic contractions of the eyelid muscles, provoking frequent and involuntary blinking or complete closure of the eyelids. Such symptoms create discomfort and can cause psychological distress.
Patients with the condition may experience frequent and rhythmic eyelid blinking. Blepharospasm can cause discomfort and limit the patient’s ability to perform everyday tasks such as reading, driving, or working on a computer.
The disease is often associated with nervous system dysfunction, particularly abnormalities in the functioning of the basal ganglia or other brain structures that control muscle movements.
Some studies suggest that there is a genetic predisposition to the development of blepharospasm. Factors such as stress, fatigue, intense light, or irritants in the environment can cause or exacerbate symptoms of the disease.
Botulinum toxin injections into the eyelid muscles help temporarily block the nerve impulses that cause spasms. Some patients may benefit from the use of medications such as myorelaxants or drugs that improve nervous system function. Physical therapy and psychological support can help patients manage stress and improve quality of life.
To achieve the best results in the treatment of the disease, it is recommended to use a comprehensive approach, including not only drug therapy and surgery, but also regular assessment of the patient’s condition and correction of the treatment plan depending on the effectiveness of the procedures performed.
It should be noted that the disease is a chronic condition and patients may require regular monitoring and treatment adjustments throughout their lives. However, with the right approach and proper medical care, most patients can achieve significant improvement and manage their condition.
Treatment of the disease requires a comprehensive approach and an individualized treatment plan tailored to the specifics of each case. Modern therapies can achieve good results and improve the quality of life of patients suffering from this unpleasant disease.
 Myopia treatment in Korea
Myopia treatment in Korea
Myopia is one of the common eye diseases characterized by the fact that vision is good only at close distances. This condition is usually caused by the eyeball lengthening or a change in the shape of the cornea. Although the condition is not dangerous, it significantly limits quality of life, especially if not treated properly.
One of the treatments for myopia is the use of special drops that can slow the progression of myopia, especially in children and adolescents. They usually contain atropine or other active ingredients that help relax the muscles of the eye and reduce the accelerated growth of the eyeballs.
Correct the vision of patients with myopia with glasses or contact lenses. These optical aids help correct the focusing of light on the retina, improving vision in the distance.
Laser corrections, such as LASIK or PRK, are an effective method of treating myopia, especially in people with moderate to high myopia. These procedures reshape the cornea of the eye to allow light to focus better on the retina, improving vision.
This method of treating myopia involves surgically implanting special lenses inside the eye to change the focus of light and improve vision. This procedure may be recommended for patients with high degrees of myopia who are not suitable for laser vision correction.
With the advancement of technology and research in the field of ophthalmology, there are new perspectives in the treatment of myopia. Some research is focusing on developing genetic treatments that may help prevent or correct myopia early in its development. In addition, nanotechnology and stem cell research also offer new opportunities to develop innovative treatments for myopia.
It should be noted that successful treatment of myopia depends on a number of factors, including the severity of the disease, the patient’s age, general health, and the presence of any associated eye conditions. Therefore, it is important to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist who will be able to determine the most appropriate treatment method for your particular case.
In addition, regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist play a key role in preventing disease progression and detecting any changes in vision at a very early age. Early detection and treatment of myopia can help prevent serious complications and preserve your vision for years to come.
It is also important to remember to take proper eye care and follow your doctor’s recommendations after treatment. This includes regular use of prescribed medications, controlling diet and lifestyle, and following a work and rest regimen for the eyes.
 Treatment of orbital hypertelorism in Korea
Treatment of orbital hypertelorism in Korea
Orbital hypertelorism, although a rare condition, requires special attention and a comprehensive approach to treatment. This condition is characterized by an increase in the volume of tissue around the orbit, which can lead to distortion of the eyeball, limitation of eye movement, and cosmetic defects. Diagnosis and treatment of orbital hypertelorism is a multi-step process that requires careful attention to symptoms and the application of various therapies.
In the initial stages of the disease, anti-inflammatory treatment may be prescribed to reduce swelling and inflammation in the orbital area. If drug therapy does not result in sufficient improvement, surgical removal of excess tissue or correction of abnormalities may be required.
Because the condition may be accompanied by cosmetic defects and emotional discomfort, patients may require the support of a psychologist or psychotherapist.
In Korea, the disease is usually treated at a high level using advanced medical techniques and technology. Korean medical facilities are known for their advanced medical technology, high level of care and skilled professionals.
Korean doctors take a universal approach to treating the disease, including drug therapy, surgery, radiotherapy and other methods, depending on the individual characteristics of each patient.
Korean medical facilities make extensive use of advanced technologies such as robotic surgery, laser therapy and high-resolution imaging to accurately diagnose and effectively treat the disease.
Doctors in Korea are highly skilled and experienced in dealing with rare and complex diseases. They undergo regular training and exchanges to keep abreast of the latest scientific and medical advances.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is carried out at a high level using advanced methods and technologies, supported by experienced specialists and individualized approach to each patient. Korean medical facilities often attract international patients due to their high level of care and advanced treatment methods.
 Uveitis treatment in Korea
Uveitis treatment in Korea
Uveitis is an inflammatory disease of the vasculature of the eye that can lead to serious complications and vision loss if not treated promptly and adequately. In Korea, as in many other countries, treatment is carried out using advanced methods and technology to achieve high results and prevent complications.
The first step in treating the disease is to accurately diagnose and determine the type and extent of inflammation. Korean medical facilities utilize advanced examination techniques including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound biomicroscopy and other technologies to provide a detailed view of the eye and assess the degree of inflammation.
One of the main treatments for the disease is the use of medications, including anti-inflammatory eye drops, steroid medications, and immunosuppressants. In Korea, modern medicines are used to effectively reduce inflammation and prevent the development of complications.
In cases where uveitis is accompanied by the formation of synechiae (adhesions) inside the eye or glaucoma, laser therapy may be used. This method can prevent or reduce synechiae, as well as reduce intraocular pressure, which helps to improve the condition of the eye and prevent vision deterioration.
One of the key features of disease treatment in Korea is an individualized approach to each patient. Korean doctors take into account not only the type and degree of inflammation, but also health conditions and other factors that may affect the results of treatment to achieve the best results and prevent recurrence.
Korean scientists and physicians are actively engaged in research on the disease in an effort to develop new methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as to understand the underlying mechanisms of the disease. This contributes to the continuous improvement of treatment methods and the efficiency of medical care.
Korean medical institutions emphasize patient care and support by providing information about the disease, its treatment and possible complications, as well as providing emotional and psychological support to patients and their families.
Treatment of uveitis in Korea is carried out using advanced methods and technologies, individualized approach to each patient and high level of scientific research. This ensures that patients receive high quality medical care and the opportunity to preserve their vision for years to come.
 Chalazion treatment in Korea
Chalazion treatment in Korea
A chalazion is a condition of the eyelid characterized by the formation of a cyst or tumor on the eyelid caused by a blockage of the small oil glands. This condition can be painful and lead to cosmetic defects, but modern treatments, especially in Korea, provide effective and safe ways to get rid of this condition.
In the initial stages of the disease, conservative treatment including hot compresses and eyelid massage may be sufficient. This helps to improve oil gland outflow and reduce inflammation.
Expression is a procedure in which the doctor manipulates the eyelid to expel the contents through a small incision. This can be an effective method for large or persistent cysts.
In cases where conservative methods are ineffective or the condition causes serious discomfort or cosmetic problems, surgical removal may be necessary. This is a procedure in which the doctor removes a cyst or tumor from the eyelid under local anesthesia.
Laser therapy is an innovative method of treating the disease that uses laser light to destroy the contents of a cyst or tumor and prevent recurrence.
After surgical removal of a chalazion, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations regarding eyelid care. This may include the use of topical medications, limiting physical activity, and wearing protective eyewear.
Korean clinics offer high-tech treatments for the disease, including advanced technology and experienced specialists to achieve high results and reduce the risk of complications.
Korea is actively involved in research on surgical treatment of the disease to develop new methods and technologies to improve surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Doctors in Korea provide patients with not only quality treatment, but also support, care and individualized attention to each case, which contributes to faster recovery and better quality of life.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is a comprehensive approach that includes various methods and technologies aimed at eliminating the tumor and preventing its recurrence. With advanced treatments and experienced specialists, patients can expect great results and quick recovery from procedures.
 Glaucoma treatment in Korea
Glaucoma treatment in Korea
Glaucoma is one of the most common and dangerous eye diseases leading to vision loss. Korea, with its advanced medical equipment and high level of specialized medical care, is one of the leaders in glaucoma treatment.
Treatment of the disease in Korea begins with a thorough diagnosis and evaluation of the eye condition. This includes measuring intraocular pressure, evaluating visual fields, checking the fundus of the eye, and other specialized tests to determine the degree and type of glaucoma.
Korean clinics are adopting advanced technology and equipment to treat glaucoma. This includes state-of-the-art laser systems, microsurgical instruments and high-tech equipment for diagnosing and monitoring the condition of the eye.
In addition to surgical methods, medication is widely used in Korea to control intraocular pressure. This may include the use of eye drops, pills or injections aimed at reducing the production of intraocular fluid or increasing its outflow.
Korea is actively involved in glaucoma research to develop new treatments and improve outcomes. Medical facilities in Korea also provide training and practice for medical professionals from various countries, promoting the spread of advanced treatment methods.
With modern methods and technology, the effectiveness of glaucoma treatment in Korea is high, and most patients achieve stable control of intraocular pressure and vision preservation.
In Korea, much attention has been given to glaucoma prevention and public education about the risks of glaucoma. Community events, education campaigns and screening programs are conducted for timely detection and treatment of glaucoma.
Korean medical institutions actively cooperate with colleagues from other countries, sharing experience, knowledge and advanced treatment methods. This promotes best practices and improves the quality of care globally.
Korean doctors and medical professionals have a responsibility to care for the health of their patients and strive to provide them with the best quality of life possible. This includes not only providing quality medical care, but also support and understanding in terms of emotional and psychological well-being.
Glaucoma treatment in Korea is a complex process based on advanced methods and technologies, individual approach to each patient and careful care of his/her health. As a result, Korea continues to be a leader in the field of glaucoma, providing high-quality medical care and reliable vision maintenance for its patients.
 Angioplasty in Korea
Angioplasty in Korea
Angioplasty is an innovative medical procedure designed to restore the patency of the arteries and allow natural blood flow in the body.
Angioplasty widens and restores the lumen of an artery normally narrowed by inflammation. This is accomplished by using special cylinders that inflate inside the vessel and expand it.
The procedure is used to treat a variety of conditions, including coronary arteries in cases of angina pectoris, peripheral arteries in cases of limb ischemia, and to restore blood supply to the renal arteries in cases of hypertension.
The process involves inserting a catheter through an artery, usually through a local anesthetic. The balloon is then expanded in the narrow area of the vessel, allowing natural blood flow to be restored.
Sometimes the procedure is complemented by stenting. The stent is placed inside the artery after the intervention, preventing the vessel from narrowing again.
Angioplasty is considered a gentle intervention. It usually requires only small incisions or can even be performed through a skin puncture. The risks of complications are reduced and the rehabilitation time takes a little time.
The intervention usually takes a relatively short amount of time and the results are usually felt immediately by the patient. After it, most patients can recover quickly and return to their normal lives.
Development prospects promise even more advanced and precise treatments. Research in nanotechnology, biomaterials, and gene therapy may lead to new approaches to address specific problems and improve the efficacy of the procedure.
The patient’s active participation in the treatment process after the procedure plays a key role in a successful outcome. This includes following your doctor’s recommendations, regular medical checkups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including weight control, physical activity, and avoiding unhealthy habits.
The procedure represents an integral part of modern medicine, providing patients with effective and innovative methods of restoring arterial patency. With the constant advancement of technology and in-depth research, angioplasty remains the focus for treating and preventing cardiovascular disease.
Although angioplasty provides an effective treatment for narrowed arteries, prevention remains an important aspect of preventing cardiovascular disease. This includes taking care of your cardiovascular health, regular medical checkups, controlling risk factors, and living a healthy lifestyle.
 Cardiac ablation in Korea
Cardiac ablation in Korea
Ablation is a procedure in which special techniques are used to create controlled localized lesions in heart tissue to correct abnormal heart rhythms. It is performed in specially equipped cardiology centers under the control of electrophysiological studies.
The procedure is used in cases of various cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal tachycardia, slow heart rhythms and other rhythm disorders that can significantly impair a patient’s quality of life.
The intervention is usually performed using electrodes inserted through the blood vessels into the heart area. Electrodes can generate heat, cold, or electrical pulses to create controlled damage in tissues, blocking the pathologic signaling pathway in the heart.
Current technology and innovations in the field include three-dimensional equipment to pinpoint the exact location of abnormalities in the heart, and endoscopic visualization to improve control during the procedure.
After the ablation procedure, the patient may require a short recovery time. Doctors recommend limiting physical activity and regular visits to monitor your heart rate.
With the constant advancement of technology and in-depth research, ablation remains an area of intense research. Research is aimed at expanding the applications of ablation, reducing potential complications, and improving the efficacy of the procedure.
Cardiac ablation is an effective and innovative method of treating cardiac arrhythmias. Modern technologies and continuous development of this field of medicine allow to improve treatment results and quality of life of patients, opening new perspectives in the treatment of cardiac disorders.
Korea is renowned for its outstanding medical facilities and cardiac centers with advanced equipment and highly qualified specialists. Cardiology experts in Korea are actively using cardiac ablation to treat a wide range of arrhythmias.
The use of endoscopic imaging gives cardiologists a more detailed view of the structures of the heart and allows them to more accurately manage the procedure. This contributes to the accuracy and success rate of ablation.
In Korea, physicians are actively incorporating robotic systems into ablation procedures. This significantly improves the accuracy of manipulation within the heart, reduces the impact on surrounding tissues, and improves the safety of the procedure.
Leading clinics in Korea offer a wide range of ablation techniques, including radiofrequency ablation, which uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to create damage in tissue, and cryoablation, where cold is used to block abnormal signaling pathways in the heart.
 Stroke treatment in Korea
Stroke treatment in Korea
Stroke remains one of the most serious public health problems requiring attention and medical attention. In Korea, as in other countries, stroke has a significant impact on public health. In this article, let’s look at the signs, causes, and modern stroke treatment in Korea.
A stroke is a condition in which blood flow to part of the brain is blocked or interrupted, which can cause damage to brain cells. This can happen because of a hemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke) or because of a blocked artery (ischemic stroke).
Signs of stroke can vary depending on the type and severity, but common ones are loss of sensation or motor skills in one part of the body, speech impairment, dizziness, severe headache and loss of consciousness. It is important to note that early recognition and prompt treatment are crucial to improve prognosis.
In Korea, as in many developed countries, the major causes of stroke are arterial hypertension, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, arterial fibrillation, and aging population. It is important to emphasize that these factors can often be supported by poor lifestyle, low physical activity, and malnutrition.
Modern stroke diagnosis includes techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, electroencephalography (EEG) and angiography. These techniques can accurately determine the type and location of brain damage.
Stroke treatment in Korea faces modern approaches such as the use of drugs to treat ischemic stroke and surgical techniques to alleviate hemorrhagic stroke. Physical therapy, rehabilitation and medication are important to restore functions lost due to stroke.
Preventive measures include controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet. Public awareness of risk factors and signs of stroke also plays an important role in preventing the disease.
Korea is renowned for its advanced medical infrastructure and technology. Numerous modern hospitals and medical centers provide high-tech equipment and professional medical care to diagnose and treat stroke.
 Angina treatment in Korea
Angina treatment in Korea
Angina, often called angina pectoris, is a heart condition associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
Angina pectoris is a symptom of pain in the chest area due to insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle. This is often due to atherosclerosis and plaque buildup in the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
The main causes of angina pectoris are atherosclerosis, coronary artery spasms and arterial hypertension. Risk factors include smoking, diabetes, abnormal blood lipid levels, physical inactivity and genetic predisposition.
The main symptoms of angina include a feeling of pressure, burning or heaviness in the chest that can spread to the arm, neck, jaw or back. Diagnosis includes electrocardiography (ECG), exercise tests, coronarography, and blood tests for cholesterol and sugar levels.
Treatment of angina pectoris in Korea is aimed at eliminating or alleviating symptoms and preventing the progression of the disease. Drug therapy includes aspirin, beta-blockers, nitrates, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), and statins to control cholesterol.
In cases where drug treatment is not effective enough, interventional cardiology techniques are used. Angioplasty and stenting procedures aim to restore normal blood flow in the coronary arteries.
In some cases, surgical intervention such as coronary bypass surgery may be required. This procedure involves creating a bypass route for blood around the blocked section of artery.
Patients with angina pectoris can improve their condition by following a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, healthy eating, smoking cessation and stress management play an important role in improving quality of life.
Physical activity plays a key role in the management of angina pectoris. Special physical rehabilitation programs help patients strengthen heart muscle, reduce weight, improve circulation and increase endurance.
Angina pectoris can have an impact on patients’ mental health. Psychological support and education on stress management strategies help patients better cope with the emotional aspects of the disease.
With timely and effective treatment, most patients with angina pectoris can lead an active lifestyle and prevent disease progression. Prevention includes controlling risk factors, regular medical checkups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Angina pectoris requires a comprehensive and long-term approach to treatment. Modern diagnostic methods, innovative drug therapies and invasive procedures create favorable conditions for controlling the disease and improving the quality of life of patients. The patient’s role in maintaining health, specialist intervention and adherence to preventive measures play a key role in combating this heart disease.
 Treatment of pyelonephritis in Korea
Treatment of pyelonephritis in Korea
Pyelonephritis is a dangerous inflammatory disease of the kidneys that requires timely intervention to prevent complications and maintain the health of the genitourinary system.
Pyelonephritis is usually caused by a bacterial infection. Risk factors include impaired urine flow (e.g., due to urolithiasis), a weak immune system, diabetes, pregnancy, and conditions that promote the growth of bacteria in the kidneys.
Symptoms of the disease can include the presence of fever, pain in the lower back, frequent urges to urinate. Diagnosis includes urinalysis, blood tests, ultrasound and CT scan to determine the extent of inflammation and possible complications.
Treatment for pyelonephritis usually involves taking antibiotics to defeat the bacterial infection. Patients may also be prescribed medications for pain relief and antipyretics. Intravenous antibiotics may be used in severe cases requiring hospitalization.
Prevention of pyelonephritis includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular urination, practicing good hygiene, eating a customized diet, and preventing genitourinary infections. Effective control of risk factors reduces the likelihood of disease recurrence.
After completing a course of antibiotics, it is important to ensure full recovery and maintenance of kidney health. Rehabilitation includes a resting regimen, drinking plenty of water, following nutritional recommendations, and monitoring physical activity.
Current trends in the treatment of pyelonephritis include the use of more accurate diagnostic techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging, and approaches to individualized therapy that take into account the type of bacterium and antibiotic sensitivity.
Timely and proper treatment usually leads to a full recovery. However, complications such as abscess formation, damage to kidney tissue, or a chronic form of the disease can occur with inadequate treatment or recurrences.
The patient’s active participation in the treatment process plays a key role in the effectiveness of therapy. This includes complying with all doctor’s appointments, following the recommendations on diet and nutrition, as well as timely seeking medical help when new symptoms appear.
Pyelonephritis requires comprehensive and careful intervention for successful treatment and recovery. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment, effective prevention play an important role in preventing complications and maintaining kidney health. Awareness and timely referral to a physician remain key in the fight against this serious disease.
 Treatment of pyelonephritis in Korea
Treatment of pyelonephritis in Korea
Pyelonephritis is a dangerous inflammatory disease of the kidneys that requires timely intervention to prevent complications and maintain the health of the genitourinary system.
Pyelonephritis is usually caused by a bacterial infection. Risk factors include impaired urine flow (e.g., due to urolithiasis), a weak immune system, diabetes, pregnancy, and conditions that promote the growth of bacteria in the kidneys.
Symptoms of the disease can include the presence of fever, pain in the lower back, frequent urges to urinate. Diagnosis includes urinalysis, blood tests, ultrasound and CT scan to determine the extent of inflammation and possible complications.
Treatment for pyelonephritis usually involves taking antibiotics to defeat the bacterial infection. Patients may also be prescribed medications for pain relief and antipyretics. Intravenous antibiotics may be used in severe cases requiring hospitalization.
Prevention of pyelonephritis includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular urination, practicing good hygiene, eating a customized diet, and preventing genitourinary infections. Effective control of risk factors reduces the likelihood of disease recurrence.
After completing a course of antibiotics, it is important to ensure full recovery and maintenance of kidney health. Rehabilitation includes a resting regimen, drinking plenty of water, following nutritional recommendations, and monitoring physical activity.
Current trends in the treatment of pyelonephritis include the use of more accurate diagnostic techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging, and approaches to individualized therapy that take into account the type of bacterium and antibiotic sensitivity.
Timely and proper treatment usually leads to a full recovery. However, complications such as abscess formation, damage to kidney tissue, or a chronic form of the disease can occur with inadequate treatment or recurrences.
The patient’s active participation in the treatment process plays a key role in the effectiveness of therapy. This includes complying with all doctor’s appointments, following the recommendations on diet and nutrition, as well as timely seeking medical help when new symptoms appear.
Pyelonephritis requires comprehensive and careful intervention for successful treatment and recovery. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment, effective prevention play an important role in preventing complications and maintaining kidney health. Awareness and timely referral to a physician remain key in the fight against this serious disease.
 Thoracic surgery in Korea
Thoracic surgery in Korea
Thoracic surgery, focused on the treatment of chest-related diseases, is an important field of medicine specializing in surgery of the chest and mediastinum. From oncology to trauma, thoracic surgeons play a key role in diagnosing and treating a variety of conditions.
Thoracic surgeons deal with a wide range of conditions including lung tumors, pleural effusions, cysts, infections, chest deformities, aortic aneurysms and other pathologies involving organs in the chest cavity.
Modern thoracic surgery is increasingly using minimally invasive techniques such as thoracoscopy and robotic surgery. These approaches allow surgeons to perform surgery through small incisions, reducing recovery time and the risk of complications.
Thoracic surgeons specialize in treating pleural diseases such as pleurisy, pleural effusions, and pleural tumors. Procedures such as thoracoscopic pleurectomy are used to drain and remove excess fluid from the pleural cavity.
Thoracic surgeons are often involved in the treatment of chest injuries such as rib fractures, lung and heart injuries. Emergency surgeries may include removal of blood from the pleural cavity, repair of damaged blood vessels, or surgery for perforated organs in the chest cavity.
Thoracic surgeons play an important role in the postoperative rehabilitation of patients. They work with medical rehabilitologists, physical therapists, and other specialists to ensure full restoration of respiratory function, supporting patients’ overall physical health.
Modern technologies such as three-dimensional modeling, the use of robots in surgical procedures and the use of new biomaterials are becoming an integral part of thoracic surgery, improving the accuracy and efficiency of interventions.
Thoracic surgeons collaborate extensively with oncologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, and other medical specialists. This interdisciplinary collaboration provides a comprehensive and effective approach to diagnosing and treating patients.
Thoracic surgery plays an important role in the treatment of a variety of thoracic diseases by providing state-of-the-art diagnostic and surgical techniques. With the constant advancement of technology and treatment methods, thoracic surgeons are helping to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
 Joint surgeries in Korea
Joint surgeries in Korea
Joint surgery has become an integral part of medical practice, providing effective treatment and restoration of joint function in patients with a variety of diseases and injuries. Modern technologies and approaches in this field have made joint surgery a field that combines high-tech techniques with care for the quality of life of patients.
Arthroscopy, or surgery using an arthroscope (a thin tube with a camera on the end), has become the primary method for diagnosing and treating joint problems. This minimally invasive approach allows doctors to perform surgery through small incisions, reducing the risk of complications and shortening the recovery period after surgery.
Joint replacement, or replacing a joint with an artificial implant, is one of the most effective treatments for chronic joint diseases such as arthritis. Modern implants are made of high-strength materials, providing long-term support for joint mobility and functionality.
Ligament reconstruction surgeries are often performed to restore lost joint stability after injury. Techniques such as reconstruction of the anterior cruciate or lateral collateral ligaments of the knee can restore normal mobility and function to the joint.
Hip replacement surgery is the standard of care for severe cases of degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis. Modern technology makes it possible to personalize the process of endoprosthetics, taking into account the peculiarities of each patient’s anatomy.
In cases where the joint has been severely damaged or is a source of chronic pain, an arthrodesis may be decided upon. This surgery aims to fix the joint, which reduces movement and pain. Although arthrodesis limits mobility, in certain cases it may be the best option for the patient.
After joint surgery, rehabilitation plays a key role in regaining full functionality. Physical therapists develop individualized exercise programs and treatments to strengthen muscles, improve mobility and reduce pain.
Modern surgical techniques on joints, particularly minimally invasive ones, offer significant benefits to patients. Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection, shorten the recovery period, and provide a more cosmetically acceptable result.
Given the variety of joint diseases and individual patient characteristics, physicians are now adopting individualized approaches to surgery. This includes selecting the best implants, taking into account the patient’s physiology, and customizing the surgical plan for the individual case.
 Treatment of hypertension in Korea
Treatment of hypertension in Korea
Hypertension is among the most common and dangerous vascular diseases in the world. This chronic pathology, if unchecked, provokes stroke, heart attack, kidney damage and other problems.
The condition is characterized by a persistently elevated blood pressure level. It is caused by a variety of factors. One of the main ones is considered to be the presence of genetic predisposition.
Often the disease does not show pronounced symptoms. However, with its prolonged course, it is possible to have headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, fatigue. Often the condition becomes the cause of serious complications – heart disease, strokes, chronic kidney failure.
For diagnosis, blood pressure is usually measured using a tonometer. Continuous BP monitoring may be necessary if hypertension is suspected. Laboratory tests are also performed to evaluate the condition of the heart, blood vessels and other organs.
An important part of managing the condition is a healthy lifestyle. This includes diet control, moderate exercise, stress management and avoiding bad habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
If there is no effect with non-medication methods, medications that can lower blood pressure are used. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, thiazide diuretics and other drugs may be used. The doctor selects the optimal combination of drugs, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Modern technology is also finding its way into the treatment of the disease. This includes the use of mobile apps to monitor blood pressure, wearable device technology that alerts you to potential blood pressure spikes, and developments in telemedicine.
Continuous monitoring and control is key. Patients are advised to keep a blood pressure diary, monitor the readings and seek medical attention in a timely manner if necessary.
One of the fundamental aspects of hypertension control remains the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, smoking cessation and moderate alcohol consumption contribute not only to lowering blood pressure, but also to the overall strengthening of the body.
A combination of medication, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular blood pressure monitoring is the key to successfully managing this condition. Modern treatment methods, active patient participation and constant attention to innovations in medicine create favorable prospects for effective control and improved quality of life for people suffering from hypertension.
 Treatment of heart defects in Korea
Treatment of heart defects in Korea
A huge number of people die from cardiovascular disease every year. The treatment of heart defects is treated with special attention. In recent decades, Korea has become known for its outstanding medical achievements and innovative treatments for cardiovascular diseases.
Korea is renowned for its medical infrastructure providing high-tech services and equipment. The country trains exceptionally qualified specialists in cardiology and heart surgery.
Surgery for the treatment of malformations is widely used in Korea. Minimally invasive procedures such as transcardiac catheterization and endovascular interventions have become routine. These techniques can reduce recovery time and the risk of complications after surgery.
Korea is actively introducing artificial intelligence technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. AI can help doctors analyze large amounts of data, providing accurate and fast results. This facilitates earlier detection of heart defects and effective treatment planning.
Korea remained at the forefront of heart and tissue transplantation. The organ harvesting, storage and transplantation system in the country is well organized, ensuring a higher chance of successful transplantation.
In recent years, the concept of personalized medicine has been actively implemented in Korean medical practice. This allows treatment to be tailored to the individual patient, improving outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Korean medical institutions are actively involved in research and clinical trials to find new treatments for heart defects. This includes testing new drugs, medical devices and innovative surgical techniques. Participation in global research projects makes Korea a center for the development of advanced treatments.
Korea actively conducts educational programs and activities to prevent cardiovascular disease. Increased public awareness of risk factors and regular health screenings help detect heart defects early, which opens up more opportunities for successful treatment.
The treatment of malformations in Korea is an impressive mix of innovation, high standards of medical practice and attention to patient needs. This experience and competence make the Korean healthcare system an attractive choice for patients from around the world, and this trend will only increase in the future.
 Treatment of germinoma in Korea
Treatment of germinoma in Korea
Germinoma is a rare form of tumors that form from germinative cells. These tumors are most commonly found in the testicles or ovary, but can also occur in other parts of the body. Understanding this disease and utilizing modern treatments are becoming key in the fight.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and biopsy are key techniques for diagnosing the disease. These technologies allow physicians to determine tumor location, size and characteristics, which is important for developing an individualized treatment plan.
One of the main treatments for the disease is surgical removal of the tumor. In cases of testicular germinoma, orchiectomy – removal of the testicle – is often performed. A biopsy may also be performed to determine the type of disease and to choose the best treatment method.
Chemotherapy is widely used in the treatment of the disease. Drugs are injected into the patient’s body to destroy cancer cells. This method is often effective when the tumor has spread beyond the primary focus.
Radiation therapy is used when the neoplasm is in a location that is difficult to access for surgery. This technique is characterized by the precise direction of the radioactive beams.
Immunotherapy is an effective method in fighting the disease. This method stimulates the body’s own immune forces to fight cancer. Modern developments offer new perspectives for improved efficacy and individualized therapy.
Targeted therapies block specific molecular targets. This promotes a more accurate and effective removal of the tumor.
While there have been significant advances in treating the disease, ongoing oncology research and new treatment techniques are improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
The latest post-operative rehabilitation techniques include innovative approaches such as physical therapy, virtual reality rehabilitation and customized recovery programs. These methods help speed up the healing process and improve the patient’s quality of life after treatment.
 Meningioma treatment in Korea
Meningioma treatment in Korea
Treatment for meningioma, like any other medical condition, depends on several factors, including the size of the tumor, its location, characteristics, and the patient’s health. However, there are common features of approaches to treating the disease.
Disease characterization begins with a thorough diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging and CT scans allow doctors to determine the size, location, and structure of the tumor.
If the neoplasm is small and shows no obvious symptoms, doctors may decide to resort to a wait-and-see tactic, monitoring tumor growth regularly.
Surgical removal of the neoplasm may be necessary, especially if there are symptoms, rapid tumor growth, or pressure on adjacent brain structures. Depending on the location of the tumor, the surgeon may use minimally invasive techniques or traditional surgery.
Radiosurgery involves the use of focused beams of radiation to destroy the tumor. Gamma Knife and CyberKnife provide high precision in directing the radiation beams, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Sometimes drug therapy may be used to control tumor growth or alleviate symptoms. This may include the use of hormonal medications or other medications.
Current therapies include molecularly targeted therapies that target specific molecular targets that promote tumor growth.
Immunotherapy research offers new perspectives for the treatment of the disease. This approach aims to activate the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer cells.
Each case is unique and the treatment approach must be tailored to the patient’s specific circumstances and needs. Ongoing research and innovation in the field of oncology complements these mainstream modalities, providing new options for effective treatment of the disease.
 Keratitis treatment in Korea
Keratitis treatment in Korea
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, the clear membrane at the front of the eye. This condition can cause serious complications, up to and including loss of vision. However, with the advent of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic methods, treatment for the disease is becoming more effective and affordable.
The initial stage of treating the disease begins with accurate diagnosis. Modern technology, such as confocal microscopy, allows doctors to examine the structure of the cornea in detail and identify possible infections, trauma, or other causes of inflammation.
If the condition is caused by a bacterial infection, antibacterial drops or ointments become an important part of treatment. Modern drugs provide effective destruction of bacteria, minimizing the risk of complications.
In case of viral origin, antiviral drugs are used. They are able to inhibit viral activity and speed up the healing process while remaining safe for the eye.
The fungal form requires the use of antifungal agents. Modern drugs allow you to effectively fight fungal infection, preventing its spread.
More severe or acute forms of the disease, such as ulcerative keratitis, may require the use of steroids or immunomodulators. These drugs help to reduce inflammation and stimulate corneal regeneration processes.
In cases where keratitis results in significant damage to the cornea, keratoplasty, a surgical procedure in which a corneal transplant is performed, may be necessary. Technologies in this field are constantly improving, and modern methods of keratoplasty allow to achieve high results.
Patients with keratitis and dry eye can benefit from innovative solutions such as the use of keratoprotectants and artificial tears. These products provide moisture to the eye and help improve the overall health of the cornea.
Current research is also focused on developing new treatments for keratitis. Innovative approaches, such as the use of stem cell technology for corneal regeneration, may provide even more effective and long-lasting results. These technologies, although still in the research phase, herald a new era in the treatment of keratitis.
Regular medical examinations and eye health monitoring remain key components of successful keratitis treatment. Conducting routine inspections helps to identify problems early and take action before they lead to serious complications.
 Retinoblastoma treatment in Korea
Retinoblastoma treatment in Korea
Retinoblastoma is a rare but serious eye disease that often affects children. In recent decades, the Republic of Korea has become a recognized center of medical expertise, and cancer treatment in this country represents an outstanding example of advanced techniques and a high-tech approach.
Modern diagnostic techniques available in Korea include high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and extensive use of computed tomography (CT). These technologies allow doctors to study the structure of the eye in detail and determine the extent and nature of the disease in its earliest stages.
Korean surgeons specializing in treating the disease use advanced microsurgery and intraoperative navigation techniques. This allows for precise and minimally invasive removal of tumors, minimizing damage to healthy tissue and reducing the risk of complications.
Korean radiation therapy specialists use advanced techniques such as intensive fractionated radiation therapy to target radiation beams to the tumor as precisely as possible. This effectively controls the growth and development of the disease while minimizing the impact on healthy tissue.
Current chemotherapy protocols and molecularly targeted therapies in Korea provide individualized approaches to treating the disease. A deep understanding of the molecular mechanisms of disease allows physicians to choose the best medications for each patient, increasing the chances of successful healing.
Modern immunotherapy research has also become part of the Korean approach to retinoblastoma treatment. Stimulating the immune system to fight the tumor opens new perspectives and may become an additional tool in the arsenal to fight this serious disease.
The disease is treated in Korea by a multidisciplinary team of experts including ophthalmologists, oncologists, surgeons, radiologists and geneticists. This combined approach provides the highest level of care and provides patients with comprehensive medical support.
Specialized rehabilitation programs and long-term patient monitoring in Korea play a key role in achieving the best possible outcomes. These programs focus not only on physical recovery, but also on supporting the psychological well-being of patients and their families.
A combined approach including surgery, radiation and chemotherapy, molecularly targeted therapies and immunotherapy can effectively fight the disease. Open perspectives and ongoing research are setting the stage for further improvements in treatment and prognosis for patients facing this serious pediatric disease.
 Astrocytoma treatment in Korea
Astrocytoma treatment in Korea
An astrocytoma is a brain tumor originating from cells that play an important role in maintaining normal nervous system function. This form of tumors can affect the patient’s quality of life and requires comprehensive and effective treatment. In recent decades, significant advances have been made in the diagnosis and therapy of the disease, opening new horizons for patients with this condition.
One of the key aspects of successful treatment of the disease is accurate and timely diagnosis. Modern medical diagnostic techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, allow doctors to examine the structure of a tumor in greater detail and determine its characteristics. Additional techniques, such as biopsy, can provide information about the type of disease, which is important for choosing the best treatment method.
One of the main methods of treating the disease is surgical intervention. The surgeon removes the tumor to reduce its size and reduce pressure on nearby tissues. Modern technologies such as navigational surgery and intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging allow surgeons to locate and remove the tumor as precisely as possible while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Radiation therapy is an adjunctive treatment for astrocytoma. Highly effective radiation techniques, such as intensive fractionated radiation therapy, aim to destroy residual tumor cells after surgery. They can also be used when surgery is not possible due to the location of the tumor or extensive spread.
Chemotherapy plays an important role in treating the disease. Modern drugs are aimed at suppressing the growth and development of tumor cells. Molecularly targeted therapies based on the study of specific molecules and mechanisms involved in tumor development provide new perspectives in personalized treatment.
Modern astrocytoma treatments are opening new horizons for patients facing this serious disease. The integration of surgical, radiation, chemotherapeutic and molecularly targeted techniques allows for more effective results. However, it is important to remember that successful treatment of the disease requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to each patient.
Treating the disease is not only about removing the tumor, but also about restoring body functions and providing the patient with support in the post-operative period. Physical therapy, speech and physical rehabilitation, and psychological support play an important role in the patient’s recovery from treatment.
 Treatment of neurinoma in Korea
Treatment of neurinoma in Korea
A neurinoma is a tumor that forms from the cells of the nerve sheath. Although these tumors are mostly benign, they can be a challenge for patients because of their location and size. There are now a number of advanced treatments designed to effectively manage neurinomas and improve patients’ quality of life.
One of the main treatments is surgical removal of the tumor. Surgery not only improves the patient’s quality of life by reducing pressure on nerve structures, but also allows for biopsies to be taken to accurately determine the type of disease. Modern microsurgery techniques and the use of better equipment provide a more precise and minimally invasive intervention.
In cases where complete removal of the tumor is not possible, radiation therapy becomes an important component of treatment. High-intensity radiation techniques aim to reduce the size of the tumor and control its growth. X-ray therapy and gamma knife provide physicians with effective therapy tools without surgery.
Medication plays an important role in treating the disease, especially when surgery or radiation therapy is ineffective. New drugs, such as growth factor inhibitors and drugs aimed at suppressing the activity of certain genes, offer encouraging prospects for controlling tumor growth and development.
Treatment of the tumor is not limited to medical interventions alone. Rehabilitation and patient support are essential to ensure a full recovery after surgery or radiation therapy. Physical therapy, speech and psychological support help patients adapt and recover.
One of the main trends in modern medicine in the treatment of disease is the individualization of therapy. Understanding the genetic characteristics of each case allows doctors to choose the most effective and safest treatments. This personalized approach helps to optimize results and minimize possible side effects.
The outlook for the treatment of neurinomas promises to be even more encouraging with the development of new treatments and innovations in medicine. Research into gene therapy, immunotherapy and the use of new technologies in diagnostics may open new horizons in the fight against the disease.
 Treatment of Arnold-Chiari anomaly in Korea
Treatment of Arnold-Chiari anomaly in Korea
Arnold-Chiari anomaly is a rare disorder characterized by displacement and deformity of the brain stem, including the cerebellum. This condition can be accompanied by various symptoms such as headaches, coordination problems, and even breathing problems.
Diagnosis of the disease usually involves magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and/or computed tomography (CT) of the brain and spinal cord. These examinations allow doctors to determine the degree of displacement of brain structures and assess the extent of the lesion.
In most cases, treatment begins with conservative methods. This requires prescribing medications to manage symptoms such as pain and headaches. Physical therapy can help strengthen muscles, improve coordination and overall well-being.
If symptoms progress or if the patient’s life is threatened, surgery may be required. Interventions may include brain stem decompression, improving spinal cord fluid circulation, or even brain stem transplantation.
Modern technology and medical research are providing innovative approaches to treating the disease. This includes the use of 3D modeling for more precise surgical planning, as well as research into gene therapy and regenerative medicine.
Rehabilitation activities play an important role in alleviating the effects of the disease. These consist of physical, speech and occupational therapy to restore and maintain an optimal level of functionality.
The disease can have a significant impact on the psychological well-being of the patient and their family. Psychological support and counseling can help you cope with the emotional challenges associated with diagnosis and treatment.
Arnold-Chiari anomaly is a serious medical condition and treatment must be individualized to fit each case. Modern techniques, including surgical and innovative methods, offer new perspectives for those facing this challenge.
 Treatment of lissencephaly in Korea
Treatment of lissencephaly in Korea
Lissencephaly is a rare and severe disorder characterized by abnormal brain development that results in a smooth surface of the cerebral cortex instead of the typical crinkles and furrows. This neurodevelopmental defect typically has serious implications for a child’s development and requires a multifaceted and comprehensive treatment approach.
Diagnosis of lissencephaly is usually made in early childhood, based on clinical signs and examinations such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. The smooth cortical surface characteristic of lissencephaly is often seen on MRI images.
There is currently no specific drug treatment for lissencephaly. However, doctors may prescribe medications to improve symptoms, such as anticonvulsants, myorelaxants, and agents to improve motor skills.
Physical therapy plays an important role in providing support for the child. Specialized physical therapy sessions are designed to improve mobility, strengthen muscles and maintain optimal tone.
Individualized learning programs tailored to a child’s development can help maximize his or her potential.
In some cases, doctors may decide to perform surgical interventions to improve the patient’s quality of life. This may include correcting scoliosis, improving mobility, and other treatments depending on individual needs.
Modern technology can also play an important role in the rehabilitation of patients with lissencephaly. Virtual reality, robotics, and other innovative approaches can be incorporated into treatment programs to improve motor skills and functionality.
Given that lissencephaly is often genetic in nature, genetic research is becoming an important area of research. Understanding genetic traits may open pathways to developing more accurate diagnostic methods and personalized treatment approaches.
The international exchange of experiences between medical professionals, scientists and parents can stimulate the development of more effective treatment strategies. Global collaboration can accelerate progress against the disease. Treatment of lissencephaly is a long-term and multidisciplinary process, and its success depends on careful planning and coordination of efforts.
 Craniostenosis treatment in Korea
Craniostenosis treatment in Korea
Craniostenosis is a condition in which the bony sutures of the skull close too early in children, which can lead to restricted skull growth and the development of problems with head shape and brain development. Treatment of craniostenosis depends on the severity of the case, the age of the patient and other factors. Intervention is usually required in early childhood.
In most cases, craniostenosis is treated surgically. Surgery is aimed at opening the closed sutures to allow normal growth of the skull. Procedures include resection (removal of part of) bones, corrective surgeries, and other techniques designed to restore the normal shape of the skull.
After surgery, children usually need long-term medical follow-up to monitor skull growth and early detection of possible complications. In some cases, physical therapy may be prescribed to help restore motor skills and muscle tone after surgery.
The treatment of craniostenosis usually involves multiple specialists such as neurosurgeons, plastic surgeons, orthodontists, pediatricians, and others. This allows you to provide a comprehensive view of the condition and choose the best treatment plan.
In developed countries, including Korea, advanced surgical techniques are commonly used to correct craniostenosis. This may include the use of minimally invasive techniques and advanced surgical devices.
Advanced medical diagnostic techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are often used to pinpoint areas of craniostenosis and plan surgery.
Treatment of craniostenosis often requires an individualized approach for each patient. Doctors strive to take into account the specifics of each case, including the age of the child, the severity of the craniostenosis, and the presence of additional problems.
 Ependymoma treatment in Korea
Ependymoma treatment in Korea
The world has been facing various public health challenges in recent years, and Korea has not been left out of these global trends. One of the key aspects determining the successful confrontation of the epidemic is an effective treatment strategy.
One of the keys to successful treatment of epidemics is early detection and diagnosis. Korea is actively adopting advanced technologies such as high-precision tests and artificial intelligence systems for fast and accurate diagnosis.
The key to successfully treating the epidemic is a coordinated effort between government agencies, treatment providers, and the community. Korea is actively applying modern crisis management techniques and coordination systems to effectively deal with epidemics.
An ependymoma is a type of tumor that develops in ependymal tissue that forms in the ventricles of the brain or central canal of the spinal cord. Treatment for ependymoma usually includes surgery, radiation therapy and, in some cases, chemotherapy. However, each case is different and the treatment plan may vary depending on a variety of factors such as the type and stage of the tumor, the patient’s age, general health, and others.
The primary treatment for ependymoma is surgical removal of the tumor. The goal of the surgery is to remove the tumor while minimizing damage to the healthy tissue around it.
Radiation therapy may be administered after surgical removal of the tumor to kill remaining cancer cells. The intensity and duration of radiation therapy depend on the characteristics of the tumor and other factors.
In some cases, chemotherapy drugs may be used to kill cancer cells or control their growth. In the field of tumor treatment, research is constantly being conducted to identify new techniques and drugs. The physician may discuss with the patient the possibility of participating in clinical trials that may provide access to advanced therapies.
A healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help maintain overall health and strengthen the immune system. Patients should discuss lifestyle modification recommendations with their physician in the context of their specific condition.
 Treatment of Crouzon syndrome in Korea
Treatment of Crouzon syndrome in Korea
Crouzon syndrome, also known as rounded head syndrome, is a rare congenital disorder characterized by an unusual shape of the skull and face. Although the condition is complex and malaise-inducing, modern medical approaches and technologies are designed to make life easier for patients facing this syndrome.
Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment of Crouzon syndrome. Modern medical imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), allow doctors to more accurately assess the condition of the skull and facial bones. This becomes the starting point for determining the best treatment plan.
One of the key aspects of treating the disease is surgical correction of deformities. Procedures include reshaping the bones of the skull and face to create a more natural shape and eliminate the breathing and vision problems that can accompany this syndrome.
South Korean medicine is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach to treating the disease. Specialists from various fields, including surgeons, orthodontists, speech therapists, and plastic surgeons, work closely together to develop individualized and comprehensive treatment plans. This coordinated approach takes into account not only surgical aspects, but also rehabilitation and patient support.
Surgical treatment of the disease in Korea is supported by innovative technology. The use of three-dimensional skull models for preoperative planning has become a common practice. This allows surgeons to more accurately determine the extent of intervention and achieve maximum effectiveness with minimal impact.
Genetic counseling in Korea plays an important role in accompanying families facing this disease. This provides families with the information they need about risks and options and supports them in making decisions about future pregnancies.
Crouzon syndrome treatment in South Korea combines patient care and advanced technology. The integration of medical innovation, the strength of a multidisciplinary approach and deep patient care create a promising platform for a future where every person facing Crouzon syndrome can expect optimal and personalized treatment.
 Hemangioma treatment in Korea
Hemangioma treatment in Korea
Hemangiomas are benign tumors that form from blood vessels. These vascular masses can occur in various parts of the body, presenting a particular challenge to the medical community. In recent decades, modern treatments for the disease have been the subject of intense research in an effort to provide the best possible outcomes for patients.
To successfully treat the disease, it is important to start with accurate and timely diagnosis. Modern examination techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound provide highly accurate images of the tumor and its surrounding tissues. This allows doctors to not only make a diagnosis, but also to choose the most effective treatment strategies.
For some forms of the disease, drug therapy becomes the treatment of choice. The use of beta-blockers such as propranolol has shown efficacy in reducing tumor size in children. This method of therapy is an innovative approach that is often preferred in cases where surgery is not necessary.
In cases where hemangiomas require surgical removal, modern surgical methods include minimally invasive techniques. Endovascular surgery and laser therapy offer the opportunity to remove the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. These innovative approaches help reduce risks and accelerate patient recovery.
Radiation therapy and radiosurgery are becoming increasingly popular treatments for hemangiomas. The use of high-dose beams can destroy abnormal blood vessels, which can be particularly effective in cases where surgery is not the best solution.
Effective treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach. Interaction between doctors of different specialties – surgeons, oncologists, radiologists – ensures comprehensive care for patients. This comprehensive approach not only ensures optimal results, but also takes into account the individual characteristics of each case.
An important part of the treatment process is follow-up rehabilitation and monitoring of patients. Regular medical check-ups and monitoring can help detect possible recurrences or complications early, allowing for a better response and improved prognosis.
The treatment of hemangiomas in modern medicine represents the promise of the future through innovative technology and a multidisciplinary approach. Patients are provided with effective and personalized treatments tailored to their unique needs and tumor characteristics. Modern medicine strives not only to provide successful treatment, but also to provide a better quality of life for those who experience hemangiomas.
 Parkinson’s disease treatment in Korea
Parkinson’s disease treatment in Korea
Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder, remains a challenge for the medical community worldwide. It affects motor function, causing tremors, stiffness and slowed movements, leading to a significant deterioration in patients’ quality of life. However, modern research and technology are providing new hope for more effective treatments.
The basis for successful treatment of the disease is accurate diagnosis. Modern screening techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and pharmacogenetics allow physicians to more accurately determine the presence and extent of the disease. This paves the way for early initiation of treatment and better symptom management.
Medications continue to be the mainstay of treatment. The drugs increase dopamine levels in the brain. However, recent pharmacotherapy research is focusing on developing new drugs that can alleviate symptoms and reduce possible side effects.
Deep head stimulation (DHS) is an innovative therapy that can significantly improve patients’ quality of life. This procedural approach involves implanting electrodes in specific parts of the brain and delivering pulses to help reduce symptoms such as tremors and rigidity.
Together with pharmacotherapy and surgical treatments, physical rehabilitation and therapy are becoming an integral part of a comprehensive approach to treating the disease. Exercises that focus on improving coordination and maintaining flexibility help patients manage their symptoms more effectively.
Current research aims to develop new treatments and slow the progression of the disease. Experimental approaches such as cell transplantation and gene therapy provide new perspectives towards effective control of this neurodegenerative disease.
While the disease remains a challenge, modern medicine provides the prospect of more effective treatments and improved quality of life for patients. The integration of new technologies, emphasis on early diagnosis, and individualized treatments create hope for a future where the disease becomes more controllable and less life-impacting for those facing this neurological disorder.
Modern laboratories around the world are actively working to identify new molecules and mechanisms that could have a positive impact on the course of the disease. Patient participation in clinical trials is becoming a key element of this process, helping scientists understand the effectiveness of new treatments.
 Treatment of cavernoma in Korea
Treatment of cavernoma in Korea
A cavernoma is a tumor formed from newly formed blood vessels that can occur in any part of the body. Although it is most commonly found in the brain, it can sometimes also appear in other organs. In South Korea, where health care occupies an important place in society, the treatment of disease is becoming the focus of medical professionals, and innovative methods are coming to the aid of patients.
Accurate and timely diagnosis is important for successful treatment. Modern medical centers in Korea are equipped with advanced technology, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), which provide the high-quality images needed to study the tumor in detail.
In South Korea, surgical therapy for the disease is supported by innovative methods. Surgical removal can be performed using microsurgery. Radiosurgery, including techniques such as gamma knife, provides treatment options without the need for open surgery, which is especially important for patients with tumors located in hard-to-reach areas.
After successful surgery or radiosurgery, doctors in South Korea pay great attention to post-operative therapy and rehabilitation. Physical therapy and regular medical checkups help patients recover faster and regain a full lifestyle.
Treatment in South Korea is the result of the combined efforts of many specialists. Neurosurgeons, oncologists, radiologists and physical therapists collaborate to provide the best possible outcome for patients. The professionalism of the staff, their extensive experience and ongoing training are important components of successful treatment.
The healthcare infrastructure in South Korea is top-notch, which is conducive to effective treatment. In addition, patients are provided with a high level of care and support throughout the entire treatment process, from diagnosis to rehabilitation.
With the advent of new technologies and the continuous development of medical sciences, the future of disease treatment in South Korea promises to be even more promising. Research in genetics and the use of innovative surgical and diagnostic techniques create hope for even more effective and individualized approaches.
Current research in genetics is providing a better understanding of the molecular features of the disease. This opens the door for individualized treatment approaches that take into account the genetic characteristics of each patient. Such personalized methods promise to increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce possible side effects.
 Arrhythmia treatment in Korea
Arrhythmia treatment in Korea
Arrhythmia, a disorder of heart rhythm, is one of the common cardiovascular diseases requiring competent and effective treatment. In South Korea, a state-of-the-art medical system, rigorous research and innovative treatments make the country a leading center for arrhythmia management.
The initial stage of arrhythmia treatment in Korea involves accurate diagnosis. Modern medical centers are equipped with advanced equipment such as electrocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological testing of the heart. These methods allow doctors to accurately determine the type of arrhythmia and its causes, which becomes the foundation for subsequent treatment.
South Korea uses advanced technology to treat arrhythmias, including catheter ablation techniques. This process allows doctors to target the areas of heart tissue causing the arrhythmia with minimal impact on surrounding areas. Minimally invasive surgery techniques allow patients to restore normal heart rhythm with less risk and faster recovery.
Some patients with serious arrhythmias may require implantation of electrical devices such as pacemakers or defibrillators. In Korea, this process has also been the subject of intensive research. Electrophysiologic testing can accurately determine which devices are best suited to a patient’s individual needs.
Arrhythmia treatment in Korea includes not only medical procedures, but also attention to the patient’s overall condition. Comprehensive post-procedure rehabilitation promotes rapid recovery and improved quality of life. Doctors emphasize the importance of a healthy lifestyle, physical activity and regular medical monitoring.
Korean medical research centers are actively integrating new technologies into arrhythmia treatment. One promising direction is the use of artificial intelligence to analyze data and predict possible complications. This not only increases the effectiveness of treatment, but also promotes a personalized approach to each patient.
Professional staff are integral to the success of arrhythmia treatment in Korea. Medical professionals are committed to continuous improvement and training to ensure a high standard of care. Collaboration between cardiologists, electrophysiologists and surgeons creates a team capable of effectively solving the most complex cases.
With its outstanding medical care, South Korea attracts patients from all over the world. Medical tourism in the country has become one of the key destinations, which shows the confidence and interest in Korean medicine.
 Heart valve replacement in Korea
Heart valve replacement in Korea
Heart valve replacement is a surgical procedure that has become an integral part of modern cardiac surgery. This intervention requires high precision, innovative techniques and careful recovery to restore normal blood flow and improve patients’ quality of life.
Congenital or acquired heart valve malformations can lead to heart valve insufficiency or stenosis, creating the need for replacement. Serious infections involving the heart valves can cause damage to them, which may also require surgery. The aging of the body and wear and tear on the valves over time can cause them to degrade and need to be replaced.
Mechanical valves are made of durable materials. They provide durability but require constant anticoagulant medication to prevent blood clots.
Biological (tissue) valves are made of living tissue. They do not require constant anticoagulant medication, but may have a more limited lifespan.
Transcardiac valve replacement (TAVR)is an innovative procedure that allows you to replace a valve without open surgery. This is especially important for patients who are not candidates for traditional surgery.
The TAVR procedure usually requires only small incisions, which reduces the risk of complications and shortens the recovery period. Patients who have undergone TAVR can often quickly return to an active life after the procedure. TAVR offers the opportunity to treat patients previously considered too fragile for open surgery.
Tissue engineering – research is enabling the creation of artificial valves using human cells, which could significantly improve compatibility and durability. Robotic surgery reduces the risk of error and increases accuracy during valve replacement surgery.
A multidisciplinary approach to heart valve replacement is crucial in modern medicine. Cardiac surgeons, cardiologists, cardiologists, anesthesiologists and other specialists work closely together to discuss each case and develop the best treatment strategies for each patient. This allows you to achieve the best results and minimize risks.
Heart valve replacement today is not only a complex surgical procedure, but also a technological art to improve the quality of life of patients with serious heart disease. Korea, with its medical system and innovative treatments, continues to play a key role in developing and improving approaches to heart valve replacement.
 Aortocoronary bypass surgery in Korea
Aortocoronary bypass surgery in Korea
Aortocoronary bypass is a surgical procedure designed to restore normal blood flow to the heart muscle. This innovative surgery plays a key role in the treatment of coronary heart disease, providing patients with effective methods to combat coronary conditions.
The procedure is performed to bypass or replace narrow or blocked vessels, allowing normal blood flow to the heart muscle. The surgery creates “shunts” – new blood pathways that bypass problem arteries and restore normal oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
The surgery is performed on patients with chronic angina pectoris or those who have unstable chest pain. Surgery may be necessary after a myocardial infarction to restore blood supply. If there is a high degree of stenosis or arterial blockage, the procedure may be an integral part of treatment.
Surgical intervention provides a lasting improvement in the blood supply to the heart, reduces the risk of heart attack and improves patients’ overall quality of life. Complications such as infections, blood clots, and reactions to anesthesia are possible, but modern techniques and technology help minimize the risks.
Modern surgeons tend to use minimally invasive approaches, which reduces the rehabilitation period and the risk of complications. Robotic surgery gives more precise access to the arteries, which can be especially helpful in complex cases.
After the procedure, good rehabilitation is important. Physical activity, blood pressure control, and lifestyle changes help patients in quick recovery and prevent recurrence.
With the constant advancement of technology, it is expected that ACS techniques will become even more precise and personalized. Research in tissue engineering may lead to new treatments and means of preventing coronary artery disease.
Current research in genetics and biomarkers is helping to develop personalized approaches to aortocoronary bypass surgery. Analyzing the genetic characteristics of patients can provide information about their propensity to respond to certain drugs and their predisposition to develop coronary complications.
Active clinical research in the field of aortocoronary bypass surgery aims to find new treatments and means of prevention. Translational medicine, which integrates research with practice, enables faster innovation in clinical practice and improved patient outcomes.
Aortocoronary bypass remains one of the most significant surgical procedures in cardiac surgery. Modern technology, a personalized approach, and ongoing scientific research make this procedure more effective, safer, and more promising. All new discoveries and innovations in medicine and technology promise to further improve aortocoronary bypass surgery and improve the lives of heart patients.
 Treatment of myocardial infarction in Korea
Treatment of myocardial infarction in Korea
A myocardial infarction or heart attack is a serious condition that usually occurs due to a disruption in the blood supply to the heart muscle. In this case, immediate intervention is necessary as the condition is fraught with serious health consequences.
The disease begins when the internal walls gradually thicken due to the accumulation of cholesterol and other substances. This is how blood clots or plaques form, blocking the normal blood supply to the heart. Other factors include the presence of high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and hereditary predisposition.
A doctor can accurately diagnose the condition using electrocardiograms, heart enzyme tests, and imaging of the heart with coronarography. Therapy consists of using medications to dissolve the clot, undergoing procedures to restore blood supply to the heart, and lifestyle changes and rehabilitation.
Korea, with its advanced medical system and technological advances, is a world leader in the treatment of heart disease. Myocardial treatment in this country encompasses a wide range of innovative methods and technologies that promote effective recovery for patients with heart problems.
One of the key techniques in myocardial treatment in Korea is coronarography. This method allows doctors to visualize arteries and identify narrow or blocked areas, which helps determine the best treatment. Korean cardiac surgeons utilize modern technologies such as minimally invasive surgery, which reduces the risk of complications and speeds up the patient’s recovery process.
Korean cardiologists have successfully used transcatheter procedures to restore normal blood supply to the heart muscle. Angioplasty followed by stenting can effectively dilate narrowed arteries and remove obstructions, which helps to normalize blood circulation.
Korean cardiologists are actively introducing innovative pharmaceuticals in the treatment of the disease. This includes newer antithrombotic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) that have been shown to be effective in improving heart function.
An important part of treating the disease in Korea is the rehabilitation and follow-up system. Patients receive comprehensive recovery treatment, including physical rehabilitation and psychological support, which promotes full recovery and prevents recurrence of cardiac problems.
 Endocarditis treatment in Korea
Endocarditis treatment in Korea
Endocarditis refers to a serious inflammatory disease that affects the inner lining of the heart, known as the endocardium. This condition, despite its relative rarity, requires careful consideration because of its seriousness and potential complications.
The disease most often develops as a result of bacterial infection, when microbes in the blood settle on the damaged endocardium and cause inflammation.
Viruses and fungi also provoke the disease, although they are less common. People with weakened immune systems are especially at risk.
Injections can be a route by which bacteria enter the bloodstream, increasing the risk of endocarditis. Symptoms of the disease can range from mild to severe and consist of joint pain, brief bouts of fever, skin rashes and worsening of the general condition.
When diagnosing, the specialist uses various methods – blood tests, echocardiography and CT scan. In serious cases, the affected valve is removed and the damage is corrected.
Clot formation on damaged valves may be more likely in people with congenital or acquired heart defects.
Korean medical facilities are actively adopting advanced diagnostic methods to accurately detect the disease. Techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and high-resolution echocardiography allow doctors to obtain detailed images of the heart, allowing for more accurate diagnosis.
Doctors in Korea attach great importance to individualized treatment, taking into account the characteristics of each patient. Genetic studies and risk factor analysis allow the development of personalized treatment programs, increasing the effectiveness of therapy and reducing the risk of complications.
Surgical treatment involves the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques. This reduces the traumatic nature of the surgery, speeds up the rehabilitation process and shortens the patient’s hospital stay.
Korean cardiologists are successfully integrating the latest medications into the treatment of endocarditis. Highly effective antibiotics and drugs aimed at reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune response are used to fight infection and prevent complications.
Treatment of endocarditis in Korea involves a transdisciplinary approach, combining the efforts of cardiologists, surgeons, infectious disease specialists and other specialists. This allows complex cases of endocarditis to be dealt with more effectively and with consideration of all aspects of the disease.
 Spinal surgery in Korea
Spinal surgery in Korea
Spinal surgery is an important field of medicine dedicated to the treatment and repair of diseases and injuries to the spine. It plays a key role in improving the quality of life of patients facing various spine related problems.
Before spinal surgery, doctors perform a thorough diagnostic workup, including exams, imaging (such as MRI and CT scans), and functional tests. This is necessary to determine the exact cause of back pain, the presence of tumors, herniated discs or other pathologies.
Preparation for surgery also includes assessing the patient’s general condition, analyzing possible risks and discussing them with them. Clarifying expectations of the surgical procedure and the recovery period is an important step.
The latest technologies such as image-guided navigation, robotic surgery and laser therapy are significantly improving the accuracy and outcomes of spinal surgeries. Navigation systems help surgeons accurately locate lesions, minimizing the risk of errors.
Current trends in spinal surgery include innovative techniques and technologies. One example is the use of 3D printing to create customized implants and prostheses specifically tailored to a patient’s anatomy. This allows for a more precise implant fit and improved surgical outcomes.
With the advent of minimally invasive techniques such as endoscopic surgery, specialists are able to perform surgery using small incisions, which shortens recovery time and minimizes the risk of complications. These techniques reduce the traumatic nature of the surgery, which is especially important in spinal surgery.
Physical therapy after spinal surgery plays a crucial role in recovery. Specially designed exercises and rehabilitation programs help patients regain muscle tone, strengthen their backs and return to an active life. Individualized approaches to physical rehabilitation ensure maximum results for each patient.
Spinal surgery continues to evolve with new techniques and technologies. Research in gene therapy, tissue engineering and the use of artificial intelligence allow us to consider the prospect of an individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the genetic characteristics and needs of each patient.
Spinal surgery is a dynamic field of medicine, where new technologies and treatments are constantly pushing the boundaries of possibilities.
The features of spinal surgery include not only the surgery itself, but also the entire treatment cycle, from diagnosis and preparation to postoperative care and rehabilitation. Current trends are aimed at increasing efficacy, minimizing risks, and improving the quality of life for patients facing back problems.
 Bone marrow transplant in Korea
Bone marrow transplant in Korea
Bone marrow transplantation is a sophisticated and technologically advanced procedure that is becoming increasingly effective in treating various blood and immune system disorders. One of the countries that is a leader in this field is South Korea.
Since the beginning of the 21st century, South Korea has been actively developing bone marrow transplant technology, offering high quality medical services to patients from all over the world. Medical centers in the country have state-of-the-art equipment and highly trained nursing staff, making them an attractive destination for patients in need of this complex procedure.
South Korean clinics are adopting advanced technologies in bone marrow transplantation, such as the use of advanced donor-recipient matching techniques, improved graft processing methods and innovative post-operative care. These innovations contribute to increased surgical success rates and improved quality of life for patients.
South Korea is actively cooperating with medical centers around the world to share knowledge and experience in bone marrow transplantation. This collaboration contributes to enriching global practice and improving the effectiveness of treatment.
The statistics of successful bone marrow transplants in South Korea demonstrate the high level of professionalism of the medical community. The country boasts high survival and recovery rates after surgery, making it an attractive destination for patients seeking advanced medical treatment.
Given the dynamic development of medical science and technology in South Korea, further improvements in bone marrow transplant procedures can be expected. This will allow the country to remain a leader in the treatment of blood and immune system disorders and continue to attract patients from around the world.
The development of multidisciplinary medical centers and laboratories in South Korea enables a comprehensive approach to bone marrow transplantation. This includes not only the surgery itself, but also the diagnosis, patient preparation, and subsequent medical follow-up.
The use of genetic engineering technologies and modern tissue processing techniques can reduce the risk of rejection and side effects after transplantation.
Medical research in South Korea is actively seeking new treatments and improved outcomes for bone marrow transplantation. In addition, research is being conducted in the field of gene therapy aimed at correcting abnormalities in the genome of patients with cancer and hematologic diseases.
The training of medical professionals is also an important aspect in the development of bone marrow transplantation in Korea. South Korean physicians actively participate in international exchanges, internships, and conferences to enrich their professional skills and knowledge.
 Hypospadias treatment in Korea
Hypospadias treatment in Korea
Hypospadias refers to a congenital abnormal condition of the urethra in male infants in which the urethral opening is located on the underside of the penis, testis. This disorder requires careful medical intervention and surgical procedures.
The initial diagnosis of the disease consists of visual inspection and evaluation of the urethra. Much depends on the location of the urethral opening. The disease is categorized as anterior (closer to the head of the penis), middle (closer to the middle), or posterior (closer to the base).
The optimal time for surgical treatment of hypospadias is usually between 6 months and 2 years of age. This is due to higher tissue plasticity and the body’s better ability to heal at an early age.
Surgical interventions are standard practice. In this way, a new urethral opening is created and normal anatomy is restored. It is possible to use the patient’s own tissues or synthetic materials for reconstruction.
Each case is unique, and the specialist chooses the method of intervention, taking into account the severity of the anomaly, tissue structures. The individualized approach allows for the best possible anatomy restoration results.
After surgery, it is important to keep an eye out for possible complications. Some patients may experience cosmetic or functional problems such as urethral stenosis or insufficient urethral length. Additional surgical correction is necessary if complications arise.
Modern technology is also contributing to the development of innovative treatments for the disease. Experimental approaches, such as the use of stem cell and tissue engineering technologies, may provide more effective and innovative techniques for anatomy repair in the future.
After surgery, post-operative care and rehabilitation is equally important. Specialized medical teams monitor the condition and provide long-term follow-up care for the child.
Hypospadias treatment is a complex, multifaceted process involving both surgical interventions and a wide range of medical and psychological aspects. Modern techniques and innovations in medicine are opening up new opportunities to effectively treat this birth defect and provide a better quality of life for patients and their families.
 Hydronephrosis treatment in Korea
Hydronephrosis treatment in Korea
Hydronephrosis is a condition in which there is enlargement of the renal calyx-lochanous system due to retention of urine in the kidneys. This is a serious condition that requires comprehensive treatment.
One of the keys to successfully treating the disease in Korea is diagnosis. Modern medical facilities in the country are equipped with advanced technologies such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, which allows doctors to accurately determine the cause of hydronephrosis and choose the best treatment plan.
Surgical intervention is one of the main techniques in Korea. Specialists in urology and kidney surgery perform high-tech surgeries to remove the obstruction that causes urinary retention and enlargement of the renal system. This includes endoscopy techniques and minimally invasive surgical procedures, which reduces the rehabilitation period for the patient.
Medication also plays an important role in disease management. Doctors select medications aimed at relieving inflammation, improving urine flow and eliminating the causes contributing to the obstruction.
Minimally invasive procedure technologies such as laser therapy and endovascular surgery are also widely used to treat hydronephrosis in Korea. These techniques provide precise exposure to the affected areas with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues.
Rehabilitation and follow-up support play an important role in the treatment of hydronephrosis. Specialized centers provide physical therapy, nutritional therapy and psychological support to help patients recover from surgery and improve their overall quality of life.
The focus on relapse prevention and long-term management of the disease is also an important part of the treatment of the disease in South Korea. Patients are provided with recommendations for lifestyle changes, including maintaining a healthy diet, weight control and regular physical activity.
Innovative treatments include the use of stem cell technology. This area of research holds promise for regenerating damaged kidney tissues and restoring their functionality. Experimental approaches such as stem cell transplantation are being actively studied at medical centers in South Korea.
It is also worth noting the active introduction of artificial intelligence and modern analytical methods in medicine. Automated systems can help optimize diagnostic and decision-making processes, providing more accurate and effective treatment for hydronephrosis.
 Treatment of hyperaldosteronism in Korea
Treatment of hyperaldosteronism in Korea
Hyperaldosteronism is a condition in which the adrenal glands produce excessive amounts of aldosterone. This hormone regulates salt and water levels in the body, which can lead to serious heart, vascular and kidney disorders.
Innovative techniques, such as the use of radiosurgery and radiation therapy, are being actively pursued to control the adrenal glands and suppress overactivity. These methods can be particularly useful in cases where surgery is not the best option due to various reasons.
Endocrine therapy is also an important part of the treatment of the disease in South Korea. Medications aimed at normalizing aldosterone levels are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. This helps to achieve stable control of the disease and prevent recurrences.
Specialized treatment centers in South Korea also focus on rehabilitation and post-treatment support for patients. Physical therapy, nutrition therapy and psychological support help patients recover faster and bring their vital signs back to normal.
With its high level of medical expertise, state-of-the-art treatments and personalized approach, South Korea is becoming a place of attraction for patients facing illness. Healthcare providers are committed to providing not only effective, but also caring treatment to ensure that patients make a full recovery.
An additional innovative area in the treatment of the disease in South Korea is research into the genetic factors that influence the development of the disease. Understanding genetic traits helps in more accurate and personalized diagnosis, as well as in developing more effective treatment strategies.
An important aspect of treating the disease in Korea is the emphasis on a multi-specialty approach. Endocrinologists, surgeons, cardiologists and other specialists work together to create a comprehensive treatment plan, taking into account all aspects of the disease and its effects on various body systems.
Research institutes and medical centers in South Korea are actively involved in clinical trials to find new treatments for hyperaldosteronism. This creates an opportunity for patients to participate in advanced therapeutic strategies and access the latest medical developments.
 Acromegaly treatment in Korea
Acromegaly treatment in Korea
Acromegaly is classified as a rare endocrine disorder characterized by excessive production of growth hormone. This provokes uncontrolled growth of tissues and organs. The treatment of acromegaly is a complex and multidisciplinary process, and in recent years South Korea has been a center of attraction for patients seeking expert care for this rare disease.
One of the key elements of successful acromegaly treatment in Korea is high-tech diagnostics. Modern medical facilities in the country are equipped with advanced technologies that allow doctors to accurately determine the level of growth hormone in the patient’s body. This allows treatment to begin early and prevent further worsening of symptoms.
An important part of acromegaly treatment in South Korea is also the constant monitoring and follow-up of the patient’s condition. Specialized centers provide a system of regular examinations and consultations to monitor hormone levels, control the size of the neoplasm and assess the general condition of the patient. This helps to respond to any changes in a timely manner and adjust therapy as needed.
Very often specialists resort to surgical intervention. Specialized surgeons with extensive experience in endocrine surgery perform surgery with a high degree of precision. Surgical removal of the tumor causing excessive growth hormone release helps stabilize the patient and improve quality of life.
Radiosurgery and radiation therapy are also an important part of acromegaly treatment in Korea. These techniques are used to control tumor growth, especially when surgery is not the primary option or when complete removal of the tumor is not possible.
The multidisciplinary approach in Korea also includes endocrine therapy to control growth hormone levels. Specialists develop individual treatment regimens optimized for the needs of each patient, taking into account possible side effects.
However, in addition to medical treatment, an important aspect of successfully managing acromegaly in Korea is rehabilitation. Patients are provided physical therapy, psychological support and rehabilitation services to recover from surgery and improve overall physical and emotional well-being.
The combination of advanced technology, highly skilled specialists and a comprehensive approach make South Korea an attractive destination for patients facing acromegaly. Local health care providers are committed to providing not only effective treatment, but also caring support every step of the way in the fight against this rare endocrine disorder.
 Myxedema treatment in Korea
Myxedema treatment in Korea
When it comes to treating myxedema, many people look at the methods and technologies available in different countries. One such country that offers modern and effective treatments for this disease is South Korea.
Myxedema is a serious condition caused by an underactive thyroid gland. This condition can lead to a host of problems such as decreased energy, swelling, decreased body temperature, and other symptoms that can significantly impair quality of life. Treatment of myxedema requires a comprehensive approach, including taking thyroid hormones, dietary adjustments, and other medical interventions.
South Korea has a high-level medical system and the country is known for its advanced methods of diagnosing and treating various diseases. Treatment of the disease in Korea includes not only standard methods, but also innovative approaches aimed at maximizing the restoration of thyroid function and improving the general condition of the patient.
One of the key therapies in Korea is the use of modern thyroid hormone preparations. Doctors in Korea are highly skilled and experienced in selecting the optimal dose and treatment regimen for each patient. This helps to achieve stable hormone levels in the body, which in turn helps to improve the overall condition of the disease.
South Korea is actively pursuing innovative treatments, such as the use of stem cell technology. These methods aim to restore thyroid function at a deeper level, which can speed up the healing process.
Diet also plays an important role in the treatment of the disease in Korea. Specialists develop individualized nutrition plans that are tailored to the patient’s needs and help maintain normal energy and metabolic levels.
It is important to note that each patient is unique and treatment should be customized to meet their individual needs. Doctors in Korea take a personalized approach to achieve the best results in treating this condition.
Apart from progressive treatment methods, South Korea is also famous for its state-of-the-art medical facilities with advanced medical equipment. Infrastructure and technology in Korean hospitals facilitate effective diagnosis and treatment of myxedema.
Rehabilitation is also an important part of myxedema treatment in South Korea. Qualified rehabilitologists and physiotherapists develop individual recovery programs that include physical activity, massage, and special procedures to improve blood circulation and reduce swelling.
 Treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis in Korea
Treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis in Korea
Autoimmune thyroiditis refers to chronic inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland. When a disease occurs, the immune system attacks its own tissues. In recent years, South Korea has become known not only for its cultural achievements, but also for its advanced treatments for various diseases.
One of the keys to treating the disease in Korea is early detection and accurate diagnosis. Modern medical facilities are equipped with advanced technology that allows doctors to perform highly accurate tests to determine antibody levels and other indicators associated with the disease. This allows treatment to begin at an early stage.
Substitution therapy is the main mode of therapy in Korea. Specialists competently select doses of medications, ensuring stable hormone levels in the patient’s body to balance thyroid function and improve the patient’s overall condition.
Innovative technologies and approaches are actively used in South Korea. For example, in the field of immunotherapy, research is being conducted to modulate immunity to curb the body’s aggressive response to its own tissues. This opens up new perspectives in the treatment of such diseases.
Specialized centers in Korea also pay attention to patients and their psychological state. Psychotherapists and counselors help patients deal with the emotional aspects of the disease, such as stress and depression, which is important for a full and comprehensive recovery.
Another promising area in the therapy of the disease is the use of stem cell technology. Research in this area focuses on repairing damaged thyroid tissue and suppressing the autoimmune response. These advanced techniques offer new treatment options, especially in cases where traditional methods have not had sufficient effect.
Multi-target clinical trials are being actively conducted in Korea. Patient participation in such studies provides an opportunity to access new treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical science.
Today, South Korea provides patients with a caring and personalized approach to each case. This medical expertise and innovative techniques make the country an attractive destination for patients seeking effective and comprehensive treatment for autoimmune disease.
 Lupus erythematosus treatment in Korea
Lupus erythematosus treatment in Korea
Lupus erythematosus, or systemic red wolf, is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting various organs and systems of the body. In recent years, South Korea has seen significant progress in the treatment of this disease, considering advanced techniques and innovative approaches.
The medical community in South Korea is actively researching the causes and mechanisms of lupus erythematosus. Research is aimed at identifying new therapeutic approaches and adapting existing ones to be effective in the treatment of this autoimmune disease.
The use of drugs that modify the immune response plays a key role in the treatment strategy. This includes the use of biologic drugs and immunoglobulins.
Introducing newer drugs that target specific molecular aspects of the disease, providing more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
The use of genetic and molecular technologies to develop individualized treatment approaches, allowing us to accurately determine the optimal treatment for each patient.
Integration of different treatment modalities such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy and psychological support to ensure a comprehensive impact on the physical and emotional well-being of patients.
Implementation of monitoring systems and regular medical check-ups to detect possible complications early and prevent their development.
Establishment of specialized scientific research centers where scientists and doctors will work in synergy to develop new treatments.
Introduce education programs for physicians and patients to raise awareness of lupus erythematosus and its treatment. Participate in international clinical trials and share experiences with leading medical centers around the world.
The treatment of lupus erythematosus in South Korea is experiencing significant progress, and implementation of the strategies described may significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients. The collaborative efforts of physicians, scientists, patients, and government will be key to achieving this goal.
 Treatment of Behterev’s disease in Korea
Treatment of Behterev’s disease in Korea
Currently, the treatment of Bechterew’s disease in South Korea is undergoing important innovations and modern techniques. At the heart of chronic inflammatory disease is the involvement of the joints and spine. This condition can significantly limit patients’ mobility and quality of life, so finding effective treatments becomes a priority.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for the success of this disease. South Korea utilizes advanced medical diagnostic techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). These technologies allow doctors to gain a detailed understanding of the extent of joint and spine damage, determine the stage of the disease and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Biologic therapies are becoming an increasingly common method of treating the disease. This approach is based on the use of a biologic drug aimed at suppressing inflammation and modulating the immune system. These injections can slow the progression of the disease, reduce pain, and improve patients’ quality of life.
Physical rehabilitation plays a key role in the treatment of Bechterew’s disease. In South Korea, modern physiotherapy techniques are used to improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Regular exercise under the guidance of experienced rehabilitators helps to improve the patient’s overall condition.
All patients are unique and successful treatment requires an individualized approach. Doctors routinely develop personalized therapy regimens, taking into account the specifics of the case. This consists of combining medication, physical activity and rehabilitation.
In cases where conservative methods do not have sufficient effect, innovative surgical methods are used. Doctors use advanced surgical techniques to correct deformities and restore functionality to affected joints.
Treating the disease requires not only intervention on the physical side, but also psychological support. Doctors and psychologists work with patients to help them cope with the emotional aspects of the disease and boost their morale.
Treatment for Behterev’s disease in South Korea has a high degree of professionalism and innovative methods. With the constant evolution of the medical industry, patients with Bechterew’s disease can expect an effective and modern approach to their health.
 Hepatitis A treatment in Korea
Hepatitis A treatment in Korea
Hepatitis A refers to infectious liver disease caused by a virus. Treatment of this disease consists of several key aspects aimed at eliminating symptoms, accelerating recovery, and preventing further spread of the virus. It is important to note that the disease usually causes an acute infection, and most patients make a full recovery with no long-term consequences.
Patients are recommended to observe bed rest for the period of pronounced ailments. This includes fatigue, abdominal pain, and nausea. Fluid loss due to vomiting and diarrhea can lead to dehydration. It is important for patients to consume adequate fluids, including electrolytes.
A light, balanced diet is recommended, avoiding spicy and fatty foods to reduce the burden on the liver. During the disease, it is important to completely eliminate alcohol consumption.
Vaccination is an effective method of preventing the disease. Vaccination is recommended for those in at-risk groups and for those traveling to endemic areas.
New antiviral drugs are being researched to treat hepatitis A, which may shorten the duration of the disease and reduce its severity.
Research into antiviral drugs for the treatment of hepatitis A provides new perspectives in the management of this virus. New drugs may offer more effective therapies and possibly shorten the duration of the disease. This is especially important for patient groups in whom the infection may have a more severe course.
Modern monitoring technologies allow for more accurate assessment of liver status and viral activity. The use of biomarkers and extensive research provide physicians with the ability to provide more individualized treatment tailored to each patient.
With the evolving research and medical technology in Korea, the future of hepatitis A treatment promises to be even more effective and aimed at ensuring complete recovery for patients. However, it is important to remember that the focus should be on prevention, including vaccination and adherence to hygiene safety measures.
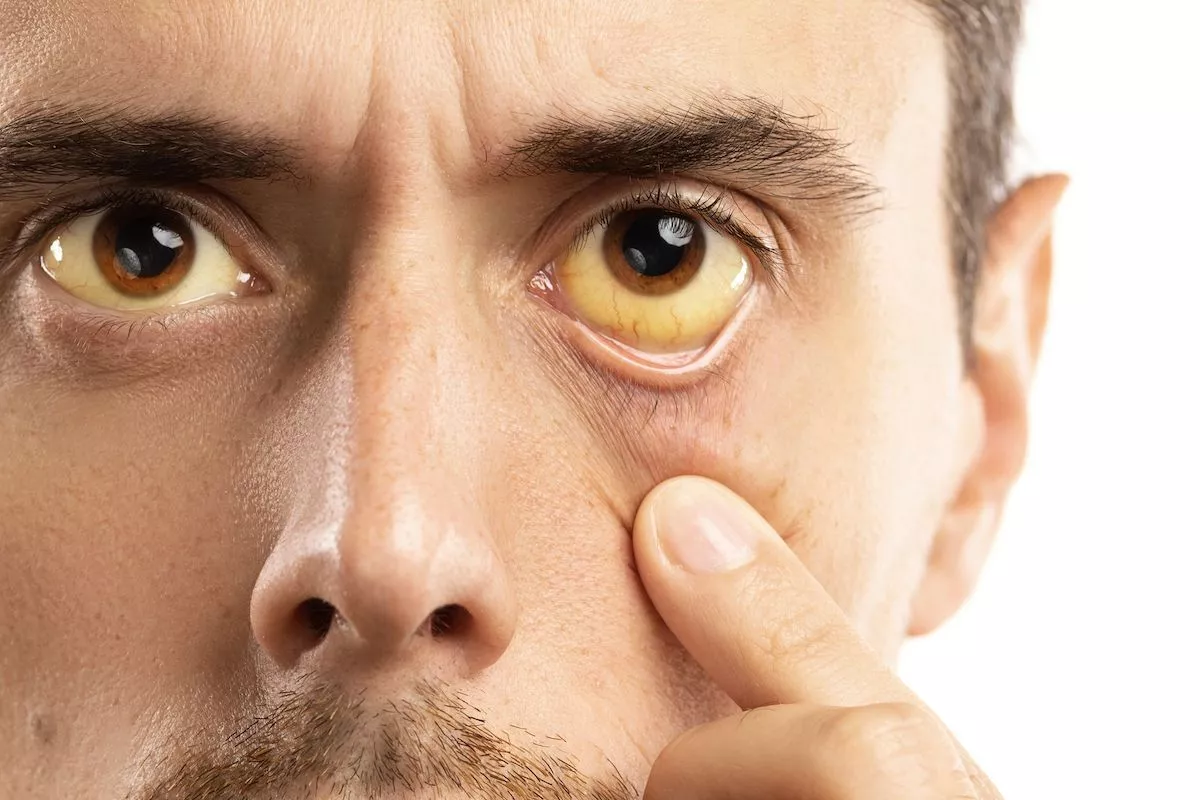 Rotor syndrome treatment in Korea
Rotor syndrome treatment in Korea
Rotor syndrome is a rare inherited disorder associated with an abnormality of bilirubin metabolism in the liver. This syndrome is manifested by elevated levels of conjugated bilirubin in the blood, leading to jaundice and other symptoms.
Rotor syndrome is caused by genetic mutations that lead to malfunction of the enzymes responsible for bilirubin metabolism. Normally, bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of red blood cells and is processed in the liver. However, in patients with Rotor syndrome, this process is disrupted, resulting in the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood.
The main symptom is jaundice, which is manifested by yellow staining of the skin and sclerae. Other possible symptoms include weakness, fatigue, insomnia, and abdominal pain. It is important to note that symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease.
Diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical manifestations, anamnesis data and laboratory tests. Tests for bilirubin, total and direct, as well as molecular genetic methods are used to detect the presence of mutations responsible for the development of this syndrome.
Treatment for Rotor syndrome focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. In most cases, no specific medication intervention is required. An important component of care for patients with this syndrome is lifestyle and diet.
Patients are advised to watch their diet and avoid consuming foods that can increase the formation of bilirubin. This includes limiting the consumption of fatty foods, alcohol, and certain medications.
Regular visits to the doctor and medical monitoring will help to monitor the patient’s condition, control the bilirubin level and respond to changes in a timely manner.
Rotor syndrome is the focus of researchers in genetics and gastroenterology. New diagnostic techniques and molecular therapies are under development that could open new horizons in the treatment of this rare inherited disease.
In addition, an important area of research is the development of individualized treatment approaches that take into account the genetic characteristics of each patient. Such approaches will allow more precise regulation of bilirubin metabolism and minimize the symptoms of Rotor syndrome.
Despite its rarity, Rotor syndrome requires serious attention and research. Current diagnostic and treatment methods are managing the symptoms of this disease, and future perspectives provide new opportunities for more effective intervention.
 Treatment of non-specific ulcerative colitis in Korea
Treatment of non-specific ulcerative colitis in Korea
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis (NUC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that requires comprehensive and effective treatment. In South Korea, the medical industry ensures that NNC patients have access to advanced diagnostics and therapies while providing close medical supervision.
In Korea, modern diagnostic methods are widely used to accurately determine the extent and nature of the inflammatory process in NPC. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging allow doctors to study the condition of the intestine in detail and choose a step-by-step method of treatment.
Treatment of NPC in Korea is based on the principles of personalized medicine. Doctors select a treatment regimen, including the use of immunomodulatory and biologic drugs, to achieve the best results in each case.
With modern techniques such as biological therapy and immunomodulation, doctors in Korea have been successful in suppressing the inflammatory process in NNC. This allows patients to maintain long-term remission and improve their quality of life.
In cases where conservative treatment is not effective enough, doctors in Korea can use advanced surgical techniques, including minimized techniques and robotic surgery. This helps to reduce the traumatic nature of the procedure and speed up the recovery process.
An important component of NNC treatment in Korea is patient support and rehabilitation. Psychosocial support programs, nutritional counseling, and rehabilitation activities to keep the patient on the road to recovery.
Korean medical institutions are actively collaborating with international clinics to ensure that patients from different countries have access to country-specific advanced treatments and global expertise while waiting for NNC.
The basic principle of treatment is the integration of advanced technology with a humane approach to patients. Sometimes the patient chooses an individualized treatment plan that includes not only the physical stan, but also psychological and social aspects.
Korea is actively pursuing innovative technologies in the treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Highly accurate diagnostic techniques such as fibrocolonoscopy and capsule endoscopy provide detailed information about the condition of the bowel and often reveal signs of recurrence.
The integration of advanced technologies, personalized approaches and versatile additional capabilities allows to achieve sufficient results in monitoring and controlling this process. Korea continues to be a leader in gastroenterology medicine, giving patients with NNC the necessary measures for health and wellness.
 Crohn’s disease treatment in Korea
Crohn’s disease treatment in Korea
Crohn’s disease is a chronic scorching lesion of the intestine that is embedded in the herbal tract. In Korea, as the glory of its advanced medical technology and high standards of medical services, patients with good crown can access practical and effective treatments.
In Korea, the medical service actively utilizes advanced diagnostic techniques to accurately determine disease status. Highly accurate medical imaging, such as CT and MRI scans, dose medications with detailed examinations and individualized treatment plans.
Hereditary predisposition of the disease is considered to be one of the main causes of crohn’s. If there is a history of inflammatory disease in the family, the risk of developing the disease may increase.
The disease can occur at any age, but most often begins in early adulthood. It is also more commonly diagnosed in people of European and African American descent.
Crohn’s drug treatment involves the use of immune and biologic medications to support the immune system. In Korea, patients can have access to a wide range of such medications that are individually dosed and tailored to the optimal regimen.
Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, or biologic drugs to control inflammation and maintain remission. If necessary, antibiotics may be used to fight bacterial infections that may aggravate the condition.
An important aspect of managing Crohn’s disease is proper nutrition. Patients may benefit from modifying their diet, incorporating certain foods, or using special diets.
When medication is ineffective or not used, surgery may occur to remove the affected areas of the intestines.
Crohn’s disease is often accompanied by periods of exacerbation and remission. With such control and treatment, most patients can lead active and fulfilling lives. However, it is important to collaborate with your doctor, observe your symptoms, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
 Alzheimer’s disease treatment in Korea
Alzheimer’s disease treatment in Korea
Alzheimer’s disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease characterized by a gradual loss of cognitive function and memory. In recent decades, Korea has shown significant interest in research and development for the treatment of this condition, aiming to offer innovative diagnostics and therapies for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
Korea is actively adopting modern diagnostic methods to detect early signs of the disease. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) are used to visualize changes in the brain and identify amyloid plaques characteristic of the disease.
Medications remain a key component of Alzheimer’s disease treatment. New drug approaches aimed at slowing disease progression and improving patients’ quality of life are being actively investigated in Korea. Cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor modulators are just a few examples of drugs used.
Recently, Korea has been focusing on innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromodulation, such as deep brain stimulation, is being investigated as a potential therapeutic option to improve cognitive function and reduce disease symptoms.
In addition to medication, rehabilitation programs and social support play an important role. Korean medical centers offer a comprehensive treatment approach including physical, speech and psychological therapies to improve patients’ functionality and facilitate daily life.
Many research groups in Korea are actively involved in clinical trials focused on finding new treatments and breakthroughs in understanding the disease. This includes studying genetic factors associated with disease onset and developing personalized treatment approaches.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is at the intersection of advanced technology and scientific research. The country’s strategy includes an integrated approach to diagnosis, pharmacotherapy and innovative treatments to better understand and more effectively manage this complex neurological condition. Over time, these efforts may lead to the development of more effective and personalized treatments for those facing the challenges of Alzheimer’s disease.
 Epilepsy treatment in Korea
Epilepsy treatment in Korea
Epilepsy treatment in Korea may involve a variety of methods, depending on the individual patient and the characteristics of the disease. Treatment of the disease takes a long time, and the effect of different methods may vary from patient to patient. Doctors choose a specific method, taking into account many factors and the frequency of attacks, general health, age of the patient and their individual characteristics.
The exact causes of epilepsy are not fully understood. They may be related to genetic factors or other undetermined factors.
Heredity may play a role in the development of epilepsy. Some forms of the disease may be associated with genetic mutations or the presence of a family history of epilepsy.
The presence of traumatic brain injuries, bruises, concussions and other types of injuries, increase the risk of developing epilepsy. People who have had viral encephalitis or meningitis have a predisposition to the disease.
Strokes, aneurysms, and various vascular diseases can lead to a lack of oxygen to the brain and therefore cause epileptic seizures.
In Korea, doctors often use advanced diagnostic techniques including neuroimaging and electroencephalography (EEG) to accurately determine the nature of epileptic seizures and choose the best treatment method.
Patients with epilepsy are advised to monitor their lifestyle, take medications as recommended by their doctor, undergo regular medical check-ups and follow all recommendations of specialists.
The use of medications to manage the symptoms of epilepsy. The doctor can select the optimal drug, taking into account the peculiarities of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
In some cases, surgical intervention such as resection (removal) of the areas of the brain responsible for causing the seizures may be considered.
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet is often used and may be effective for some patients with epilepsy.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a technique in which a device is implanted to stimulate the vagus nerve, which can help control seizures.
In some cases, alternative methods such as acupuncture or physiotherapy may be used, but their effectiveness for treating epilepsy may be limited.
 Choriocarcinoma treatment in Korea
Choriocarcinoma treatment in Korea
Choriocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive disease associated with an unusual form of cancer cells that develop from placental tissue. It presents a challenge to the medical community, and in this area, South Korea has attracted attention for its innovative treatments and outstanding results.
South Korea has a multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of choriocarcinoma. It includes a team of highly qualified specialists such as oncologists, gynecologists, surgeons, radiologists and geneticists. This team collaborates to develop individualized treatment plans, taking into account all aspects of the disease and patient characteristics.
Korean medical institutions are adopting advanced technologies to accurately diagnose and treat choriocarcinoma. Modern educational techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), allow for more accurate determination of the extent of tumor spread and surgical planning.
Surgical techniques play a key role in the treatment of choriocarcinoma. Korea has successfully utilized innovative surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures. This helps reduce trauma, shorten the recovery period, and provide more favorable outcomes for patients.
A combination approach of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is the standard treatment protocol for choriocarcinoma in Korea. Individual selection of drugs and doses allows for more effective suppression of cancer cells while minimizing side effects. Radiation therapy is used to localize and destroy tumor foci.
With the significant progress in genetic research, Korea is actively introducing genetic testing to identify individual tumor characteristics and its response to therapy. Immunotherapy, which aims to activate the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells, also represents a promising avenue of treatment for choriocarcinoma.
Korean medical research centers are actively interacting with global counterparts, participating in clinical trials and sharing experiences. This provides access to the latest treatments and technology, which is key to improving the effectiveness of therapy.
Special attention in Korean medical institutions is paid to psychological support for patients. This includes counseling, support from social workers, and group sessions to support and restore patients’ psychological well-being.
Treatment of choriocarcinoma in South Korea is an example of successful synthesis of advanced medical technologies, high qualification of specialists and attention to patients. An integrated approach, the use of state-of-the-art technology, ongoing research and patient support all contribute to improved treatment and prognosis for those facing this rare and difficult disease.
 Leukoplakia treatment in Korea
Leukoplakia treatment in Korea
Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by the appearance of white spots or warts on the oral mucosa. This phenomenon can result from a variety of factors including irritation, injury, infection or inflammation. South Korea, with a known interest in advanced treatments, has a unique approach to the diagnosis and therapy of leukoplakia.
In Korea, doctors use high-tech methods to diagnose leukoplakia. One of the key tools is endoscopy, which allows visual assessment of the condition of the mucosa. Biopsy is also commonly used to identify structural changes and clarify the cause of leukoplakia.
Leukoplakia treatment in Korea often begins with the development of an individualized plan. This is important because the causes of leukoplakia can be varied and the treatment approach should be tailored to the patient’s specific situation. Techniques such as laser therapy, cryotherapy (cold treatment method), and electrosurgery can be used depending on the nature of the pathology.
South Korea is renowned for its advanced technology in medicine, and this includes the treatment of leukoplakia. The use of high-power lasers to remove diseased tissue, as well as the use of innovative treatment methods, contribute to a more effective and faster recovery of the mucosa.
Korean medical institutions are actively collaborating with academic research centers to continuously improve the treatment of leukoplakia. This includes research to identify new methods of diagnosis and treatment, ensuring that standards of practice are kept up to date.
An important component of the Korean approach to health care is the emphasis on preventive measures and patient education. Patients are routinely provided information about the risks and factors that contribute to the development of leukoplakia, as well as education on self-checking and timely seeking medical attention.
Leukoplakia treatment in Korea is a comprehensive and advanced approach that includes diagnosis, technological innovation, prevention and psychological support. A commitment to continuous practice improvement and attention to patient needs make this experience an important contribution to global standards of care.
 Chemotherapy in Korea
Chemotherapy in Korea
Chemotherapy is one of the most important cancer treatments that uses medications to destroy or slow the growth of cancer tissue. This method of therapy epitomizes ongoing technological and scientific advances, bringing to the hands of medical professionals an effective tool in the fight against cancer.
A chemotherapy regimen includes many different drugs, each acting on cancer cells in a specific way. This allows the treatment to be tailored to the specific type of disease.
The active ingredients are distributed through the bloodstream, reaching cancer cells as in any distant sites. The course is conducted in cycles – periods of active treatment and recovery time. This allows the body to rest and recover.
The procedure often helps to relieve symptoms and increase the life expectancy of patients.
Therapy can help prevent the cancer from coming back after surgery, which is especially important for tumors with recurrence.
The effectiveness of the method is shown in the therapy of any type of oncology, which makes this method universal and available to a large number of patients.
Chemotherapy can reduce symptoms of the disease, such as pain and discomfort, which helps improve the patient’s overall condition.
Despite these benefits, it is important to note that chemotherapy can come with some side effects such as hair loss, nausea, and fatigue. However, modern research methods and medical technology seek to minimize these negative aspects.
The decision to use this technique is always made on an individual basis, taking into account the type and stage of cancer, the general condition of the patient and other factors. It is important to support patients and provide them with all the information they need to know about how this therapy can help them manage their disease.
Chemotherapy continues to be an important tool in the fight against cancer, providing a wide range of applications and affecting different stages of the disease. It has demonstrated its effectiveness in combination with other treatment modalities and remains an integral part of modern oncology practice. At the same time, ongoing research and development is aimed at finding new, more effective and less invasive chemotherapy methods.
 Robotic surgeries in Korea
Robotic surgeries in Korea
The field of medicine has been undergoing a revolution in recent decades, with robotic surgeries becoming one of the most impressive technological innovations. These advanced systems provide surgeons with new tools for precise and complex interventions, revolutionizing the way surgeries are performed.
Robotic surgery systems include a surgical robot controlled by a surgeon using a console. This robot is equipped with instruments that accurately mimic the surgeon’s movements, but with maximum stability and reduction of abnormal movements.
The surgeon receives a high-quality three-dimensional image of the surgical field, which provides a clearer visual perception and allows to perform operations with high precision.
The robot’s instruments can penetrate very small spaces, which is useful for complex surgeries with minimal impact on surrounding tissue.
The surgeon can control the robot from a console even at a great distance from the operating room, opening up opportunities for remote surgery and training.
Robotic systems provide a level of precision unattainable by the human hand. This is especially important for operations in areas where maximum precision is required.
Due to the precision and miniaturization of the instruments, robotic surgeries usually involve less damage to surrounding tissues and organs.
Patients who have undergone robotic surgery often have faster recovery times and less pain after the procedure. With careful process control and minimal exposure, robotic surgeries can be accompanied by reduced blood loss and risk of infection.
Robotic systems allow surgeons to perform complex manipulations that would be difficult or even impossible using traditional methods. Robots can provide access to hard-to-reach areas of the body, which is especially useful in treating tumors and other diseases.
Robotic surgeries not only provide surgeons with powerful tools, but also offer new perspectives in treatment development and training. Their use is the future of medicine, where precision and efficiency will be key to treating the most complex diseases.
 Causes of cancer
Causes of cancer
Cancer, or cancers, remain one of the leading causes of death in the world. Scientists around the world are actively researching various aspects of oncology to identify the causes of the disease and develop more effective treatments.
Heredity plays a key role in the development of cancer. Mutations in certain genes may predispose to cancer. Genome studies can identify genetic mutations that can cause cancer.
Lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet and physical inactivity are considered to be the main causes of many cancers. The research aims to understand the molecular mechanisms involved in the effects of bad habits.
Certain types of viruses, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B and C virus, can increase the risk of cancer. Research on vaccines and prevention methods is aimed at preventing viral infections.
Expanding genome research is helping to identify genetic mutations linked to cancer. The development of genetic therapies could be the newest step in cancer therapy. Scientists are developing new ways to activate immunity and overcome tumor resistance.
The research aims to identify molecular markers that may predict cancer development. This will allow for earlier diagnosis and personalized treatment.
The application of nanotechnology in the field of diagnostics can improve the accuracy of early cancer detection, which significantly improves prognosis.
The unique genetic characteristics of tumors are becoming a focus for researchers. Genetic therapies correct abnormalities in the DNA of cancer cells with new prospects for precise and personalized treatments.
Current research focuses on the development of new methods, such as CAR-T therapies. These technologies improve the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Big data analytics and the use of artificial intelligence are helping to identify patterns in cancer progression, which is helping to better diagnose and predict treatment outcomes.
Advances in the technology of liquidation biopsies allow the examination of tumor cells released into the bloodstream, which facilitates earlier diagnosis and monitoring of treatment efficacy.
Tumor vaccine research aims to create personalized vaccines that can stimulate the immune system to better fight cancer cells.
Epigenetic studies provide insight into changes in the genome that may be associated with cancer development. The development of drugs that regulate epigenetic mechanisms provides new treatment options.
 Genetic predisposition test for cancer in Korea
Genetic predisposition test for cancer in Korea
Cancer diagnosis is a comprehensive process that includes a variety of methods to detect tumor masses. The first step is to analyze family history to identify cases of cancer in the family.
If there is a family history of cancer, especially at a young age, or if several family members have experienced the same type of cancer, this may warrant genetic testing.
Current tests may include analysis of specific genes known as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. For example, such tests can detect mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
The test results provide information about the presence or absence of certain genetic variations. It is important to note that positive results do not mean that cancer will necessarily develop, and negative results do not rule out the possibility of cancer.
Genetic tests can also provide information about the overall risk of developing cancer based on genetic inheritance. This allows patients and health care professionals to develop more effective screening and prevention plans.
The introduction of genetic tests raises questions about data privacy and ethical standards. It is important to take strict measures to protect personal information and ensure transparency when discussing test results.
A genetic test can also draw attention to family history of cancer, which helps identify at-risk groups among relatives and provides an opportunity for them to undergo appropriate genetic testing.
After receiving the results, the patient works with their doctor and genetic counselor to discuss possible steps to reduce their risk, such as regular health screenings, preventive measures, or even surgery.
Genetic testing is just one tool in an overall cancer prevention strategy. The test results can be integrated into an overall health care plan that includes regular checkups, healthy lifestyles, and other preventive measures.
 Radiation therapy in Korea
Radiation therapy in Korea
Radiation therapy is one of the key treatments for a variety of diseases, including cancer. In South Korea, as a leading medical powerhouse, radiation therapy is undergoing constant change and innovation, providing patients with access to advanced treatments.
One of the main features of modern radiation therapy in Korea is efficacy. Using advanced technologies such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and cyberknife, doctors can precisely direct radiation beams while minimizing the impact on healthy tissue.
Radiation therapy in South Korea is becoming increasingly integrated with other treatments such as surgery and chemotherapy. Combination approaches can fight cancer more effectively, increasing the chances of recovery for patients.
The development of new technologies plays a key role in improving radiation therapy. In South Korea, innovative methods such as tomotherapy and proton therapy are being actively introduced to ensure the highest level of treatment effectiveness and safety.
Patients in South Korea have access to the best medical care, including radiation therapy. The increasing number of modern oncology centers and the introduction of new methods create prospects for improving the effectiveness of treatment and the quality of life of patients.
South Korea is actively cooperating with international partners in medical research and exchange of experience in radiation therapy. This ensures the exchange of best practices and experience, which contributes to the professional development of medical professionals.
The future of radiation therapy in South Korea promises even greater advances. Research and development of new technologies will continue, aimed at improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
One of the key components of improving radiation therapy is the training of highly qualified specialists. In South Korea, emphasis is placed on training physicians, physicists and radiation therapy technicians to provide the highest level of medical care.
Radiation therapy in South Korea does not just follow global standards, but is an innovative component of cancer treatment. State-of-the-art technology, personalized approach and active international cooperation make radiation therapy a key element in the successful fight against cancer in the country.
Radiotherapy, as one of the key treatments for cancer, is central to medical practice in South Korea. Modern technology, high professionalism of medical staff and continuous scientific research make radiotherapy an effective tool in the fight against cancer in this country.
Radiotherapy is an important cancer treatment that uses high-energy rays to destroy or damage malignant cells. Modern radiotherapy technology offers a number of advantages that have made this method more effective and safer for patients.
Modern systems create three-dimensional beam maps, allowing for more detailed planning of radiation therapy. This improves the accuracy and predictability of treatment.
Radiotherapy is widely used to treat complex tumors in the brain, cervix, prostate and other places where surgery may be difficult or impossible.
Radiotherapy in Korea strives for a personalized approach to each patient. The use of education methods and precise dosage ensures maximum effectiveness with minimal impact on the body. This is especially important when treating early-stage cancer, when preserving healthy tissue is paramount.
Medical research in radiotherapy is actively pursued in South Korea. Scientists are striving to improve treatments by developing innovative approaches to fighting cancer. Clinical trials play a key role in determining the efficacy of new methods and their safety.
One of the priorities in radiotherapy is the training of highly qualified professionals. Medical professionals undergo specialized training programs and maintain the highest standard of professionalism. This ensures that every patient receives the highest level of care.
In the future, radiotherapy in South Korea will continue its development. New technologies, improved diagnostic techniques and the development of innovative approaches to cancer treatment are expected.
Radiotherapy in South Korea is becoming an increasingly important element of cancer treatment. The integration of new technologies, the pursuit of a personalized approach and active research make this method an effective tool in the fight against cancer in this country.
 Immunotherapy in Korea
Immunotherapy in Korea
Immunotherapy as an advanced treatment method is gaining popularity in South Korea, and this trend is due not only to global standards but also to the unique features of the country’s medical system.
One of the key benefits of immunotherapy in South Korea is the ability to accurately diagnose. Modern techniques such as genetic tests and biomarkers allow doctors to more accurately determine the nature and characteristics of each case of the disease, opening the door to more effective treatments.
The introduction of personalized medicine techniques has become the norm in South Korea. Immunotherapy provides the opportunity to create individualized treatment regimens, taking into account the genetic characteristics of the patient. This not only increases the effectiveness of therapy, but also reduces the risk of side effects.
Physicians in South Korea are actively integrating immunotherapy techniques into standard treatment protocols. This maximizes the benefits of this therapy, ensuring that patients have access to advanced techniques even in the early stages of the disease.
South Korean medical institutions are actively participating in global research on immunotherapy. Sharing experience with leading specialists allows the country to rapidly introduce new treatment methods and improve outcomes.
Immunotherapy in South Korea has been successfully used not only to treat cancer, but also for other medical problems related to autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory processes.
Health care systems in South Korea are actively adopting the latest technologies to improve the efficacy of immunotherapy. The use of modern devices and data processing methods increases the accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment.
Physicians in South Korea have access to high quality education and training. The system of continuous professional development allows specialists to stay abreast of the latest trends in immunotherapy and implement them in practice.
Patients in South Korea become active participants in their treatment. Awareness and participation in treatment decisions create a supportive atmosphere for the use of immunotherapy, as patients are more likely to participate in clinical trials and innovative programs.
South Korea actively cooperates with international medical organizations and research centers to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and experience in the field of immunotherapy. This global collaboration facilitates the best solutions for patients.
 Targeted therapy in Korea
Targeted therapy in Korea
Targeted therapy is an innovative approach to treating a variety of diseases, including cancer, that targets specific molecular changes inherent in certain cell types. In South Korea, this treatment method has a prominent place in medical practice, and its benefits are seen in several key aspects.
Targeted therapy allows the creation of individualized treatment regimens, taking into account the genetic characteristics of patients. This results in increased efficacy and reduced side effects, which is especially important for patients in South Korea.
South Korea’s medical infrastructure is at the frontline of applying advanced technology. High-tech equipment and advanced research methods create favorable conditions for successful implementation of targeted therapy.
South Korea is actively involved in clinical research and development of new drugs, including targeting therapies. Cooperation with the world leaders in medical science creates conditions for advanced implementation of new technologies.
Due to the precision in disease approach and the use of modern technology, targeted therapy in South Korea demonstrates high treatment efficacy. This is particularly important for patients with cancer, where the use of targeted therapies can significantly improve therapy outcomes.
Targeted therapy in South Korea is a promising treatment method based on modern scientific advances and high technology. The benefits of this approach broaden the horizons of possibilities in the treatment of various diseases, making it an important element of modern medical practice in South Korea.
The introduction of targeted therapies in South Korea continues to evolve, providing promise for the future. With the constant updating of techniques and drugs, this approach will remain a key element in the strategy to combat various diseases.
Targeted therapy in South Korea is not only a modern treatment method, but also a systematic approach to disease control. The benefits of this therapy, such as its personalized approach and use of advanced technology, make it an effective tool in the hands of the medical community, contributing to the health and well-being of patients in South Korea.
 Treatment of Sesari syndrome in Korea
Treatment of Sesari syndrome in Korea
Modern medicine strives for continuous improvement, and Korea has been successful in integrating advanced technology into traditional treatments for Sézary syndrome. This integration results in more accurate diagnoses and more effective treatments.
Korea is known for its outstanding medical facilities that provide services to treat the disease. These clinics offer patients a full range of services, from traditional methods to modern procedures.
Korean clinics often offer cultural and educational programs for their patients. This allows patients to better understand Korean medical traditions, including history, philosophy and treatment methods.
Oncology treatment in Korea has been recognized for its effectiveness and innovative approach. Patients from all over the world make positive comments about the results of the treatment and the unique experience they have had by undergoing therapy in Korea.
Many clinics in Korea provide services for international patients, providing interpreters, cultural adaptations and a high standard of care.
One of the advanced treatments is immunotherapy, which aims to strengthen the immune system to fight malignant cells. Monoclonal antibodies can be used to block tumor growth.
New drugs that target specific molecular targets in cells may provide more effective and pinpointed effects on cancer cells with minimal damage to healthy tissue.
Experimental methods include gene therapy, which aims to modify genetic material to improve the body’s response to cancer cells.
In South Korea, there are several challenges related to the treatment of Sézary syndrome. First, the rarity of the disease makes it less well-studied, and thus medical professionals may find it difficult to accurately diagnose and treat. Second, the need for local staff may be due to a lack of experience and training in rare cancers.
The formation of specialized centers specializing in rare cancers can provide local specialists with the necessary expertise.
Establishing collaborations with international medical centers and research organizations can facilitate the exchange of experience and best treatment practices.
 Carcinoid treatment in Korea
Carcinoid treatment in Korea
Carcinoid is a rare type of tumor that can develop in various organs such as the lungs, stomach, intestines, and others. Modern technology and medical approaches offer new perspectives for effective treatment of this type of cancer. South Korea, renowned for its advanced medical technology, provides patients not only with high quality treatment, but also with innovative methods to fight carcinoid.
South Korea continues to strengthen its position in medical innovation by providing carcinoid patients with better treatment options. This is not only due to the use of advanced techniques, but also due to the continuous optimization of treatment practices.
South Korean medical institutions are actively participating in international clinical trials to identify new drugs and approaches to oncology treatment. This research allows for innovation in practice and better outcomes.
The development of personalized medicine techniques allows for a more precise definition of the characteristics of each carcinoid case. This includes genetic analyses of tumors, enabling doctors to provide individualized treatment that best suits the needs of the individual patient.
South Korean specialists actively participate in international medical conferences and symposiums, sharing their experience and learning advanced techniques from leading experts in the field. This contributes to maintaining a high standard of care and integrating best practices in the treatment of carcinoid.
Realizing the importance of combating the high costs of medical procedures, including carcinoid treatment, is driving the adoption of more efficient and cost-effective methods. This lowers the financial barrier for patients, ensuring they have access to quality health care.
South Korea, at the center of global medical advances, continues to improve the treatment of carcinoid through innovative approaches, active participation in international research and experience sharing. This not only improves patients’ chances of recovery, but also raises the bar for quality healthcare globally.
 Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma in Korea
Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma in Korea
Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of malignant tumor that can affect various organs, including the lungs, head and neck, skin, bladder, and others. In light of ongoing medical research and technological innovation, South Korea has attracted the attention of many patients seeking advanced treatments for squamous cell carcinoma.
South Korea has an integrated medical approach that combines advanced diagnostics, surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. This approach aims to provide comprehensive and effective treatment.
South Korean surgeons are actively pursuing advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures and robotic surgery. This reduces the traumatic nature of surgery, shortens the recovery period and increases the chances of successful treatment.
The use of advanced technology in radiation therapy allows radiation beams to be more precisely directed at the tumor, minimizing the impact on healthy tissue. This helps to kill cancer cells more effectively and reduce side effects.
Immunotherapy and targeted therapy are promising avenues for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma. In South Korea, advanced techniques are being introduced to stimulate the immune system and block specific molecules responsible for tumor growth.
After treatment, the rehabilitation phase is important. Korean medical facilities provide comprehensive rehabilitation support, including physical therapy, psychological care and support for patients to recover from treatment.
South Korea’s medical system is considered one of the best in the world, providing high quality and innovative treatment. Doctors in Korea often have extensive training and international experience, which contributes to a high level of medical expertise.
Modern medical centers in South Korea are equipped with advanced equipment and offer a wide range of medical services. Patients can enjoy the unique cultural environment and hospitality of the country during their treatment.
Many medical facilities in Korea provide special programs for international patients, including interpreters, medical tourism coordinators, and adapted service for the comfort of foreign nationals during treatment.
 Treatment of multiple myeloma in Korea
Treatment of multiple myeloma in Korea
Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor caused by the division of plasma cells in the bone marrow. This form of blood cancer can lead to various complications such as weakened bones, impaired bone marrow function, and kidney damage. Korea has become globally recognized in the field of cancer treatment, offering advanced diagnostics and innovative therapies.
Heredity may play a role in the development of multiple myeloma. If a family member already has the disease, other family members may be at increased risk.
A weakened immune system caused by infections, certain medications, or diseases can contribute to the development of multiple myeloma. The risk of multiple myeloma increases with age, and it is most often diagnosed in people over the age of 65.
Patients may experience pain in the back, pelvis, or chest. The disease can lead to anemia, which causes general weakness and fatigue. Multiple myeloma can damage the kidneys, causing problems with their function.
Calcium levels in the blood can be elevated, leading to problems with the kidneys and other organs. The disease can cause weight loss and decreased appetite. Patients may experience insomnia and general weakness.
Korea is known for its advanced cancer treatments, and multiple myeloma is no exception. The use of medications to kill malignant cells. Doctors in Korea use innovative chemotherapy drugs with fewer side effects.
Bone marrow transplantation may be recommended for patients at high risk of recurrence. Korea is known for its expertise in performing successful bone marrow transplants.
Korea’s medical system is of world-class standards, providing highly trained doctors and state-of-the-art equipment. Treatment of multiple myeloma in Korea is based on the principle of an integrated medical approach, including modern methods of diagnosis, surgery and rehabilitation.
Korea is actively involved in medical research and clinical trials, which allows us to utilize the latest scientific advances in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
 Melanoma treatment in Korea
Melanoma treatment in Korea
Melanoma, a type of cancer that develops from melanocytes, the cells that produce the pigment melanin, presents a serious challenge to patients and the medical industry. Over the past decade, oncology treatment in Korea has become a paradigm of innovation, precision and high technology.
Successful treatment of the disease begins with early diagnosis. Korean clinics use advanced educational examination technologies such as dermatoscopy and magnetic resonance imaging to detect even small lesions and metastases.
Surgical removal of the tumor remains an effective treatment option. Advanced microsurgery techniques are being introduced in Korea to precisely define tumor boundaries and minimize damage to surrounding tissues.
Korean oncologists are actively introducing targeted therapies and immunotherapy to treat melanoma. These innovative techniques target specific molecules or cells identified in the tumor, providing more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Consideration of the genetic characteristics of the patient and the tumor has become a key aspect of melanoma treatment in Korea. Genetic diagnostics can identify specific mutations to help select the most effective and personalized approach to therapy.
Oncology treatment in Korea includes not only fighting the disease itself, but also a systematic approach to rehabilitation. Specialists provide comprehensive patient support, including physical therapy, psychological support and adherence to a consistent recovery plan.
Korean medical centers actively involve patients in clinical trials, introducing new treatments and evaluating their effectiveness. This provides patients with access to cutting-edge therapies under investigation.
In recent years, Korea has been actively introducing artificial intelligence technology in cancer diagnosis. Machine learning systems are helping doctors to analyze images and data more accurately, which is contributing to earlier detection and effective treatment of melanoma.
The medical field is constantly changing, and doctors in Korea are actively involved in continuing education programs and international medical conferences. This allows them to keep abreast of the latest trends in oncology and introduce new treatments.
In addition to treatment, an important aspect of melanoma control in Korea is the prevention of the disease and recurrence. Organizations conduct public campaigns to raise awareness of risk factors and the need for regular check-ups.
 Neurofibroma treatment in Korea
Neurofibroma treatment in Korea
A neurofibroma is a tumor that develops from nerve cells and can occur in various parts of the body. This rare form of tumor disease requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment.
The disease may be associated with genetic mutations, particularly mutations in genes responsible for regulating cell growth. For example, a better known disease is neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) caused by mutations in the NF1 gene.
Some cases of the disease may be coincidental and not related to heredity. They can occur due to random genetic changes in a person’s body that are not related to inheritance.
Some people have an increased risk of developing cancer because of a family history of the disease. If parents have the disease, the likelihood of passing the mutated gene to offspring increases.
Accurate diagnosis plays a key role in the effective treatment of the disease. Doctors typically use a variety of examination techniques including medical history, physical examination, computed tomography (CT) scan, and magnetic resonance imaging. A biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
In some cases, doctors perform surgery to remove the tumor. However, it is important to consider the location and size of the tumor, as well as its impact on surrounding tissues and organs. Doctors strive to minimize damage to healthy tissue during the tumor removal process.
Radiation method shows the most effective result of oncology treatment. With the use of advanced technology (radiation therapy) with intensity modulated dose (IMRT) using linear gas pedals, doctors can more precisely target the neoplasm while minimizing the impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
For common or complicated forms, chemotherapy may be required. The development of new drugs and therapeutic approaches that target the molecular targets of the tumor is opening new horizons in the treatment of this disease.
Research is actively underway to identify new therapies and improve outcomes. Molecular and genetic screening helps to understand the biological features of the tumor, which can lead to the development of personalized therapies.
 Neuroblastoma treatment in Korea
Neuroblastoma treatment in Korea
Neuroblastoma is a tumor that develops from nerve cells and can affect different parts of the body, most commonly found in children. However, modern medicine offers new perspectives for the treatment of this disease. In recent years, Korea has become one of the leading countries in medical science and technology, providing innovative treatments for the disease.
Advanced diagnostic techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are widely used in Korea. This allows doctors to pinpoint the exact location and stage of tumor development, which is important for choosing the best treatment method.
South Korea used advanced treatment methods such as surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy. Particular attention is paid to an individual approach to each patient, which allows to maximize the effectiveness of the fight against oncology.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is carried out by a team of highly qualified specialists: surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, observers. This multidisciplinary approach allows us to create optimal conditions for successful treatment and rehabilitation of patients.
Korean medical facilities provide modern facilities for patients that include comfortable tents, modern equipment and infrastructure. This allows for faster self-healing and overall sensitivity in patients.
Korea is actively pursuing research and economic trials to develop new therapies and technologies. This ensures that treatment methods are constantly updated and improved.
Korea is developing specialized centers in the region that have the expertise and resources to provide more effective treatment. These centers provide highly trained professionals and advance equipment, setting the stage for the best possible outcome in each case.
Korean medical institutions are actively collaborating with colleagues around the world to disseminate experience and best practices in treatment. This international exchange helps to enrich knowledge and improve patient outcomes in Korea and beyond.
Oncology treatment in Korea constitutes the entire field of medical research and practice. Modern diagnostic techniques, advanced treatment technologies, teamwork among specialists and active participation in research make Korea a key player in the region with this complex disease. This multifaceted approach opens new horizons for effective treatment and gradual progress in patient recovery.
 Treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Korea
Treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Korea
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) is a group of advanced cancers of the lymphatic system that can affect lymph nodes, organs, and tissues. Treatment of this type in South Korea differs from previous research methods, multimodal approach and focus on personalized treatment.
Chemotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment for this disease. Patients may be offered different protocols depending on the type and stage of cancer. In Korea, innovative chemotherapy regimens can improve the effectiveness of treatment.
Drugs targeting molecular targets in lymphoma cells represent a promising approach to individuals. They can provide more precise and effective targeting of cancer cells by minimizing mutational effects.
In some cases of NHL, bone marrow or stem cell transplantation may be preferred to restore healthy cells after intensive chemotherapy.
In addition to active treatments, rehabilitation and psychological support to manage the effects of treatment are mandatory elements of patient care.
In South Korea, patient care is not just limited to gentle treatment. Physicians and medical staff maintain high standards of care and provide patients with comfort and understanding during difficult periods of treatment.
Many medical centers in South Korea actively collaborate with global clinics and research centers, learning from experience and advanced treatment methods.
South Korea is renowned for its efficient healthcare logistics. Patients receive high quality care, from quick diagnosis to effective treatment.
Doctors and staff observe the cultural characteristics of each patient and create an individualized treatment plan, taking into account not only medical aspects, but also psychosocial and spiritual factors.
Treatment of the disease in South Korea is different not only for the patient himself, but also for his family. Providing educational programs and group sessions helps family patients cope with challenges and understand the treatment process.
Oncology treatment in South Korea provides patients with unique benefits based on advanced technology, high standards of medical care and customized treatment. These factors, combined with cultural sensitivities, make South Korea an attractive look for treating the disease.
 Adenocarcinoma treatment in Korea
Adenocarcinoma treatment in Korea
Adenocarcinoma, a type of tumor that develops from glandular cells, is a dangerous disease that requires high-tech and advanced treatment. In South Korea, the medical system is known for its advanced level and comprehensive approach to cancer, making the country one of the leaders in adenocarcinoma treatment.
The process of treating the disease begins with an accurate diagnosis. Korea uses advanced technologies such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET scan), providing high sensitivity in the detection and evaluation of tumor masses.
Effective treatment of the disease requires the interaction of specialists from different fields – oncologists, surgeons, radiation therapists, geneticists and others. Multidisciplinary teams provide a comprehensive exposure to the tumor and allow for optimal treatment options.
Modern surgical techniques in Korea include the use of robotic systems for minimally invasive surgeries. This ensures accuracy, reduces trauma and shortens recovery time after surgery.
Oncology treatments often include Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) and 3D conformational radiotherapy, which aim to target cancer cells in a targeted manner, minimizing the impact on healthy tissue.
Many medical facilities in Korea are actively involved in research and clinical trials, giving patients access to the latest treatments under development.
Future treatments for adenocarcinoma include a better understanding of the genetic mutations underlying this type of cancer. This allows the development of personalized therapies that target specific molecular targets.
The research aims to develop new targeted drugs that provide more effective tumor growth suppression with minimal side effects.
The development of robotic systems for surgical procedures promises even greater precision and less trauma, which shortens the recovery period of patients after surgery.
Advancing medical technologies, such as telemedicine and mobile apps for monitoring patient health, are improving the accessibility and effectiveness of care.
All of these directions indicate that the future of oncology treatment in Korea will focus on an in-depth understanding of the biology of the disease, a personalized approach, and efforts to improve the quality of life of patients after completion of active treatment. The collaborative efforts of the scientific community, physicians and patients will be key in making new advances in the fight against this type of cancer.
 Glioblastoma treatment in Korea
Glioblastoma treatment in Korea
Glioblastoma is a malignant tumor that often develops in the brain. It is one of the most aggressive forms of cancer, requiring a comprehensive approach and advanced treatment methods. In South Korea, where the medical system is renowned for its technological advances, the treatment of the disease includes a number of innovative methods.
Research into targeted therapies aims to use drugs that directly target molecular abnormalities in cells. Immunotherapy also represents a promising approach by stimulating the immune system to fight cancer cells.
A variety of chemotherapeutic protocols are used to suppress tumor growth. Research is underway on new drugs that may improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Artificial intelligence is being actively applied to analyze medical data and images to help doctors identify tumor characteristics faster and more accurately and develop individualized therapeutic regimens.
Fighting the disease in Korea is not limited to current treatments. Research and development of new technologies offer hope for better control and treatment of this aggressive cancer.
Existing research focuses on understanding the genetic mutations that lead to the development of cancer. This may lead to the development of more effective approaches using drugs that target specific molecular abnormalities.
Immunotherapy remains the focus of researchers. Experiments with vaccines that activate the immune system to attack cancer cells represent a promising method of treating the disease.
The development of new chemotherapeutic drugs that can more effectively penetrate the tumor and destroy cancer cells is the subject of active research.
The integration of new neuromonitoring technologies to better define tumor margins and avoid damage to healthy tissue during surgical removal is becoming an important area of focus.
Participation in clinical trials and collaboration with international medical centers increase access to advanced therapies and provide an opportunity for rapid adoption of new technologies.
 Glioma treatment in Korea
Glioma treatment in Korea
Glioma, a tumor that develops in the brain tissue, is a complex and serious disease that requires highly technical and individualized treatment. In South Korea, the medical system is known for its advanced level of excellence, giving glioma patients access to advanced therapies and optimal treatment outcomes.
Treatment of the disease in Korea begins with a highly accurate diagnosis. Modern techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) allow doctors to get a detailed picture of the location and nature of the tumor.
Treating oncology requires the collaborative efforts of various medical specialists, including neurosurgeons, oncologists, radiation therapists, and geneticists. Multidisciplinary teams provide a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Modern surgical techniques using robotic systems allow for precise tumor removal with minimal damage to healthy tissue. This promotes faster recovery and reduces the risks of postoperative complications.
The use of advanced radiation therapies such as Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) and chemotherapy drugs helps inhibit the growth and development of cancer cells.
Targeted therapies that target specific molecules in cancer cells provide effective treatments with minimal side effects.
Doctors in Korea have a wealth of experience and a high level of professionalism. Glioma treatment is based on the individual characteristics of the patient, taking into account their genetic background and the peculiarities of the disease.
In some cases where the treatment of the disease involves bone marrow transplantation, Korea provides advanced techniques to ensure the success of this procedure.
Glioma treatment in Korea is a balanced and advanced approach that combines technological expertise, high professionalism and concern for the psychological well-being of patients. This ensures not only effective treatment, but also an improved quality of life for patients facing glioma.
 Treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Korea
Treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Korea
Hodgkin’s lymphoma, a rare form of lymphoma that has remained under the scrutiny of the medical community because of its complexity and diversity. In today’s medical society, particularly in South Korea, where innovation and advanced treatment methods have been adopted to serve patients, thorough research and an integrated approach are becoming key aspects in the fight against this type of cancer.
The disease is characterized by changes in the cells of the lymphatic system resulting in the formation of special cells. This understanding allows physicians to accurately diagnose and classify disease types to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Diagnosis of the disease in South Korea incorporates advanced technologies such as PET scans, MRI and biopsy to ensure that the stage of the disease is more accurately determined and the best treatment approach is planned.
Treatment of the disease requires coordination between various specialists, including hematologists, oncologists, radiation therapists, and surgeons. Multidisciplinary teams guarantee a comprehensive and effective approach.
Modern chemotherapeutic regimens, including combinations of different drugs, as well as spot and intensive radiation therapy, can successfully manage tumors and reduce the risk of recurrence.
In some cases, especially relapsed or high-risk cases, bone marrow transplantation may be considered as a treatment option to provide replacement of damaged cells.
The use of targeted drugs that target specific molecules in cells provides new treatment prospects with fewer side effects.
Collaboration between medical institutions in Korea and global centers can enrich the exchange of knowledge and experience, contributing to the development of advanced treatment methods.
All of these trends indicate that the future of oncology treatment in Korea will focus on innovation, personalized approach, and a commitment to improving treatment outcomes. The collaborative efforts of the scientific community, physicians and patients are driving progress in the treatment of this rare but highly concerning disease.
 Leukemia treatment in Korea
Leukemia treatment in Korea
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood that requires a highly specialized and integrative approach to treatment. South Korea provides innovative treatments for leukemia tailored to the individual patient.
Leukemia treatment in Korea begins with a thorough diagnosis, including extensive genetic testing. This allows the exact type and subtype of leukemia to be determined, which is important for choosing the best treatment strategy.
Medical centers in Korea form multidisciplinary teams including hematologists, oncologists, geneticists and other specialists. This provides a comprehensive assessment and allows the best treatment plan to be developed.
Chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, immunotherapy and targeted therapies are all used in treating the disease in Korea. The use of innovative methods can increase the effectiveness of treatment and improve prognosis.
In cases where the disease requires bone marrow transplantation, Korea provides high-tech services using modern compatibility techniques and advanced transplantation technologies.
In Korea, immunotherapy is widely used to activate the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer cells. This includes the use of monoclonal antibodies and other innovative approaches.
Many medical centers in Korea are actively involved in clinical trials, giving patients access to new drugs and therapeutic strategies under development.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is based on the individual characteristics of each patient. This includes taking genetic traits and response to therapy into account, allowing for personalized treatment plans.
Robotic surgical systems are used in surgeries when necessary. This allows for precise and minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery time and risks to the patient.
After active treatment is completed, rehabilitation and psychological support are important components. This is aimed at the patient’s recovery and overcoming emotional difficulties.
Oncology treatment in Korea is tailored to the individual needs of the patient. Flexibility and consistency in the treatment plan ensures adaptation to the dynamics of the patient’s changing condition.
Treating the disease involves not only fighting the tumor, but also maintaining quality of life after treatment. Advanced rehabilitation programs help to restore the patient’s physical and psychological fitness.
 Lymphoma treatment in Korea
Lymphoma treatment in Korea
Lymphoma, a group of cancers involving the lymphatic system, requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment. In South Korea, where the medical system is at the forefront, patients with this disease are provided with innovative therapies to ensure a high chance of successful recovery.
Oncology treatment in Korea begins with accurate diagnosis. Modern techniques include CT and MRI scans, positron emission tomography and genetic tests to determine the type and stage of the disease.
Medical teams in Korea consist of various specialists such as hematologists, oncologists, surgeons, and radiologists. This multidisciplinary approach provides a comprehensive evaluation and the best treatment plan.
The use of advanced chemotherapy, as well as targeted drugs that target specific molecules in cancer cells, increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces side effects.
In cases where the disease requires bone marrow transplantation, advanced techniques such as compatibility and careful preparation for the procedure are utilized in Korea.
Immunotherapy, which activates the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells, plays an important role in lymphoma treatment in Korea. Where surgery is necessary, doctors in Korea use modern techniques, including minimally invasive procedures and robotic surgeries.
Many medical facilities in Korea are actively involved in clinical trials, giving patients access to advanced treatments and new drugs.
Oncology treatment involves not only physical recovery, but also care for the psychological and social well-being of patients. Support programs help you cope with emotional and social challenges.
After active treatment is completed, comprehensive rehabilitation programs are provided to restore physical activity and improve quality of life.
Treatment of the disease in Korea combines advanced therapies, high-tech equipment and a personalized approach to provide patients with the best chance of recovery and improved quality of life.
 Squamous cell cancer treatment in Korea
Squamous cell cancer treatment in Korea
Squamous cell cancer, which is a form of epithelial tissue oncology, requires special attention and effective treatment. In Korea, thanks to its advanced medical system, specialized programs and technology provide patients with state-of-the-art treatments.
The initial phase of treatment begins with accurate diagnosis and determining the stage of the disease. Korea uses advanced educational techniques including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) to more accurately determine the nature of the tumor and its spread.
Surgical treatment is one of the key steps. Doctors in Korea are skilled in innovative surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures and robotic surgeries. This allows the tumor to be removed precisely while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
The use of radiation therapy to eliminate squamous cell cancers involves carefully constructed programs designed to destroy cancer cells and prevent their further growth. This refers to a shift in modern technologies such as variable modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
Depending on the stage and course of the cancer, patients with cancer may be offered systemic treatment, including chemotherapy and targeted therapies. This is aimed at inhibiting the growth and multiplication of cancer cells.
Immunotherapy shows high results in controlling the disease. Activation of your own immune system is done more effectively with cancer cells.
Genetic testing is available to patients if they have conditions that affect the development and treatment of cancer. This allows you to personalize your approach to individuals and identify more effective strategies.
After completion of the active phase of treatment, patients are provided with comprehensive rehabilitation programs, including physical therapy, psychological support and assistance in restoring normal life activities. There are also educational programs for patients and family members about the disease, symptoms.
 Treatment of sarcoma in Korea
Treatment of sarcoma in Korea
Korean medical centers have highly skilled teams of doctors specializing in oncology. Experts from different regions collaborate to develop a treatment plan that provides the highest standard of care.
Active early detection and screening programs play an important role in the carcinoma region. Regular medical examinations and modern techniques help detect tumors in their early stages, which improves prognosis and allows for better treatment.
Korea is implementing an integrated approach to carcinomas, combining advanced surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and other innovative technologies. This allows for the best individualized treatment plan for each patient.
Korean medical centers have successfully used robotic systems to perform cancer surgery. These systems utilize more precise and less invasive procedures, resulting in faster patient recovery and reduced surgical risk.
In the case of carcinoma, the second role includes targeted therapy and immunotherapy. The essence of the technique is the administration of drugs directed at individual molecular targets in cancer cells, as well as activation of the immune system to fight tumors, allows to increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce residual effects.
Korea is actively engaged in research and testing of new treatments for carcinoma. Patients may have access to advanced technologies and drugs under development.
Modern medical centers in Korea are equipped with advanced technology and provide a high level of services. This includes multidisciplinary clinics, specialized departments and high-tech operating units.
After completing the active phase of treatment, patients have access to rehabilitation programs that help restore physical activity, psychological well-being and social adaptation.
Some medical developments in Korea are successfully implementing artificial intelligence technologies to analyze medical data and determine the best treatments based on large amounts of information.
Pediatric sarcoma emphasizes specialized programs including multidisciplinary methods, psychological support and play therapy.
Korea has become one of the leaders in medical tourism, attracting patients from all over the world with its high quality medical care and advanced cancer treatments.
 Carcinoma treatment in Korea
Carcinoma treatment in Korea
Korea is famous not only for its rich culture and history, but also for its advanced medical system, which is actively innovating in the treatment of cancer, including carcinomas.
Korea has an integrated approach that combines advanced surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and other innovative technologies. This allows for the best individualized treatment plan for each patient.
Korean medical centers have successfully used robotic systems to perform oncology surgery. These systems utilize more precise and less invasive procedures, resulting in faster patient recovery and reduced surgical risk.
In the case of carcinoma, the second role includes targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Using drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells, as well as activating the immune system to fight tumors, can improve treatment efficacy and reduce residual effects.
Early detection and screening programs play an important role in treating the disease. Regular medical examinations and modern techniques help detect tumors in their early stages, which improves prognosis and allows for better treatment.
Korean medical centers have highly skilled teams of doctors specializing in oncology. Experts from different regions collaborate to develop a treatment plan that provides the highest standard of care.
Korea is actively engaged in research and testing of new treatments for carcinoma. Patients may have access to advanced technologies and drugs under development.
In addition to physical treatment, psychological support for patients and their families is emphasized. Psychotherapists and social workers provide assistance in coping with the stress of diagnosis and treatment.
Modern medical centers in Korea are equipped with advanced technology and provide a high level of services. This includes multidisciplinary clinics, specialized departments and high-tech operating units.
After completing the active phase of treatment, patients have access to rehabilitation programs that help restore physical activity, psychological change and social adjustment.
Korea has become one of the leaders in medical tourism, attracting patients from all over the world with its high quality medical care and advanced cancer treatments. Carcinoma treatment in Korea is characterized by standard quality, advanced technology and a comprehensive approach to patient care.
 Vocal cord cancer treatment in Korea
Vocal cord cancer treatment in Korea
Vocal cord cancer is a disease that can affect the voice and sound-producing structures of the larynx. Understanding the symptoms and causes of these cancers is critical for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Smoking is one of the major risk factors for developing the disease. Frequent and/or excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of the disease. As we age, the likelihood of developing cancer increases, especially after the age of 40 – 45.
Persistent problems with acidity and gastroesophageal reflux can trigger the onset of the disease. Heredity can also play a role in cancer development, especially if there is a family history of cancer.
Hoarseness, long-term changes in tone of voice, or loss of voice may be the result of problems with the vocal cords. Difficulty or pain in swallowing, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat.
South Korea’s cutting-edge treatments for cancerous ligament voices are being utilized. The Korean medical system combines innovative approaches, modern technology and a high level of medical staff.
Radical laryngectomy consists of surgical removal of the larynx during surgery may be used in cases of massive selective rectal ligament. In some cases, minimally invasive endoscopic laryngectomy is used.
Drugs destroy or slow the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be used before or after surgery.
After surgery, especially when the vocal cords are removed, the main role is a rehabilitation program and sessions with a speech therapist to restore voices and communication skills.
Korea has become a leading tourist destination due to its high-tech medical infrastructure and quality services. Many international patients choose Korea for oncology treatment, gaining access to advanced techniques.
The use of radiotherapy, modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or proton beam radiotherapy, allows the rays to be more precisely applied to the neoplasm without affecting healthy tissue.
 Urethral cancer treatment in Korea
Urethral cancer treatment in Korea
Urethral oncology refers to rare diseases that develop in the urethra. Women after the age of 40 are usually at risk. At the slightest suspicion, it is necessary to consult a doctor for further diagnosis.
The doctor performs a visual examination of the external area of the ureters to detect the species. A cystoscopy is a procedure in which the doctor inserts a flexible tube with an electric light (cystoscope) into the urethra to visually examine the inside walls of the urethra and bladder.
If suspicious masses are identified during cystoscopy, biopsy material may be taken. This allows the lab to determine if the mass is malignant.
Ultrasound waves are used to produce images of internal organs. Ultrasound can help assess the size and structure of the topography and apply it to the surrounding tissues.
PET scans use radioactive markers to detect areas with increased cell activity, which can lead to cancer and metastasis.
If suspicious changes are detected in the ureter or bladder, the doctor may take a tissue sample for further examination under a microscope. This can ensure the presence of malignant cells.
CT scans provide more detailed images of internal organs and allow you to assess the shape and spread of the tumor. MRI provides detailed images of soft tissue and tissue can be a signal to determine structural information about the tumor.
PET scans use radioactive markers to detect areas of increased cell activity, which can lead to cancerous lesions.
Many medical institutions in South Korea have specialized departments and centers, specializing in research and finding the latest methods and drugs.
Korean medical institutions actively participate in global research projects, which provides access to the latest treatments and technologies.
Treatment is tailored to the stage of the disease. This allows you to combine different techniques to achieve the best results. Utilizing advances in science to develop new diagnostic and therapeutic methods that facilitate the transition from research to clinical practice.
Treatment of urothelial cancer in South Korea is carried out using advanced methods and tailored to each patient. This multifaceted approach ensures improved treatment efficacy and adherence to patient prognosis.
In some cases, radical resection of the urethra is performed. This is the surgical removal of the affected area of the ureter. If the cancer has spread, surrounding tissue and lymph nodes may also be removed.
 Testicular cancer treatment in Korea
Testicular cancer treatment in Korea
Testicular cancer is a disease that affects the male sex gland, testicles and scrotum. Understanding the causes, early symptoms, and current treatments for this disease is critical to its effective control.
Heredity may play a key role in the development of the disease. If there are male relatives in the family who have had this disease, it is necessary to monitor the state of health.
Failure of the testicles to fall into the scrotum (cryptorchidism) increases the likelihood of developing cancer in the future. Even one undescended testicle can trigger the disease. Men with Klinefelter syndrome, characterized by adult X chromosomes, are also at risk.
Some conditions such as non-infectious epididymitis (inflammation of the testicular appendage) or varicocele (varicose veins of the testicle) may also be causes.
Treatment in Korea often includes rehabilitation programs to recover from treatment and improve patients’ quality of life. An important aspect is an individual approach to each patient and the use of advanced technologies in medical practice.
In South Korea, comprehensive programs are often used that combine different treatment modalities and provide a multidisciplinary approach.
It is worth noting participation in medical research that allows patients access to new treatments under development.
Methods that stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells are actively used. It is possible to use drugs that target specific molecular targets in cells.
Radical orchidectomy is the surgical removal of the testicles. If the disease has spread, the surgeon may also remove lymph nodes. It is possible to use drugs aimed at destroying cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be used both before and after surgery.
Radiation therapy is necessary to destroy cancer cells. It may be part of a comprehensive treatment or used after surgery. Robotic systems are used for more precise and less invasive surgical procedures.
Experimental methods, including immunotherapy and targeted therapies, are being investigated to improve treatment efficacy.
 Treatment of tonsil cancer in Korea
Treatment of tonsil cancer in Korea
Tympanic oncology is a malignant mass affecting the root of the tongue, the palatine tonsils, the back of the pharynx, and the palatine glands. A malignant tumor does not have clear boundaries. Its difference lies in its rapid development and the appearance of metastases.
Smoking and tobacco use are possible risk factors for cancer. Tobacco smoke contains many carcinogens that can damage tonsil cells and surrounding tissues.
Frequent and/or excessive alcohol consumption has also been linked to the risk of developing pharyngeal cancer. The combined effects of tobacco and alcohol can be particularly dangerous.
Some cases of the disease increase with infection with the HPV virus, especially HPV types 16 and 18. This virus is spread sexually and can be a risk premise for developing the disease.
Heredity may play a role in increasing the risk of developing cancer. Certain genetic mutations can increase susceptibility to cancer.
One of the most obvious manifestations is pain or discomfort in the throat area, which can worsen when eating or talking. An increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes can be a sign that cancer cells have spread to the surrounding tissue.
Hoarseness, changes in voice timbre, or difficulty speaking may be due to damage to the vocal cords. Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) may occur due to narrowing of the pharyngeal tumor.
The disease can cause swallowing and digestive difficulties, which negatively affects the quality of life of patients. In some cases, surgery may be used for treatment due to the global localization and spread of the tumor, which may limit its use.
Korean medical institutions are actively innovating immunotherapy for cancer treatment by stimulating the patient’s own immune system to fight the tumor.
Patients may have access to cutting-edge medical research that provides the opportunity to utilize new treatments that are under development.
Rehabilitation programs in Korea include physical and speech therapy to help patients recover from treatment. Korean medical facilities adhere to these high standards, and treatment procedures are carried out in accordance with international standards. Patients traveling to Korea for treatment usually receive a high level of hospitality and care from both medical staff and service.
These features make Korea an attractive destination for cancer treatment, and many patients choose this country in search of effective and personalized treatment in the fight against cancer.
 Prostate cancer treatment in Korea
Prostate cancer treatment in Korea
Prostate oncology is a malignant neoplasm that develops in the prostate, the glandular gland of the male reproductive organ. This form of the disease is often found in men.
The disease often develops slowly remains inside the gland without causing side effects or sensations. In some cases, the disease can become aggressive and spread beyond the prostate, including the lymph nodes or bones, causing metastasis.
Prostate cancer depends on male sex hormones such as testosterone for its growth. Therefore, it is necessary to control hormones in this case together with the attending physician.
Patients often have difficulty initiating urination. Periodic interruptions in urination are noted. The presence of blood in semen or urine can be one of the signs of the onset of the disease. Decreased semen volume during ejaculation may be the result of a tumor blocking the urethra.
Erectile dysfunction, decreased interest in sex and other sexual problems can occur due to the disease. If metastases are present, pain in the pelvic bone and urinary problems may occur.
The disease is most often diagnosed in men after the age of 50. It is worth noting that African Americans are more likely to suffer from the disease.
The presence of certain genetic changes may increase susceptibility to disease incidence. Treatment is tailored to each patient, age, well-being, stage and presence of other diseases.
In Korea, the use of effective methods of targeted therapy and immunotherapy, which contribute to the rapid destruction of cancer tissue and activation of the immune system, is in particular demand. It is possible to take hormones to reduce male sex hormones that stimulate tumor growth.
These features come together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that is thus tailored to the patient’s individual needs and the characteristics of their disease. Supporting patients and their loved ones through the treatment and recovery process is also an important element.
 Bronchial cancer treatment in Korea
Bronchial cancer treatment in Korea
Bronchial oncology is a serious disease that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to diagnosis and treatment. The disease can occur at any age and is independent of a person’s gender.
One of the major risk factors for developing the disease is tobacco smoking. Smoking leads to constant exposure of lung tissue to carcinogens, causing mutations in cells and promoting the development of tumors.
People who are around smokers are also at an increased risk of developing lung cancer due to inhaling harmful substances in tobacco smoke. Hereditary factors may also play a role in the occurrence of lung cancer. Some genes associated with cancer risk can be passed from generation to generation.
Diagnosis of lung cancer involves a variety of techniques and procedures to accurately determine the exact type of tumor, its stage and spread, allowing the best individualized treatment plan to be developed.
The doctor performs a thorough physical examination and collects a medical history, including information about symptoms, risk factors (e.g., smoking, occupational exposures), and heredity.
A CT scan provides a more detailed image of the lungs and surrounding tissues, allowing you to determine the size of the tumor and its structure. Examination of the bronchi using a thin, flexible tube with a camera at the end. Allows the doctor to take a sample of tissue or fluid for biopsy. Analyzing the structure of cells and tissues under a microscope to accurately determine the type of cancer and its characteristics.
A very important step is to determine the presence of markers and biomarkers that may indicate the presence of cancer and its characteristics. Taking a sample of fluid from the pleural cavity to assess the possible presence of cancer cells.
Treatment of bronchial oncology involves a combined approach using modern methods of medical science and technology. The use of chemotherapy and drugs that target molecular targets in the tumor to suppress and kill cancer cells.
An important step is to determine the genetic characteristics of the tumor in order to select the optimal therapy. Surgical removal of the tumor or even the lung can be used in the early stages of lung cancer.
Patients in South Korea can have access to state-of-the-art treatments through participation in clinical trials, which allows for the use of the latest methods and technologies.
 Salivary gland cancer treatment in Korea
Salivary gland cancer treatment in Korea
Salivary gland cancers are among the rare and poorly understood types of cancer. The disease is most often diagnosed in people over the age of 50. As the disease progresses, large glands are affected.
One of the first signs may be the detection of lumps or swelling in the salivary gland area, which can be seen by palpation. Pain in the salivary gland area, especially when eating or talking, may be one of the first symptoms.
The disease can lead to difficulty swallowing and changes in the sound of speech. The appearance of blood in saliva or in secretions from the salivary glands requires immediate attention and examination. Involuntary weight loss for no apparent reason may be associated with salivary gland oncology. General fatigue and weakness may be a consequence of the progression of the cancer process.
Prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Hereditary factors may increase the risk of developing salivary gland cancer.
Some viruses, such as the Epstein-Barr virus, can increase the risk of developing tumors. Some studies suggest that women may have a higher risk of developing the disease compared to men.
Cancer treatment in Korea is carried out using advanced methods and technologies. Many medical facilities in the country have a high level of medical expertise and equipment, making Korea a popular destination for cancer treatment.
Surgery remains one of the mainstay treatments for oncology. Korea uses advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive surgeries and robotic surgical systems.
Using advanced radiation therapy techniques such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and particle (proton) therapy to precisely irradiate tumors with minimal impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
Using information on tumor genetic characteristics to select the best therapeutic approaches. Comprehensive rehabilitation support after the completion of active treatment, including physical therapy, speech therapy and psychological support.
Treatment in Korea has a high level of quality, so patients can access advanced methods and technologies that provide effective and personalized cancer treatment.
 Throat cancer treatment in Korea
Throat cancer treatment in Korea
Throat oncology is among the diseases that can significantly alter a person’s condition and is very dangerous. At the first symptoms, you should see a specialist to establish a diagnosis.
One of the major risk factors for developing the disease is smoking. Harmful substances in tobacco can cause mutations in throat cells, promoting the development of tumors.
Frequent and excessive alcohol consumption is also associated with an increased risk of developing the disease. The combination of smoking and alcohol consumption may increase this risk.
Some types of HPV may be linked to the development of cancer. This factor is particularly important in HPV-associated laryngeal and tonsil cancers.
Hereditary factors may also play a role in causing the disease. If family members have a history of throat cancer, the risk increases. Exposing your throat to certain chemicals can also have a negative effect.
One of the early symptoms of the disease may be a sore throat or neck that does not go away after treatment with conventional medications.
A persistent cough, especially with blood or a change in the timbre of the voice, can be a sign of throat cancer. Difficulty swallowing, dysphagia, can occur due to the presence of a tumor in the throat creating an obstacle to the free passage of food.
Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or settling of the voice, may be associated with illness. Oncology can cause swelling in the neck area as well as enlarged lymph nodes. Weight loss that is not related to diet or physical activity may be a sign of a neglected stage of the disease.
Throat cancer can affect different parts of the larynx, pharynx, tongue, and tonsils. Depending on the exact location of the tumor and its type, symptoms and treatments may vary.
The doctor performs an external examination and palpation of the cervical lymph nodes to look for swelling or increased size. An examination using an endoscope allows the doctor to examine the internal structures of the throat, tongue and pharynx. The structure of the cells is analyzed under a microscope to help establish an accurate diagnosis.
 Tongue cancer treatment in Korea
Tongue cancer treatment in Korea
Tongue oncology poses a serious risk to humans. Understanding the characteristics of this type of disease allows for success in the treatment program.
The initial stages of tongue cancer are characterized by pain and discomfort in the tongue area. The pain may be localized and spread to adjacent areas.
The formation of ulcers on the tongue that do not heal for a long time may be a sign of the disease. The disease can cause swallowing difficulties, especially if the tumors spread to neighboring organs, such as the larynx. Speech is most often altered because the tongue is affected.
Treatment of the disease usually requires a multidisciplinary approach and rehabilitative measures.
Surgery is often used to remove cancerous growths on the tongue. This refers to the partial or complete removal of the tongue. The stage of the disease is taken into account. Radiation therapy is used to eliminate cancer cells, especially if the tumor cannot be completely removed surgically.
After completing active treatment, patients undergo rehabilitation programs including physical, occupational and speech therapy to restore functionality and improve quality of life.
The diagnosis can have a serious impact on the patient’s psychological state. Counseling by a psychologist plays an important role in alleviating emotional distress and adapting to a new situation.
Korean medical facilities are actively utilizing the best diagnostic techniques to detect the disease in its early stages. High-resolution endoscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography may be used.
Immunotherapy and targeted therapies targeting specific molecular targets in the tumor represent advanced therapies available in Korea.
After treatment is completed, patients receive comprehensive rehabilitation support, including physical therapy, speech therapy and psychological support to restore language functionality and adapt to new environments.
 Kidney cancer treatment in Korea
Kidney cancer treatment in Korea
Kidney cancer, also known as renal carcinoma, is a serious cancer that can have a significant impact on health. Understanding the symptoms and causes of this condition is key to early diagnosis and effective treatment.
One of the most characteristic symptoms of kidney cancer is lower back pain. This pain may be aching and felt in one side of the abdomen.
The presence of blood in the urine, medically known as hematuria, can be a sign of disease. Blood may give the urine a pinkish or reddish color.
Patients with cancer may experience increased urination. The disease can cause weight loss and loss of appetite. These symptoms may be related to a general health disorder. The appearance of fatigue and weakness that is not due to physical activity may be a sign of a neglected stage of the disease.
Smoking is a risk factor for developing cancer. Tobacco contains substances that can damage kidney tissue. Patients with high blood pressure have an increased risk of developing the disease.
Hereditary factors may play a role in the onset of the disease. Certain genetic syndromes are associated with increased risk. Overweight and obesity also affect the course of the disease.
Early diagnosis plays a key role in successful treatment and increased chances of recovery. Patients who notice symptoms such as lower back pain, blood in the urine, or rapid urination should see a doctor for diagnostic tests, including kidney evaluation with ultrasound, CT or MRI.
It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, get regular medical checkups, especially if risk factors are present, and live a responsible lifestyle to prevent the disease. The earlier the disease is identified, the more successful its treatment can be.
Leading medical facilities in Korea are equipped with state-of-the-art equipment to accurately diagnose oncology. Korean surgeons specialize in minimally invasive surgical techniques to remove kidney tumors. Laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgeries offer faster recovery and lower risk of complications.
 Oral cancer treatment in Korea
Oral cancer treatment in Korea
Mouth cancer is a cancer that affects different parts of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, gums, and palate. This diverse disease is a serious health threat, and understanding its characteristics and early warning signs is key to successful treatment.
Korean medical facilities are actively using laparoscopy, robotic surgery and other minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery after surgeries.
Advanced radiation therapy techniques such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and radiation therapy using linear gas pedals with high precision are widely used in Korea.
Korean clinics customize chemotherapy drugs according to the patient’s characteristics and type of cancer.
The use of molecular drugs is a treatment that targets specific molecular targets in cancer cells, can increase the effectiveness of therapy and reduce side effects.
Korea is known for its advanced medical equipment, high standard of physician training and strong emphasis on innovation in oncology. These factors make Korea’s medical system attractive to patients seeking advanced cancer diagnosis and treatment.
In Korea, comprehensive, multidisciplinary rehabilitation programs that include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and psychological support are widely used. This approach aims to ensure that the patient’s functionality is fully restored.
Patients who have undergone treatment may experience physical limitations. Physical therapists in Korea design customized recovery programs, including exercises to improve strength, mobility and coordination.
Occupational therapists help patients regain everyday skills such as dressing, feeding, and grooming. They also teach the use of adaptive devices and technology to increase independence.
For patients who have undergone treatment for this condition, speech therapists help restore and improve speech and communication. This includes the use of prosthetics and learning alternative methods of communication.
Cancer and its treatment can have a significant impact on a patient’s psychological well-being. Psychologists in Korea provide support and counseling to help patients cope with emotional difficulties, as well as teaching relaxation and stress management techniques.
Special programs are designed for recovery from chemotherapy and radiation therapy, including remedies for side effects such as physical weakness, sleep disturbances and emotional difficulties.
Rehabilitation in Korea covers not only the period after the main treatment, but also in the following years. Patients can receive support and rehabilitation long term to maintain their quality of life.
 Colorectal cancer treatment in Korea
Colorectal cancer treatment in Korea
Colorectal cancer is a serious disease that ranks as the leading cancer worldwide. Korea is renowned for its advanced competitive technologies and innovative treatments for such diseases.
Treatment of the disease in Korea is carried out using advanced methods and technologies, providing patients with a high level of medical care.
Korea uses a multidisciplinary approach that brings together doctors from different specialties – surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, gastroenterologists and others. This allows for an individualized treatment plan, taking into account the characteristics of each patient.
Surgical removal of tumor remnants and diseased tissue is the primary treatment. Korea utilizes advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures that reduce recovery time after surgery.
The use of advanced diagnostic technologies, such as high-resolution endoscopy and CT scans, provides more accurate tumor detection and monitoring of tumor spread.
The use of modern chemotherapy drugs and targeted therapies that target specific molecular targets allows for more effective destruction of cancer cells.
The disease requires comprehensive treatment including surgery, chemotherapy and modern targeted therapies. Regular medical check-ups and symptoms are mandatory factors for early diagnosis and treatment of this type of cancer.
Using external beam radiation therapy to precisely target the tumor minimizes the impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
The use of molecular genetic testing to modify individual tumor characteristics, allowing for a more thorough approach to be chosen for individuals.
After the active phase of treatment is completed, rehabilitation and psychological support programs are conducted to restore physical and emotional well-being.
Treatment of colorectal cancer in Korea is a comprehensive and modern approach focused on maximizing the effectiveness and safety of the tumor, minimizing exposure factors, and ensuring a high quality of life for patients after treatment.
 Ear cancer treatment in Korea
Ear cancer treatment in Korea
Ear oncology includes different types of cancer – of the external ear canal, middle ear and inner ear. Treatment for these types of cancers depends on the type of cancer and how far it has spread.
External ear canal oncology is a rare type of cancer. May manifest as ulcers or neoplasms in the external ear canal. The most common causes include prolonged exposure to UV rays, trauma, chronic infections, scarring, or being in the water.
Middle ear oncology can usually spread to shorter structures. Ear pain may occur and hearing may be preserved. The disease is caused by chronic moderate infections, especially in children, as well as genetic factors.
Oncology of the inner ear begins in the cells of the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for balance. There may be dizziness, but hearing is preserved. Vestibular nerve neuroma can occur due to gene mutation or random genetic changes.
Smoking can be a threat to the development of pathologies of the larynx and ear, including the inner and outer ear canals. Prolonged exposure to chemicals and radiation can increase the likelihood of developing cancer.
Long-term infections, especially viral infections (e.g., human papillomavirus), can increase the risk of cancer. A weak immune system can prevent cancer cells from developing in the body. One of the first signs may be hearing loss or a feeling of a stuffy ear.
Surgical removal of the cancerous tumor is considered the most radical method. It may also be possible to remove part of the organ or vestibular nerve depending on the extent of spread. In cases where surgery results in hearing loss or compromised ear appearance, it is completed with prosthetics. After treatment, it is important to monitor the patient’s condition regularly, including check-ups with the doctor and tests.
Oncology is a serious disease that requires comprehensive and individualized treatment for each individual. Early diagnosis and the use of advanced treatment methods can significantly increase the rate of recovery and health maintenance.
 Lip cancer treatment in Korea
Lip cancer treatment in Korea
Lip cancer is one of the diseases that require attention and competent treatment. Korea utilizes modern and multidisciplinary oncology treatment methods combining advanced medical technologies, innovative approaches and highly qualified specialists.
Early stages of the disease may manifest with ulcers, severe pain, or bleeding that does not heal for extended periods of time. Advanced cases of the disease may be accompanied by swelling, changes in skin color and texture. Changes in sensitivity or numbness in certain areas of the lip are also noted.
The disease can cause painful sensations when eating. Smoking, alcohol consumption, prolonged exposure of the lips to sunlight, and the human papillomavirus (HPV) can increase the likelihood of developing cancer.
The doctor performs a visual inspection of the lip and surrounding tissues to detect changes. He then takes a small tissue sample from the affected area for laboratory analysis. Laboratory testing can accurately determine the type of cancer and its characteristics. Pet scans are needed to more accurately determine metastases and how far the cancer has spread.
Molecular genetic testing is about choosing the best treatment approach given individual tumor characteristics. If cancer cells spread, it is possible to remove the affected lymph nodes and surrounding tissues. Microsurgery is used to precisely repair tissues and organs after tumor removal.
External beam radiation therapy is the targeting of rays to the tumor from the outside using a linear gas pedal. The essence of internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy) is to inject a radiation source directly inside or near the tumor for a more precise effect.
Immunotherapy involves the use of drugs that can unblock the immune system, allowing it to fight cancer cells. Vaccines are used to stimulate the immune system and enhance its response to cancer.
Organ transplants are used when cancer affects organs such as the kidneys or liver. Acupuncture and herbal treatments are used in addition to modern techniques to improve the patient’s overall condition and reduce the side effects of treatment.
Korean medical institutions are actively pursuing these methods with a focus on individualizing treatment and providing a high standard of care for patients.
 Adrenal cancer treatment in Korea
Adrenal cancer treatment in Korea
Adrenal cancer is a rare and poorly understood cancer that affects small glands located above the kidneys. This type of cancer is rare, making it difficult to diagnose and treat due to the lack of widespread experience of doctors.
Some adrenal tumors can produce hormones, which can cause a variety of symptoms associated with an excess of these substances in the body.
Symptoms of the disease can be nonspecific, including high blood pressure, weight loss, abdominal pain, and general weakness, making early diagnosis difficult.
Adrenal oncology can cause excessive release of adrenaline and other hormones, raising blood pressure. Increased production of ACTH (a hormone that stimulates the adrenal cortex) can cause dark skin discoloration, especially in the hands, face, and mucous membranes.
The production of certain hormones can stimulate an accelerated metabolism, resulting in weight loss and appetite loss. An enlarging tumor can cause discomfort and pain in the abdominal area.
Pressure from the tumor on nerve structures in the abdomen can cause vague pain in the back. The disease may be accompanied by anemia and general weakening of the body. Hormone production can affect kidney function, leading to increased frequency of urination.
Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) assess the size and structure of the tumor, as well as possible metastasis. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is used to more accurately assess tumor activity.
Laboratory analysis helps confirm the presence of cancer and determine the type of cancer. Measuring hormone levels helps identify adrenal hyperfunction and tumor type.
Surgical interventions include tumor excision – surgical removal of the tumor and affected tissues, as well as adrenalectomy – removal of the entire adrenal gland, sometimes with part of the surrounding tissues.
Radioablation involves the use of radioactive material to treat tumor remnants after surgery. The use of hormones occurs to compensate for their deficiency after removal of the adrenal gland.
This disease presents a challenge to physicians because of its rarity and difficulty in diagnosis. Nevertheless, innovative treatments and modern technologies in Korea and around the world aim to improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients suffering from this rare disease.
 Nasopharyngeal cancer treatment in Korea
Nasopharyngeal cancer treatment in Korea
Nasopharyngeal oncology is a serious disease that affects the nasal cavities and pharynx. Samsung Korean Medical Center has highly qualified specialists who successfully treat this condition.
Patients primarily experience difficulty breathing due to impaired nasopharyngeal patency. Persistent or private nosebleeds can be a sign of illness. There is also a feeling of pressure in the nose associated with the gain.
Deterioration of the sense of smell or hearing problems may be associated with damage to the structures involved. Pain in the throat, nose, back of the head or ears can be an indicator of cancer progression. Swallowing difficulties, especially in the initial stages, can be noticeable.
Visual inspection of the nasopharynx using a flexible and rigid endoscopic tube to detect tissue changes. A tissue sample is taken for laboratory analysis to confirm digital cancer cells.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans are used to determine tumor size, spread, and the extent of surrounding tissue.
Examination of the larynx is performed with a special instrument to detect changes in the vocal cords and preserving structures. Analyzing a tissue sample under a microscope determines structural and cellular changes.
Early diagnosis plays a key role in the successful treatment of the disease. Patients with identified symptoms, especially those at risk, are recommended to have regular medical examinations and consultations with an otolaryngologist.
The medical field in Korea is actively adopting advanced technologies and innovations. Many clinics are equipped with state-of-the-art electrical devices and technology to provide highly accurate diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Doctors in Korea are educated and experienced in the best medical institutions in the world. Korean clinics actively utilize integrative treatments, including traditional Korean methods, psychological support, and innovative therapies. This allows not only the physical but also the psychological and emotional aspects of the disease to be covered.
In some countries, long treatment times, especially when advanced techniques are used. In Korea, due to good health care organization, patients can often receive treatment as soon as possible.
Korea is actively implementing global research and clinical trials that allow patients to access the latest technologies and medicines.
 Esophageal cancer treatment in Korea
Esophageal cancer treatment in Korea
Esophageal cancer remains one of the most complex and aggressive cancers, presenting a challenge to the medical community worldwide. In recent decades, Korea has become a center of excellence and innovation in the fight against this type of cancer.
Cancer symptoms can vary depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and where the tumor is located. Constant fatigue unrelated to physical or mental activity may be a sign of cancer. Loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, and metabolic problems may be linked to cancer.
Unexplained changes in the frequency of urination or stools may be signs that the disease is developing. Blood tests can show the presence of certain markers that may indicate the presence of cancer cells. X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), are used to visualize internal organs and detect changes.
Cancer cells lose their ability to autoregulate and can multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Cancer cells can affect surrounding tissues and organs, as well as spread through blood and lymph vessels, forming metastases to distant parts of the body.
Tumors can be heterogeneous, containing different cell subtypes with different genetic and molecular characteristics. This creates treatment challenges and may lead to differences in response to therapy.
Cancer cells can develop mechanisms that help them avoid detection and attack by the body’s immune system. Mutations in genes that control cell growth and division can lead to the development of the disease. These genetic changes may be inherited or may result from exposure to various environmental factors.
Individual differences in tumor genetic profile and patient characteristics can make different cancers more or less sensitive to certain treatments.
Cancer cells can change their characteristics to adapt to the environment and changes in the body, making treatment more difficult and leading to recurrences.
Radical resection and minimally invasive surgical techniques such as laparoscopy are widely used in Korea to treat the disease. These techniques ensure a quick recovery from surgery and reduce the risk of complications.
Innovative radiation therapy techniques such as Intensity Fractionated Radiation Therapy (IFRT) and proton therapy are used to precisely irradiate the tumor with minimal side effects on surrounding healthy tissue.
Korean physicians favor an integrative approach to oncology treatment, taking into account the physiological and psychological aspects of the disease. Clinical trials are aimed at finding new treatments that can improve the effectiveness of therapy and the quality of life of patients.
 Treatment of prostate oncology in Korea
Treatment of prostate oncology in Korea
Prostate oncology remains one of the most common cancers in men, and its diagnosis and treatment continue to pose a challenge to the medical community.
Korean medicine provides highly accurate diagnostic methods for early detection of prostate cancer. PSA testing, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and biopsy provide detailed data on the condition of the prostate gland, which greatly influences the choice of optimal treatment.
In some cases, especially slow-growing tumors, an active surveillance strategy is used. This method involves regular medical examinations and monitoring of the tumor, with no immediate need for surgery or radiation treatment.
Korea has advanced surgical treatments for prostate cancer, including robotic surgery. This provides more precise and minimally invasive surgery, reducing recovery time and minimizing the risk of complications.
The use of innovative radiation therapy techniques such as Intensity Fractionated Radiation Therapy (IFRT) allows for more precise targeting of radiation beams to the tumor, reducing the impact on healthy tissue.
In cases of advanced prostate cancer, Korean doctors are actively using chemotherapy and targeted therapies. These methods aim to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and improve the quality of life of patients.
Immunotherapy, which stimulates the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells, is also a promising treatment for prostate cancer. Research and clinical trials in this area are being actively conducted in Korea.
Korean doctors prefer an integrated approach to prostate cancer treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. Patients are provided with treatment options based on scientific research and modern medical advances.
Prostate oncology continues to be a focus of research and development in the medical community. Modern technology and innovations are providing patients with more accurate diagnostic methods and effective treatment strategies, providing hope for successfully overcoming this cancer.
 Heart cancer treatment in Korea
Heart cancer treatment in Korea
Cardiac oncology, despite its rarity, presents a major challenge in the field of medical science. Korea, known for its innovative medical technology, has become a center that offers hope to patients with this disease.
Cardiac oncology is a rare but very serious disease that requires special attention and modern methods of diagnosis and treatment. In recent years, the scientific and medical communities have paid increasing attention to research in this area in an effort to provide effective tools to combat cancerous tumors affecting heart tissue.
Cardiac oncology can include different types of tumors such as sarcomas, lymphomas, and other rare forms of cancer. Each type requires an individualized approach to treatment.
Determining cardiac oncology is challenging because of its rarity and specificity. However, modern technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) can more accurately detect tumor masses in the heart region.
Modern diagnosis of cardiac oncology in Korea is performed using advanced imaging techniques including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). These technologies provide high accuracy and early detection of tumors in the cardiac region, which is a key factor in effective treatment.
Korea uses advanced surgical techniques, including laparoscopic surgery and the use of robotic systems. These technologies provide more precise and minimally invasive surgeries, which shortens the patient’s recovery period and improves prognosis after surgery.
The use of innovative radiation therapy techniques, such as Intensity Fractionated Radiation Therapy (IFRT) and proton therapy, allows radiation beams to be precisely targeted to the tumor, minimizing the impact on healthy tissue around the heart.
In Korea, individualized chemotherapy and targeted drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells, minimizing side effects, are being actively researched and implemented.
Korea is also engaged in immunotherapy research for the treatment of cardiac oncology. Activating the immune system to fight cancer cells represents a promising avenue in the treatment of this rare but serious disease.
In Korea, modern technology, advanced treatment methods and a focus on an individualized approach make the treatment of cardiac oncology more effective and reliable. The unique combination of medical innovation and in-depth research makes Korea a leader in the fight against cardiac oncology, opening new horizons for patients and specialists around the world.
 Treatment of duodenal oncology in Korea
Treatment of duodenal oncology in Korea
Duodenal oncology is becoming a major challenge for the medical community worldwide, and Korea is presenting its innovative treatments and integrative approach to combat this type of disease.
Advanced surgical techniques such as minimally invasive surgery using robotic systems are widely used in Korea. This allows surgeons to remove the neoplasm more precisely, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues and speeding up the recovery process.
Korean medical institutions are actively adopting the latest radiation therapy technologies, including proton therapy. This method of irradiation provides a more precise direction of the rays on the neoplasm without affecting healthy tissues and organs.
In Korea, early diagnosis of duodenal oncology is emphasized. Modern medical technology, such as endoscopy and CT scans, can detect the tumor in its early stages, opening up more options for effective treatment.
Surgical treatments remain the primary way of dealing with this condition. Minimally invasive surgery, including laparoscopic and robotic surgeries, is widely used in Korea. These techniques provide a faster recovery from surgery and reduce the risk of sequelae.
Innovative radiation therapy techniques such as Intensity Fractionated Radiation Therapy (IFRT) and proton therapy allow for more precise targeting of radiation beams to the cancerous tissue. This is especially important in duodenal oncology, where preservation of organ functionality plays a major role.
Instead of one-size-fits-all approaches, Korean specialists are increasingly considering individualized methods. Such approaches include targeted therapies and immunotherapies that target specific molecular gland characteristics and activate the natural immune response.
Korea is actively developing medicine that combines traditional methods and modern scientific approaches. Psychological support becomes a necessary component in the onset of cancer.
Korea is at the center of innovation in duodenal cancer development, applying a wide range of advanced techniques and an integrative approach to treatment to patients. This approach aims not only to effectively destroy the tumor, but also to provide meaningful patient support.
 Spine cancer treatment in Korea
Spine cancer treatment in Korea
Spinal oncology is a complex and serious condition that requires highly skilled and individualized care for the person. South Korea is spreading its advanced traditional technologies that can cure a person within a short period of time.
The most characteristic symptom is pain in the body area, which can be constant or vary depending on the condition of the body. The disease can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots, causing weakness or numbness in the limbs.
Persistent pain may be the first signal, especially when moving or at rest. Pain may be localized to the area of the tumor. In the later stages of the disease, patients may experience changes in general condition, weight loss and loss of appetite.
Patients may experience sensory changes, such as jiggling or burning in certain areas of the body. Cancer can affect the spinal cord, causing problems with coordination and movement.
A tumor in the spine can put pressure on the bladder or rectum, causing difficulty urinating or defecating. Patients may notice changes in their gait, such as shakiness or instability.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of the spine, show the presence of damage, and identify characteristics.
X-rays allow evaluation of bone features and characteristic signs of deformity caused by the tumor. Myelography refers to a technique that uses a contrast agent injected into the spinal canal to highlight spinal cord structures and identify compression or deformity.
Positron emission tomography evaluates metastases and determines the extent of disease spread. Testing for tumor markers in the blood can serve as an additional diagnostic method.
Pain blockade is used to relieve the condition. They use robotic systems for more precise and minimally invasive surgical procedures. Targeted therapies use drugs that target specific molecular targets in the tumor.
In Korea, an integrative approach is often used, combining different treatments to achieve the best results. Of course, each case is unique, and the treatment plan is tailored individually based on the type of tumor, stage of the disease, and the patient’s condition.
 Gallbladder cancer treatment in Korea
Gallbladder cancer treatment in Korea
Gallbladder oncology is a disease that requires a skilled and innovative approach to each individual. South Korea is one of the countries that provides high quality medical care.
Constant and recurrent pain sensations in the right side of the abdomen may be the first sign of the disease. Jaundice is the coloring of the skin, whites of the eyes, mucous membranes in yellow due to a violation of the outflow of bile. It is caused by blockage of the bile ducts in the disease. In some cases, the neoplasm can be felt on palpation.
In Korea, molecular genetic tests are widely used to characterize tumors in order to choose the most effective treatment methodology.
Korean medical centers are actively using immunotherapy and targeted therapies for oncology treatment to improve treatment efficacy and reduce side effects.
Surgical removal of the neoplasm and biliary is the mainstay of treatment. Robotic and laparoscopic surgery are often used in practice.
In a cholecystectomy, the entire gallbladder is removed. In some cases, in the early stages of cancer, it is possible to remove nearby lymph nodes and part of the liver. When spread to an organ, sometimes part of the liver is removed at the same time as cholecystectomy.
Radiation therapy is used as an additional treatment after surgical intervention. This method can be used to reduce the size of tumors before a surgical procedure.
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs that destroy and slow the growth of cancer cells. It may be performed before or after surgical intervention.
These innovative therapies aim to activate the immune system and target specific molecular targets in cancer cells. Chemoradiotherapy includes chemotherapy and radiation therapy given to enhance the effectiveness of both.
Cancer treatment in Korea provides patients with reliable and effective treatment focused on the best possible outcomes. Korea remains a leading country in the field of oncology and gallbladder, providing advanced techniques and a high level of medical care.
 Bladder Oncology Treatment in Korea
Bladder Oncology Treatment in Korea
Bladder oncology is a serious disease whose treatment will be most successful in a medical center in Korea. Therapy is a complex and multifaceted process that requires an individualized approach.
Patients who are diagnosed with bladder cancer are encouraged to discuss all treatment options with their doctor and have an active exchange of information to make informed decisions. The support and involvement of oncology professionals is key in the fight against this disease and growth.
Patients often have hematuria – blood in the urine. It can be visible (macrohematuria) as well as invisible (microhematuria). Patients often have difficulty urinating, frequent visits to the toilet.
Painful or discomforting sensations occur as tumors develop. Specific symptoms such as fatigue and malaise occur in the later stages of the disease.
Performing a cystoscopy involves inserting a tube with an electric light to examine the walls and detect abnormalities.
During the procedure, it is possible to take tissue samples (biopsy) for laboratory analysis and diagnosis. Ultrasound can be used to evaluate the structure of an organ.
In transurethral resection of the urinary organ, the cancerous tissue is removed by cystoscopy. It is used for the therapy of early stage oncology.
A cystectomy is a surgical organ with tissue preservation. After this procedure, there is a new outflow of urine (ureterostomy) as well as an opening of the urinary tract (neourosystems).
External beam radiation therapy targets the neoplasm without x-ray irradiation. Radiation therapy is given before or after surgery.
Early detection and diagnosis are critical to successful development. When symptoms occur, it is important to see a doctor in time for tests and diagnosis. The medical center in Korea is equipped with the best technology. The facility employs specialists of the highest category who will return any patient to a normal life.
 Rectal cancer treatment in Korea
Rectal cancer treatment in Korea
Rectal oncology is a serious disease that requires a comprehensive and innovative approach to individualized treatment. South Korea is the only country that provides high quality medical care and advanced techniques for this disease.
Hereditary factors may play a crucial role in the development of the disease. If there have been cases in the family, the risk of contracting this disease increases. Genetic syndromes such as hereditary colonic polyposis (FAP) and hereditary neoplastic polyposis colorectal syndrome (HNPCC) may also increase risk.
The risk of rectal cancer increases with age. This type of disease is most often diagnosed in people over the age of 50. Tobacco and alcohol are factors in the onset of the disease.
Some inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, can contribute to the development of cancer. Also, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can cause disease.
Lack of activity and sedentary lifestyle play a significant role. Overweight and obesity are also associated with the disease.
Doctors and surgeons specializing in the occurrence of rectal oncology in Korea are highly qualified and experienced. They put into practice the best techniques of treatment and surgical intervention.
Korean medical centers have innovative equipment, including robotic surgery. They favor minimally invasive surgeries and functional anastomoses in their work.
Molecular genetic tests are widely used in Korea to provide therapy according to the individual characteristics of the patient and the neoplasm.
Korean medical centers are actively using immunotherapy and targeted therapies to treat colorectal cancer, which can improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the severity of sequelae.
Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery for stage II disease to destroy residual cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be given as adjunctive treatment for relapse of the primary factor or at later stages.
 Lung cancer treatment in Korea
Lung cancer treatment in Korea
Lung oncology is one of the most deadly cancers in the world. However, thanks to advanced diagnostic and treatment methods and outstanding specialists, Korea has become one of the leaders in the fight against this disease.
Smoking tobacco is a major cause of the development of the disease. Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens that damage the DNA in lung cells, causing them to divide uncontrollably.
Inhalation of radon gas, which occurs when radioactive uranium spreads in soils and rocks, can increase the risk of disease.
Hereditary predisposition can also increase the risk of developing lung cancer, but it plays a smaller role compared to other factors.
Diagnosis of cancer involves a number of methods aimed at determining the indicators and characteristics of tumors. Early detection of lung cancer plays a crucial role in effective therapy.
Chest radiography may reveal the presence of a tumor or abnormality in the lung cells, but does not always provide a complete picture of the characteristics of the neoplasm.
CT scans provide more detailed images of tumors, if present. PET scans can give information about metastases in other parts of the body.
A punch biopsy involves inserting a needle into the lungs under the control of an X-ray or CT scan. In some cases, a surgical biopsy may be performed.
Measuring levels of tumor markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) may be a factor in determining additional lung cancer rates and dynamics.
Korea has oncologists and pulmonologists with extensive experience in lung cancer diagnostic measures. Korea is distinguished by its use of advanced cancer techniques, including high-resolution computed tomography (HCT) and PET-CT, which allows for more accurate determination of the stage and nature of the tumor.
Korea is adopting the latest techniques, including surgical measures and robotic techniques, immunotherapeutic and targeted modalities, and biologic therapies.
 Treatment of cervical oncology in Korea
Treatment of cervical oncology in Korea
One of the most common types of cancer in women can be called cervical cancer. This condition can be diagnosed at any age. However, in women after the age of 45, the risk increases significantly.
HPV infection, especially high-risk HPV infection (types 16 and 18), is considered the leading cause of cervical cancer. This virus is spread sexually and can cause changes in the cervix that cause cancer.
Becoming sexually active at a young age contributes to the risk of HPV infection. Regular gynecologic examinations and Pap tests help to detect precancerous changes and the initial stage of cancer.
A Pap test is a consequence in which the doctor takes cells from the surface of the cervix and sends them for analysis. This test can detect precancerous changes in the cells of the cervix. This test establishes the presence of HPV in the cells of the cervix. It can be used as an adjunct to the Pap test.
A biopsy involves tissue samples from the cervix for laboratory analysis. This allows the presence of cancer and its stage to be determined. MRI and CT scans can be used to assess the spread of cervical cancer, especially in the later stages of the disease.
Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound may be performed to determine international metastases to adjacent organs and lymph nodes.
Korea utilizes advanced diagnostic techniques, Pap test, Human Papillomavirus (HPV) test, colposcopy, MRI and biopsy to accurately determine the diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Radiation therapy is used to destroy residual cancer cells after surgery. New treatments – immunotherapy and targeted therapies are showing excellent results and can be used to identify cervical cancers.
Korean medical centers pay close attention to patient-centered care. Patients are supported at all stages of treatment, including psychological support and rehabilitation.
Cervical cancer treatment in Korea involves a high degree of financial solvency and medical competence. The doctors and medical staff have extensive experience in cancer care, as well as state-of-the-art medical equipment. This allows the patient to receive high quality and effective treatment for cervical cancer.
 Gastric Oncology Treatment in Korea
Gastric Oncology Treatment in Korea
Gastric cancer is a serious cancer that affects the stomach, a digestive organ that plays a key role.
Gastric cancer develops when normal stomach cells become malignant tumors. Helicobacter pylori infection can cause chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, which increases the risk of cancer.
Diets rich in salty, smoked and canned foods, as well as a lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet can contribute to the disease. Hereditary predisposition is also important.
For diagnosis, the Korean medical center uses gastrofibroscopy, a procedure in which a flexible tube with a connector is inserted into the stomach for visual inspection. It can be used to detect tumors and take biopsies.
Barium radiography uses beams to create an image of the stomach after it has been filled with barium. It may be a manifestation of abnormalities such as ulcers or tumors.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans combined with CT scans can provide more accurate data about the cancer and its metastases. Surgery may involve removing part or all of the stomach. In some cases, surrounding lymph nodes are also removed.
Radiation therapy in Korea is used to fragment the tumor before surgery or as a stand-alone treatment in later stages. Chemotherapy may be given before surgery, after surgery, or as a stand-alone treatment.
New drugs that target specific molecular targets in cancer cells provide more targeted treatments. In advanced stages, when the cancer is not amenable to any individual case, palliative care aims to relieve symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment of gastric oncology in Korea is a complex and multi-step process that requires an individualized approach to each patient. Doctors have vast experience in treating such diseases. In their practice, they use only innovative drugs and modern equipment.
 Blood cancer treatment in Korea
Blood cancer treatment in Korea
Blood oncology is a group of diseases including leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma that affect the hematopoietic system. Recently, Korea has become one of the world’s leading centers for selected cancers, engaging in advanced diagnostics and innovative technologies.
Samsung Medical Center offer a wide range of advanced treatments for blood cancers, including chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, immunotherapy and targeted therapies. These methods can combat various forms of disease and achieve the best results.
The medical institution adheres to the principles of an individual approach to each patient. Treatment plans are tailored to the disease, age and general condition of the patient.
The physicians and medical staff are highly qualified and have extensive experience in blood oncology. This guarantees a high level of medical care.
Samsung Medical Center is equipped with innovative technology and conveys high-tech services in diagnosing and stopping cancer.
The basis for accurate diagnosis of blood oncology is blood chemistry tests, CT and MRI. These methods can detect pathological changes in the blood and visualize pathological changes in organs.
Korea has maintained its innovation in the treatment of cancer. This includes advanced bone marrow transplantation, immunotherapy, targeted therapies and biologic therapies.
Korean Medical Center is distinguished by its patient-centered approach. In addition to medical care, it provides psychological support. Attention is paid to quality of life and post-treatment care.
Cancer treatment in Korea provides significant progress in healing and quality recovery. Patients have access to advanced techniques and technology, highly trained professionals and support at every stage of treatment.
 Thyroid cancer treatment in Korea
Thyroid cancer treatment in Korea
Thyroid oncology is a serious condition that can affect quality of life and requires a competent and up-to-date approach to individuals. Samsung Medical Center in South Korea, with its advanced infrastructure and outstanding specialists, has become one of the leaders in the field of this disease.
The facility favors advanced diagnostic techniques, including ultrasound and biopsy. An important aspect is a thorough examination to determine the exact size of the neoplasm. Korean specialists scrutinize the results of the research and develop an individualized therapy plan.
Surgical interventions are performed in many cases. The surgeons are highly experienced in gland surgeries including thyroidectomy and lymphadenectomy. They seek to minimize the risk of damage to surrounding tissues and nerves to preserve organ function and minimize pronounced effects.
Radioactive iodine therapy is commonly used after surgical intervention. This technique targets residual cancer cells. The Korean medical facility is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities for these procedures, allowing you to receive quality care during the entire process.
If the cancerous tissue has spread or recurred, other treatments such as immunotherapy and radiation therapy may be used. Immunotherapy is becoming increasingly important in cancer and helps stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells.
Patients seeking treatment in Korea find that the high level of comfort and care provided by constitutional facilities. Personalized approach and high standards of medical care create a comfortable environment for patients.
Samsung has become one of the leading medical centers for the treatment of glandular cancer, using state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment methods, high level of research and concern for patient comfort. The combination of advanced medical practices and human intervention makes the facility attractive to patients in need of care.
 Skin cancer treatment in Korea
Skin cancer treatment in Korea
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers but, in most cases, is successfully treated when detected at an early stage.
New moles or spots on the skin that grow or change shape and color should alert you. Any change in the texture of existing moles is an alarming symptom.
If vertical black streaks appear under your fingernails, you should be examined for melanoma. Prolonged presence of non-healing ulcers on the skin, may be associated with oncology. If the formations on the skin begin to bleed or crust over, this is also an alarming symptom. Itching and pain in the skin area or on the surface of masses may accompany skin cancer.
The doctor at the Korean Medical Center performs a visual examination of the skin. He’s evaluating all the changes. Dermatoscopy is used to examine neoplasms in more detail. This method can detect changes in moles and spots that may not be visible to the naked eye.
If skin cancer is suspected, the doctor takes a tissue sample from the mass for further laboratory analysis. This allows you to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of cancer. The doctor may also check the lymph nodes in the area close to the cancerous mass to make sure the cancer has not spread to the lymphatic system.
In rare cases, if metastasis or spread of the cancer is suspected, additional tests such as MRI, CT or PET scans may be required.
Surgical removal of the tumor is the most common method of treating skin cancer. The doctor may remove the tumor as well as a small area of healthy skin around it.
Radiation therapy in Korea can be administered after surgery to destroy residual cancer cells or when surgery is not possible. Immunotherapy stimulates the immune system to fight cancer cells and can be used in the treatment of melanoma.
Regular use of sunscreen with a high SPF helps protect your skin from UV rays. Try to avoid the sun at its peak (10am-4pm) and wear protective clothing and hats. Check your skin regularly for new moles, changes in existing moles, sores, spots or other unusual growths.
 Bone cancer treatment in Korea
Bone cancer treatment in Korea
Bone oncology or osteosarcoma is a dangerous type of disease that localizes in bone tissues. The disease is commonly diagnosed in children, adolescents, and young adults. This disease can affect different bones in the body, but most commonly affects long bones such as hips, shoulders, and shins.
Osteosarcoma of bone is found in the cells responsible for forming new bone tissue. The disease often develops in the long tubular bone. Chondrosarcoma develops in the cells that make up cartilage. This type of cancer is found in the flat bone, ribs, and pelvis. Evans sarcoma is localized in soft tissue and bone and can affect other organs. The disease is not very common, but is characterized by a dangerous course.
The most characteristic symptom of the disease is considered to be pain that increases at night. The site of the bone lesion is often swollen and painful to the touch. The disease can significantly limit movement in joints close to the affected bone.
X-rays reveal abnormalities. They allow us to judge changes in bone structure. CT scans provide detailed images of the bones and can determine the spread of the tumor. Magnetic resonance therapy allows evaluation of soft tissue and bone structure.
A biopsy is performed to obtain a tissue sample for laboratory analysis and to confirm the diagnosis. Positron emission tomography combined with CT scans can help determine cancer cell activity.
The physician collects the patient’s medical and family history and examines the patient for symptoms and changes in skin and bone conditions. X-ray images can reveal abnormalities in bone structure, such as tumors or bone destruction.
Diagnosis of bone cancer requires a high degree of professionalism and expertise and is performed at a specialized medical center in Korea. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial to the effectiveness of treatment.
 Liver cancer treatment in Korea
Liver cancer treatment in Korea
Liver cancer is one of the most aggressive and deadly types of cancer. The liver, which performs many important functions in the body, including filtering blood and participating in the digestive process, can be a target for malignant tumors.
The disease occurs when normal liver cells begin to change and irreversibly multiply improperly, forming a tumor. It is the most common type of cancer and usually develops against a background of diseases such as cirrhosis, chronic inflammation, hepatitis B or C.
Cirrhosis is a major risk factor for cancer. It is caused by long-term alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease and other causes.
Frequent alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing the disease. This also applies to fatty liver dystrophy caused by diabetes mellitus, hereditary diseases – hemochromatosis and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency increase the risk.
A doctor at a Korean medical center performs an exam, discusses medical and family history, and discusses symptoms that may be related to cancer.
Blood may be analyzed to detect levels of certain markers – alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Elevated levels of these markers may be associated with liver cancer, although they are not always accurate indicators.
Ultrasound allows visualization of the liver and tumor. This method can help determine the size, number, and location of tumors in the liver. CT scans provide more detailed images of the liver and can assess the extent of tumor spread.
Chemotherapy can be administered in various forms, including oral medications and infusions. It is used to kill cancer cells and control tumor growth.
 Brain cancer treatment in Korea
Brain cancer treatment in Korea
Brain cancer is a rare and complex disease that has a serious impact on the nervous system and can have a variety of clinical manifestations.
This type of cancer is an abnormal growth of cells inside the skull. These abnormalities can arise from glial cells that support neurons and provide structural integrity to the brain.
Gliomas arise from glial cells and include astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas. These tumors form from other brain cells, such as brain membranes or vascular cells, and include meningiomas, hemangioblastomas, and other types of tumors.
Headache: This is one of the most common symptoms, especially in the morning, and it often gets worse when bending over. Changes in atmospheric pressure can worsen headaches.
The doctor at the Korean center performs a general physical examination and discusses the patient’s medical and family history, as well as symptoms that may be related to brain cancer.
MRI is the primary method for imaging a tumor and assessing its size, shape, location, and characteristics. CT scans can provide additional information about the structure of the tumor and its relationship to surrounding tissues. PET scans can be used to determine tumor activity and assess tumor metastasis.
A biopsy, in which a tissue sample is taken from the tumor, may be taken to finally confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of cancer. CSF examination may be done to look for cancer cells and metastases, especially if cancer is suspected to have spread to the spinal cord.
In the late stages of the disease, when treatment cannot provide a cure, the emphasis at the Korean Medical Center shifts to palliative care. This aims to relieve symptoms, increase the patient’s quality of life and manage pain and discomfort.
Immunotherapy can activate the immune system to fight cancer cells and can be used in the treatment of some types of brain tumors.
 Pancreatic cancer treatment in Korea
Pancreatic cancer treatment in Korea
Pancreatic cancer is considered one of the most aggressive and deadly forms of oncology facing modern medical science and practice. It is a small but important organ in the human body, and its malignancy is often detected at a late stage, which complicates therapy.
The pancreas is responsible for the production of insulin. Malignant formation is manifested when normal cells begin to irreversibly change and reproduce improperly. This type of cancer can be aggressive and can affect other organs.
Symptoms of the disease can be mistaken for another disease. Most often patients complain of painful sensations. This is a characteristic symptom of the disease. The exacerbation is usually seen with meals.
Patients often lose weight for no apparent reason. It is a very common condition in which the skin and eyes turn yellow due to the accumulation of bile in the body. Jaundice can be caused by compression of the bile ducts by a pancreatic tumor.
Oncology can lead to digestive disorders that cause diarrhea, constipation, and painful bloating. Patients may experience general weakness, fatigue, and malaise.
The treatment of malignancy at Samsung Korean Medical Center depends on the stage of the disease. However, in the later stages, the disease is more difficult to manage. Therapy is aimed at alleviating symptoms.
Pancreatectomy (complete or partial) may be performed. During this surgery, part or all of the organ is removed along with the surrounding tissue. Sometimes parts of the stomach, bile and biliary tract are also removed.
Chemotherapy is a common method of therapy for dangerous diseases. It is used to reduce the size of the neoplasm and eliminate the remaining cancerous tissue. Sometimes chemotherapy and radiotherapy are combined.
Radiotherapy uses high energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It is performed both before and after surgical procedures. Radiotherapy can help shrink the neoplasm, relieving symptoms. Immunotherapy is also actively used to treat the disease.
Samsung Medical Center is staffed with top-notch specialists. They perform diagnostics with state-of-the-art equipment and use the latest drugs in the practice. Oncology doctors will restore your well-being and get your lifestyle back on track.
 Breast cancer treatment in Korea
Breast cancer treatment in Korea
Everyone knows such a dangerous disease as oncology. Breast cancer takes the lead among the other varieties. This disease seriously affects women’s health and can be fatal. In this regard, women need to perform diagnostic measures annually to detect irregularities in time.
Patients over 50 years of age are at risk. The disease can appear at an earlier age as well. An inherited mutation in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes contributes to the development of the disease. Recurrences are possible with prolonged use of hormonal medications.
Women can perform breast self-palpation. In this way you can identify seals, nodules, changes. Clinical examination by a physician should be performed at the slightest suspicion of disease.
The first thing they do at Samsung Medical Center is a mammogram – to detect small tumors, even if they can’t be felt. This method is recommended for women over the age of 40 on a regular basis and earlier if there is a genetic disposition.
Ultrasound can be used to further evaluate seals. It can be used to see changes or clarify results in a mammography exam. MRI facilitates the visualization of detailed images of the breast.
Treatment of the disease usually requires a combined approach. Oncologists at Samsung Korean Medical Center develop a therapy plan individually with each patient.
If treatment is ineffective, the focus shifts to palliative care. This is aimed at alleviating symptoms and reducing pain and discomfort.
Hormone therapy is often used in the treatment of this condition. This is how estrogen and progesterone levels are controlled. The technique consists of taking medications that block hormones. Targeted method targets specific molecules and proteins in malignant tissue.
 How a gynecologist can see cervical cancer
How a gynecologist can see cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a serious cancer affecting patients of all ages. Early diagnosis and treatment promotes recovery and a return to a normal lifestyle. The gynecologist identifies risks and symptoms of cancer and conducts regular checkups.
The pap test is used to identify the risks of developing cancer. Doctors take swabs from the vagina and send them to a laboratory for analysis. Regular testing is recommended for women of a certain age and risk.
The papillomavirus contributes to the development of a dangerous disease. A test may be performed to detect the virus in a woman.
If HPV tests show abnormal results, the gynecologist may decide to perform a colposcopy. During this procedure, the gynecologist uses a special magnifying device (colposcope) to view the cervix in greater detail. This allows the doctor to detect changes and abnormalities that are not always visible on a routine exam.
If the gynecologist detects suspicious changes during colposcopy, he or she may decide to take a tissue sample from the cervix for laboratory testing. A biopsy can accurately diagnose the disease.
Ultrasound is used to examine the structure and thickness of the uterine walls in more detail and to determine the presence of tumors.
It is important that women realize the importance of regular checkups and follow the doctor’s recommendations. Late detection of cervical cancer can increase the difficulty of treatment and decrease the chances of recovery. Together with a gynecologist, women can develop an individualized prevention and screening plan to keep their reproductive health at the highest level.
 What day of the cycle is the ultrasound
What day of the cycle is the ultrasound
Ultrasound (USG) is one of the key methods in gynecology for diagnosing and monitoring the condition of female reproductive organs. For many women, it is important to know which day of the cycle to have an ultrasound to get the most accurate information possible.
If your doctor schedules an ultrasound to track ovulation, this exam is usually done mid-cycle, sometime between days 12 and 16, starting on the first day of your period. During this period, mature follicles in the ovaries can be observed, which helps determine the optimal time to conceive if the patient is planning a pregnancy.
To evaluate the condition of the uterus and the presence of abnormalities such as myoma or polyps, ultrasound can be performed on any day of the cycle. However, transvaginal ultrasound (where the transducer is inserted into the vagina) is usually preferred because it provides a clearer image.
Doppler ultrasound allows you to study blood flow in the pelvic organs. You can come in for this ultrasound on any day of your cycle, depending on the goals and objectives of the study.
Hormonal tests are performed on certain days of the cycle, according to the doctor’s recommendations. For example, to assess estradiol levels, the study may be ordered in the second half of the cycle.
Mammography and breast ultrasound are performed on any day of the cycle, but preferably in the first half of the cycle when the mammary glands are less sensitive.
Ultrasound is an important tool in gynecology that allows doctors to diagnose and monitor various female reproductive conditions. For different types of ultrasound, there are different recommendations as to which day of the cycle it should be performed. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate type of ultrasound and indicate the optimal time for the study.
 How a gynecologist can identify an ectopic pregnancy
How a gynecologist can identify an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which the development of a fertilized egg does not occur in the uterus.
Doctors begin the examination by taking a history and discussing the patient’s symptomatology. Typical signs include lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and delayed menstruation.
Gynecologists perform external and internal gynecologic exams. An ultrasound scan is considered a reliable method. In this way it is possible to visualize the location of the fertilized egg and determine whether it is inside or outside the uterine cavity.
HCG levels are often significantly reduced. Ongoing testing allows the gynecologist to monitor its dynamics.
In the absence of effectiveness of other methods of diagnostic do not give certain results doctor conducts laparoscopic intervention. This is an examination with a thin tube that has a video camera, which is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall.
When a patient’s life is diagnosed as life-threatening, surgery is required. The laparoscopic method is categorized as minimally invasive. The surgical intervention does not require long rehabilitation.
The laparotomic method is preferred in very serious situations where a larger incision is needed. It is important to note that ectopic pregnancy is a condition that requires immediate medical intervention. The decision for surgical removal is determined based on clinical presentation and diagnostic data. At the slightest suspicion or the appearance of pain, bleeding from the vagina, immediately contact doctors to get professional evaluation and treatment.
 How a gynecologist examines children
How a gynecologist examines children
Gynecology is a medical specialty concerned with the care of women’s reproductive health. However, sometimes it is necessary to perform examinations and consultations in children, especially when certain medical problems are present.
Pediatric gynecology specializes in diseases and conditions related to the female reproductive system in children and adolescents. Physicians in this area receive additional training and experience in pediatric reproductive medicine.
Usually, children and adolescents don’t see a gynecologist until certain problems or indications arise. Parents bring their children for consultation in case of delayed or irregular menstruation, the appearance of pain in the abdomen and noticeable discomfort, problems with urination or pain at this time, the appearance of discharge, itching, burning, unusual odor.
Children are examined with special attention to their age and psychological readiness. This refers to an external inspection to look for visible abnormalities and problems.
During palpation, the specialist feels the abdomen and pelvic area to assess the condition of internal organs. Ultrasound is considered a safe and non-invasive procedure that allows visualization of organs within the pelvis and uterus. Sometimes blood or urine tests may be needed to check for infections or other conditions.
Adolescence can be particularly challenging psychologically. Physicians who specialize in pediatric gynecology understand this sensitivity and work to create a trusting relationship with their patients and ensure comfort during exams.
Gynecologists are also available to talk to parents and teens about vaccination issues related to reproductive health. For example, vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV) can help prevent cervical cancer in girls in the future.
Gynecologists can provide information about menstruation, explain how to take good care of hygiene during this period, and help girls and their parents understand normal cycles and symptoms that need attention.
Gynecologists can also make recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including nutrition, physical activity, and stress management. It is important to remember that a healthy lifestyle affects reproductive health.
 How to normalize hormones
How to normalize hormones
The health of women and men is directly related to hormonal balance. Disruptions in this balance can cause a variety of problems including insomnia, weight changes, skin and hair problems, serious diseases like diabetes and infertility. To avoid this problem, you need to adjust your diet.
Proteins derived from meat, fish, eggs, nuts and seeds are key in the synthesis of hormones. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish also help normalize hormonal balance.
Vegetables and fruits have a huge content of vitamins and minerals that support a healthy hormonal system. Including them in your diet helps to maintain the proper balance.
Consumption of processed foods rich in trans fats leads to hormonal imbalance. Limiting these foods in your diet helps keep you healthy.
Regular physical activity usually normalizes hormones. Exercise reduces nervousness and insulin resistance.
Lack of sleep can cause an imbalance of hormones, including appetite and stress hormones. To support a healthy hormonal rhythm, sleep duration should be around 8 hours. Stress also has a negative impact. Relaxation in the form of yoga, meditation and deep breathing, helps reduce stress.
Being overweight and having thyroid problems can cause an imbalance of hormones. The thyroid gland is actively involved in the regulation of hormones, and regular monitoring and treatment of diseases of this gland are important in case of hormonal disruptions.
Some natural supplements – poppy, succession help normalize hormones. However, you should make an appointment to consult a specialist before starting any supplements.
Normalizing hormonal balance is an important aspect of maintaining healthy individuals. By keeping the above recommendations in mind, you can prevent a lot of problems associated with its disruption.
 When and why a gynecologist prescribes birth control pills
When and why a gynecologist prescribes birth control pills
Many women see a gynecologist to prevent unwanted pregnancies. Specialists prescribe certain drugs, taking into account the individual needs of patients.
The main purpose of birth control pills is to prevent unwanted conception. If taken correctly and regularly, 100% results are observed
These remedies also regulate the menstrual cycle. They help to reduce pain and discomfort during menstruation, as well as normalize the cycle.
Some women benefit from this therapy to improve their skin condition. This is due to the reduction of sebum activity.
They reduce menstrual soreness and decrease the amount of bloody discharge. Women feel much better about themselves. This is especially necessary for women who suffer from severe menstrual pain or irregular menstruation.
The remedies can be used to treat various gynecological diseases. For example, they help manage polycystic ovarian syndrome, endometriosis, and many other conditions.
Menopausal women may use birth control pills to manage symptoms such as hot flashes and irregular periods.
In treating some conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, birth control pills can be used to prevent pregnancy when other medications may be dangerous.
They are used in combination with other treatments to prevent pregnancy while taking medications that can be harmful to the fetus.
Medications are not one size fits all. Their use may be contraindicated in the presence of certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, genetic tendencies to thrombosis, smoking, and certain other risk factors. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor and have medical tests before starting birth control pills.
 Why a gynecologist examines breasts
Why a gynecologist examines breasts
Breast examination by a gynecologist is an important part of a woman’s examination, even though at first glance it may seem somewhat unexpected within a gynecologic practice. However, this examination is important for the prevention and diagnosis of disease.
One of the main aspects of a breast exam by a gynecologist is the early detection of breast cancer. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women.
Early detection of breast cancer can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment. A gynecologist examining the breasts may detect palpable lumps, swelling, or changes in the nipples, which may indicate the presence of a tumor or other abnormality.
Breast exams are also used to monitor overall breast health. In addition to cancer, there are fibroids and mastitis that cause painful sensations in the breast. A specialist is able to identify these changes and prescribe appropriate treatment or monitoring.
The gynecologist also teaches women how to examine their breasts. Knowing how to perform self-exams allows women to be more mindful of their health and monitor their breasts on a regular basis. This is an important skill that can help to detect changes early and seek medical attention in a timely manner.
Breast exams by a gynecologist fit into an integrative approach to women’s health. Gynecologists provide care not only for the reproductive organs, but also for other aspects of women’s health, including the mammary glands. This helps to warn patients of potential threats.
It is worth noting that every woman is unique and the level of risk of having cancer can vary. For example, women with a family history of breast cancer, genetic mutations, or other risk factors may be more susceptible to the disease. The gynecologist can tailor his or her approach to breast exams depending on the individual characteristics of each patient.
 What is serosometra
What is serosometra
Serotose in gynecology is a medical term that describes the presence of fluid in the abdomen or pelvis of a woman. This condition can be caused by a variety of reasons and requires careful medical observation and treatment.
Serotosis in gynecology is a condition that can be caused by a variety of reasons, including inflammation, tumors, and trauma. If you have symptoms associated with fluid in the abdomen, it is important to see a gynecologist for diagnosis and treatment. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner can help prevent complications and improve a patient’s quality of life.
Serous is a fluid that is secreted from the papillary glands of the cervix and vagina. This secretion contains various elements such as proteins, salts and cells, and its composition can change depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and various diseases.
Changes in the level and composition of serosa may indicate the presence of inflammation in the vagina or cervix. The study of serosa can help in assessing fertility because the composition of serosa changes during different phases of the menstrual cycle, which may be useful for couples planning a pregnancy. The composition of serosa may also change during pregnancy, and the serosometer can be used to monitor pregnancy and uterine health.
The use of serozometer in gynecology allows doctors and patients to obtain information about the condition of the female reproductive organ. This can be particularly useful when inflammatory conditions are identified or in preparation for pregnancy.
A serosometer is used to measure the level of serosa in vaginal secretion. The doctor inserts a serozometer into the patient’s vagina and takes a sample of serosa. This sample is then analyzed to determine its composition and level.
 Why does a gynecologist refer to a neurologist?
Why does a gynecologist refer to a neurologist?
Women’s health is a complex and multifaceted field, and sometimes problems related to gynecological conditions can have neurological aspects.
A common complaint among women is pelvic pain. These pain sensations can be associated with various gynecological conditions – endometriosis, inflammatory diseases, fibroids or ovarian cysts.
However, if the pelvic pain is chronic or vague and not associated with known gynecologic causes, the gynecologist may decide that a neurologist consultation is required. A doctor specializes in the study of the nervous system and can help identify neurological causes of pelvic pain, such as nerve compression or neuralgia.
Hormonal changes that occur during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can affect the body and cause neurological symptoms.
For example, some women may experience headaches, migraines, nervousness, or insomnia due to hormonal changes. In such cases, the gynecologist may refer the patient to a specialist to evaluate neurologic symptoms and recommend treatment.
Some gynecologic diseases can have an effect on the nervous system. For example, endometriosis can affect the nerves and cause chronic pain.
A gynecologist may refer for a consultation with a neurologist to find out how the gynecologic condition affects the nervous system and what measures can be taken to alleviate symptoms.
Many women may experience psychosomatic symptoms that are related to psychological conditions such as stress, depression or anxiety. These conditions can affect the nervous system and manifest themselves through physical symptoms. A gynecologist may recommend a consultation with a neurologist to evaluate the neurologic aspects of these symptoms.
The relationship between gynecologic and neurologic conditions can be complex and multifaceted. The decision to refer to a neurologist is made by the gynecologist based on symptoms, history and examination findings.
Collaboration between a gynecologist and a neurologist can help identify and address issues related to both areas of medicine and provide comprehensive care for women.
 How gynecology affects the bowel
How gynecology affects the bowel
The health of a woman and her reproductive organs is closely linked to the health of other organs and systems in the body, including the intestines. The hormonal changes that occur throughout a woman’s life, including the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and menopause, can have an impact on bowel function.
Changes in levels of female sex hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can affect bowel sensitivity and defecation frequency in some menstruating women.
Pregnancy can cause changes in the location and compression of organs in the abdominal cavity, which can lead to bowel compression and cause stomach and intestinal distress. Decreased estrogen levels during menopause can affect the intestinal mucosa and cause symptoms such as constipation.
Some gynecologic procedures can have an effect on the bowel. This applies to hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, which can alter the anatomical structure of the abdomen and impact bowel function.
Performing a transvaginal ultrasound scan can put pressure on neighboring organs, including the intestines, and cause discomfort.
Endometriosis can affect the intestines, causing pain, constipation, or diarrhea. Large uterine tumors can press on the bowel and cause symptoms associated with bowel disruption.
Gut health is closely related to the state of the microflora in the gut. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can affect the immune system and inflammation in the body. Gynecology can affect the gut microflora through antibiotic treatment and hormonal contraceptive methods.
Understanding the relationship between gynecology and gut health is an important aspect in ensuring a woman’s total health. Regular visits to your gynecologist, taking care of your hormone balance, and monitoring your gynecological conditions can help maintain and improve the health of both your gut and reproductive organs.
 When a gynecologist does an ultrasound
When a gynecologist does an ultrasound
Ultrasound has become a mandatory procedure in modern gynecology, which gives the opportunity to monitor the condition of female reproductive organs. Gynecologic ultrasound allows you to diagnose various diseases, monitor pregnancy and evaluate the female body.
It is often included in a woman’s regular checkup plan to detect changes in the pelvic organs early and ensure timely treatment.
If the patient has symptoms – lower abdominal pain, unusual discharge, irregular monthly cycles and others, the gynecologist may prescribe ultrasound for a more detailed diagnosis.
It is performed to evaluate the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes, which is necessary for infertility and treatment planning. The examination is a method of monitoring pregnancy, allowing to assess the development of the fetus, the condition of the placenta and identify possible anomalies.
It is used to evaluate the condition of the uterus, ovaries, and other female organs, which can be important when abnormalities, tumors, or other changes are suspected.
In the transabdominal method, the ultrasound transducer is guided over the surface of the patient’s abdomen. Pre-application of gel. In this way, the pelvic organs are examined.
The transvaginal variant is referred to as a more informative examination. When the transducer is inserted, it is possible to obtain clearer images, which allows you to assess the condition of the organs of the reproductive system.
The resulting image is analyzed for abnormalities, changes and pathologies. Based on the ultrasound results, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis and recommendations. If there are any abnormalities detected or the patient’s condition, additional tests or treatment may be performed.
A Doppler examination evaluates blood flow to diagnose abnormalities and tumors.
Gynecologic ultrasound is a powerful tool that is used to diagnose and monitor the condition of the female reproductive organs. It is a safe, affordable alternative to invasive diagnostic methods.
Regular visits to the gynecologist and fulfill his recommendations on ultrasound will help to maintain women’s health and timely detect possible changes and diseases.
 When a gynecologist gives a referral to a maternity hospital
When a gynecologist gives a referral to a maternity hospital
A maternity hospital is a specialized medical facility where women receive medical care during pregnancy and childbirth. The gynecologist, as a women’s health specialist, plays a key role in preparing pregnant women for childbirth and deciding whether to refer them to a maternity facility.
The main criterion for referral to a maternity hospital is pregnancy. Usually, a woman starts seeing a gynecologist as soon as the pregnancy is established. From the first weeks of pregnancy, the gynecologist monitors the woman’s condition and the development of the fetus.
The specialist determines the gestational age based on your last menstrual period and ultrasound results. Depending on the term and nature of the pregnancy, the gynecologist can decide when to refer a woman to a maternity hospital.
If complications or medical problems arise during the pregnancy, your doctor may decide on emergency hospitalization for maternity care. This can include conditions such as high blood pressure, premature labor, bleeding, and other complications.
In the case of a normal labor, the gynecologist recommends that a woman go to the birth center when contractions begin or when the pregnant woman feels that labor is beginning. A gynecologist can also provide guidance on how to proceed when labor begins.
Before referral to the maternity hospital, the gynecologist may perform additional testing and evaluation of the woman and fetus to make sure they are ready to deliver.
The specialist takes into account the individual characteristics and wishes of each pregnant woman. This includes the choice of anesthesia methods, birth plan, and other aspects.
The doctor provides information about the progress of the pregnancy, preparation for labor, signs that labor has begun, and other important aspects. This helps the pregnant woman feel confident and prepared for the upcoming event.
The decision to refer to a maternity hospital is made by the gynecologist based on many factors, including the gestational age of the pregnancy, the health of the woman and the fetus, the presence of complications, and the wishes of the pregnant woman. A gynecologist works with a woman to ensure a safe and comfortable birth by providing the necessary medical care and support.
After delivery, the specialist continues to care for the health of the woman and the newborn. At the birthing center, she is medically evaluated, and examinations and tests are performed to make sure she recovers normally after delivery. The gynecologist also schedules postpartum visits to assess the condition and healing of labor complications.
 Gynecological smear
Gynecological smear
Gynecological smear is one of the traditional procedures in gynecology, designed to determine the state of the female reproductive system and detect pathologies.
A smear allows you to determine what phenomena are predominant in the vagina. Changes in the balance of microflora can lead to infection or dysbiosis.
A smear allows you to determine what bacteria and tests inhabit the vagina. Normal microflora consists of lactobacilli, which help maintain vaginal health. Altered microflora indicates the presence of bacterial vaginosis or vaginal infections.
Vaginosis, vaginal candidiasis (fissures), and trichomoniasis can be found. This is important for accurate diagnosis and further treatment. Gynecological smears can be used to detect cellular changes that characterize a precancerous or cancerous condition in the cervix.
The specialist recommends annual or regular check-ups to monitor the patient’s condition. If you have symptoms such as dryness, burning, unusual discharge, lower abdominal pain, or unusual periods, your gynecologist may take a swab for diagnosis.
During pregnancy, a smear may be taken to monitor the vaginal microflora and identify factors that may be harmful to pregnancy.
An explanation of gynecologic smear taking is usually done at a gynecologist’s appointment. The doctor uses special medical equipment called a vaginal mirror to ensure safety inside the vagina.
A cotton swab and pre-brush are then used to take a sample from different areas of the vagina and cervix. The material obtained is subjected to laboratory examination.
After analyzing the smear, the specialist will measure the results and decide if any treatment is needed. If detected, may unexpectedly prescribe antibiotics or other antimicrobials. If cellular abnormalities are suspected, additional tests such as colposcopy or cervical biopsy may be performed.
 Mixed flora
Mixed flora
Mixed flora is a term that is often used in gynecology to describe the state of a woman’s vaginal microflora. This term indicates the presence of various types of microorganisms in the vagina, including bacteria, fungi, and other microbes.
A healthy vagina contains many different movements that coexist in dynamic balance. This microflora includes bacteria, the predominant ones usually being Lactobacillus, fungi of the genus Candida and other types of microbes. This set of devices plays a crucial role in maintaining vaginal health.
Changes in hormone levels, such as during menstruation, pregnancy or menopause, can affect the composition of the microflora. Taking antibiotics can upset the balance of the microflora, destroying beneficial bacteria and promoting the multiplication of pathogenic microbes.
The body’s defenses can affect the balance in the vagina. Decreased immunity can allow widespread spread of pathogens.
Changes in the composition of the flora can cause inflammatory processes in the vagina and cervix. Diagnosis of mixed flora in gynecology is usually made by swabbing and subsequent microbiologic analysis. If a microflora imbalance or infection is detected, the gynecologist will include treatment, including antibiotics, probiotics, or other medications.
If the smear reveals pathogenic reactions, the gynecologist may prescribe antibacterial or antimicrobial treatment to restore the balance of the microflora. Mixed flora should also be considered during pregnancy to prevent illnesses associated with possible infections.
Mixed flora in gynecology is a complex phenomenon, reflecting the composition of what occurs in the vagina. Understanding this concept is important for gynecologists as it focuses on the study and treatment of various gynecologic conditions.
Regular and gentle washing with gentle hygiene products can help maintain normal microflora. However, avoid over hygienizing as this can upset the balance.
The use of harsh soaps and showers, as well as scented showers, can negatively affect the composition of the microflora. Use neutral hygiene products.
Antibiotics should only be taken when prescribed by a doctor. Using a course of probiotics after antibiotics can help restore healthy microflora.
Stress can have a negative impact on health, including the composition of microflora. Relaxation and stress management techniques can be key.
 Femoflor screen
Femoflor screen
Femoflor Screen refers to an innovative research method designed to analyze the microflora of the vagina of women. This analysis helps to assess the state of the vaginal microflora and identify the presence of pathogens. It is of importance in obstetric and gynecologic practice and can be a useful tool for the diagnosis and treatment of various female diseases.
It is a biochemical analysis of a sample of vaginal microflora to determine the bacterial composition and level of diversity of microorganisms in the vagina. The assay is based on the examination of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, which allows the identification of the bacterial species present in the sample and their quantitative ratio.
The Femoflor Screen allows the detection of pathogens such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Candida spp. and various types of anaerobic bacteria that can cause vaginal infections. This is important for accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Analyzing the vaginal microflora helps to determine its condition, including the predominant bacterial species, diversity and level of beneficial microorganisms. Knowing this can be helpful in dealing with infertility problems and preventing recurrence of vaginal infections.
Determining the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics using the assay helps to select the most effective treatment for vaginal infections, as well as to prevent vertical transmission from mother to newborn.
Femoflor Screen is used in gynecology to diagnose and monitor vaginal infections, assess the state of microflora in various gynecological diseases and provide individualized treatment to patients.
In pregnancy, the test can help in preventing vaginal infections and early diagnosis of their occurrence. This is important to maintain the health of both mother and baby. It can be a useful tool in infertility research, as the state of the vaginal microflora can influence the success of conception.
The test is a modern method of analyzing vaginal microflora, which is important in obstetric and gynecological practice. This test helps diagnose and treat vaginal infections, assess the microflora and prevent pregnancy complications. With its help, gynecologists can develop individualized recommendations and treatment regimens for patients, which helps to maintain and restore women’s health.
 When a gynecologist prescribes hormones
When a gynecologist prescribes hormones
Gynecology is a medical specialty concerned with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of female reproductive diseases. In the course of practice, gynecologists often have to prescribe hormones as part of a comprehensive treatment for various conditions and diseases.
Hormonal medications may be used to correct irregular menstrual cycles, including periods that are too frequent or infrequent, abnormal bleeding, premenstrual tension syndrome, and dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation).
Hormones can be used in the treatment of women facing infertility problems related to ovulation disorders or other hormonal disorders. Medications such as clomiphene or gonadotropins can stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy.
Hormone therapy can be used to manage endometriosis symptoms such as pain and bleeding. Drugs containing hormones can decrease endometrial cell activity.
Gynecologists may prescribe hormones during menopause to relieve symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, insomnia and changes in vaginal microflora. Hormone replacement therapy can help improve women’s quality of life.
Hormones can be used to manage symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenopause, including mood disturbances, irritability, and physical pain.
Gynecologists may use hormone therapy to treat breast diseases such as mastitis, cysts, or fibroid breast disease.
Hormonal contraceptive methods such as oral contraceptives, patches, IUDs and injections are often prescribed by gynecologists to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
It should be noted that hormone therapy, like any other medical therapy, can come with risks and side effects. It is the gynecologist’s responsibility to carefully evaluate the patient and consider her medical and family history before prescribing hormonal medications. This helps minimize risks and maximize the safety of the treatment.
Hormone therapy plays an important role in the practice of gynecologists and is an integral part of the treatment and management of female reproductive diseases and conditions. Correct and individualized prescription of hormones can significantly improve the quality of life of women, help them achieve pregnancy in case of infertility, cope with unpleasant symptoms of menopause and other problems.
 Gastroenterology and acne
Gastroenterology and acne
Gastroenteritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. The main symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain and general malaise.
Recent studies have shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome may influence the development of inflammatory skin conditions, including acne. Gastrointestinal diseases, such as irritable bowel syndrome or dysbacteriosis, can affect the skin due to inflammation and increased mucosal permeability.
Inflammation plays a key role in the development of acne. Acne contains the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), which can affect inflammation in the body. Uncontrolled inflammation can be associated with imbalances in the microbiome and systemic inflammatory responses.
There is speculation that certain foods, such as high-calorie carbohydrates and dairy products, may influence the development of acne.
Some studies suggest that a diet high in sugar and dairy products may contribute to the inflammation associated with acne.
Patients with acne can benefit from reducing their intake of high-calorie carbohydrates and sugar, as well as reducing their intake of dairy products.
Adding probiotics to your diet can help restore the gut microbiome and reduce inflammation. It is important to identify and treat gastrointestinal conditions that may be affecting the skin. Stress and nervous system can also have an impact on skin conditions, including the development of acne. Stress can lead to changes in the gut microbiome and activation of inflammatory responses.
Regular consumption of fiber-rich foods and water can promote normal bowel function. Foods that contain prebiotics and are rich in dietary fiber can support a healthy microbiome.
The link between gastroenterological aspects and acne emphasizes the importance of ganzweid disease, gut microbiome and nutrition in maintaining skin health. Identifying individual factors and targeted treatment can help reduce the inflammation associated with acne.
 What hematology studies
What hematology studies
Hematology is a medical specialty that studies the properties and diseases of the blood, bone marrow, and inflammatory system. It is required in diagnostics to detect various hematopoietic and immunologic diseases.
What hematology studies
One of the main tasks of hematology is the study of the formation and development of hematopoietic cells, as well as their functions. Hematologists study the process of blood formation in the bone marrow, including the development of different cell lines such as red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. They hypothesize different stages of differentiation and mechanisms of regulation of the formation of these cells.
The major fields of hematology specialize in the analysis of blood composition, blood cell structure and function, blood clotting mechanisms, immunology, and hemostasis. Hematologists also practice transfusiology – the study of blood and blood substitute transfusions, their samples and their use in clinical practice.
Hematology evaluates a pathologic condition related to the blood and inflammatory system. This is done by analyzing and reviewing the different types of anemia, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, leukemia, lymphoma, and other cancers.
Hematologists perform laboratory tests such as blood, bone marrow, and inflammatory tissue tests to detect abnormalities and determine their type and stage.
One aspect of hematology is immunohematology, which evaluates blood grouping, matching, and its role in transfusion medicine. Physicians perform antibody tests related to hematopoiesis and immune studies and find laboratory diagnostic methods to detect immunohematologic diseases.
Hematology also plays an important role in the treatment of cancer. Physicians specialize in providing chemotherapy, immunotherapy, bone marrow transplants and other treatments for patients with leukemia, lymphoma and other diseases.
Hematology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of various cases related to blood and hematopoietic fibers. Some common blood disorders are associated with anemia (decreased hemoglobin or red blood cell count), thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count), leukemia (cancerous blood cells), and hemophilia.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of hematologic manifestations may involve blood transfusion, drug therapy, surgery, and bone marrow transplantation. Hematologists also routinely provide preventive care for diseases associated with regular weight loss and counsel patients on maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Hematology helps diagnose and detect diseases related to blood and hematopoietic fibers. The study of the structure and functions of the blood allows specialists to determine the presence of pathological processes, as well as prescribe the necessary methods of treatment.
Modern advances in hematology give high results in the treatment of diseases, improve the health and quality of life of patients. The latest technology can cure even the most serious diseases in this area.
 Gastroenterology – pharmacology without errors
Gastroenterology – pharmacology without errors
Gastroenterology and pharmacology are closely related in medicine. Taking modern medications for gastrointestinal diseases is a key aspect of success in the clinical practice of a gastroenterologist.
A gastroenterologist must perform a thorough evaluation of the patient and establish an accurate diagnosis of treatment prescription. In this way, mistakes and incorrect prescribing of medications can be avoided. All individual characteristics and possible allergic reactions to preparations are necessarily taken into account.
Pharmacologic groups of drugs have different mechanisms of action and are used for different indications. The gastroenterologist should choose the medication that is best suited for the patient’s particular condition.
The dosage of medication is acceptable according to the recommendations of the specialist and the instructions for the drug. The gastroenterologist should inform the patient about the possibility of side effects. Patients should know what symptoms to watch for and when to seek medical attention.
It is important to educate patients on taking medications correctly, following the dosage and regimen. Explaining treatment goals and expected outcomes to patients in detail increases patient cooperation and awareness.
Each patient is unique and treatment must be tailored to their individual needs and characteristics. Periodic evaluation of treatment results and response to medications allows for adjustments in therapy to achieve the best results.
The gastroenterologist should consider possible drug-drug interactions, especially when prescribing multiple drugs at the same time. It is important to know which medicines can strengthen or weaken each other to prevent unwanted effects.
Gastroenterology and pharmacology are interrelated in the treatment of GI diseases. Correct prescribing, choosing the right drugs, adhering to dosage, personalized approach and avoiding drug-drug interactions are crucial to successful therapy.
 Prevention of hematologic diseases
Prevention of hematologic diseases
Hematologic diseases significantly impair people’s health and quality of life. However, many of these diseases can be prevented or the risk of developing them can be reduced by taking appropriate preventive measures.
Preventive measures
Some of the most effective preventive measures include:
- A balanced diet rich in nutrients, including iron, vitamins (especially vitamin B12 and folic acid) and other micronutrients, helps prevent anemia and other hematologic disorders. Consumption of red meat, organic vegetables, eggs and fortified cereals is recommended;
- Exercise – to support the heart, improve circulation and reduce the risk of thrombosis. This includes walking, swimming, bicycling, and fitness;
- Refusal from bad habits, as they negatively affect the blood condition and can increase the risk of hematologic diseases.
Prevention of anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells in the blood decreases. Preventive measures in this case consist of:
- proper nutrition – eat foods rich in iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid to prevent deficiency of these substances and the development of anemia. Including meat, fish, nuts, vegetables and fruits in your diet can help maintain normal levels of these vitamins and minerals;
- hygiene – refuse common hygiene items such as toothbrushes and razors, which can be sources of infections, especially in the presence of hemolytic anemia or hemoglobinopathy.
Prevention of thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in blood vessels that lead to serious illness (stroke or heart attack). Preventive measures consist of:
- physical activity – helps improve circulation. It is recommended to take breaks while sitting or standing for long periods of time, especially when traveling for long periods of time;
- Weight control – being overweight increases the risk of thrombosis. Maintain a healthy weight by eating right and exercising;
- avoiding long-term use of hormonal medications – due to increased risk of thrombosis;
- avoiding contact with the environment that may contain lead. This applies to painted walls or soil.
Prevention of hematologic diseases prevents the development of serious illnesses. Healthy lifestyle, avoiding alcohol, cigarettes are key measures to reduce the risk of hematologic diseases. Regular visits to the doctor and following the recommendations of specialists will also help keep you healthy.
 Symptoms in gastroenterology
Symptoms in gastroenterology
The main task of gastroenterology is to recognize symptoms that indicate the presence of various pathologies. Symptoms characterize the primary indicator of the patient’s condition and help determine the next steps in therapy.
Painful or discomforting sensations in the abdominal region, especially in the epigastric zone (above the navel), determine various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It may be hypersensitivity to pressure, sharp pain, tumescence or aching sensation that requires differential diagnosis.
Dyspepsia is a general term that describes an uncomfortable feeling in the upper abdomen, including feelings of fullness, belching, nausea, and even vomiting. This symptom can be the result of various problems including gastritis, ulcers, reflux esophagitis and others.
Loss of appetite or, conversely, an excessive feeling of hunger may indicate gastrointestinal disorders. Changes in appetite can result from a variety of conditions, including infections, inflammation, and even cancerous processes.
Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing. It can result from structural problems such as strictures (narrowing), esophageal tumors, or muscle dysfunction. This symptom may require further investigations such as endoscopy.
Changes in stool frequency, consistency, or color can be associated with a variety of conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, or tumors. It is important to pay attention to any unfamiliar changes.
Symptoms play an important role in gastroenterology, helping physicians navigate the diagnostic process. If symptoms occur, especially if they are prolonged or worsen, you should see a qualified gastroenterologist for further evaluation and, if necessary, diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and adequate symptom management can significantly affect the prognosis and quality of life of patients.
 Why the hematocrit is low
Why the hematocrit is low
Pediatric gastroenterology is an important area of pediatrics because GI health plays a key role in the overall development and well-being of children.The pediatric GI tract has its own characteristics that distinguish it from the system in adults.
Newborns and breastfed infants may have functional digestive disorders such as colic, dysbiosis, and reflux. Children also have different anatomical structures of the GI tract, which makes the diagnosis and treatment of some diseases in children more specific. Some of the most common diseases include:
- Gastritis and ulcers – inflammation of the gastric mucosa (gastritis) and ulcerative lesions can occur in children of all ages;
- Gastroesophageal reflux – a condition in which stomach contents rise into the esophagus, which can cause heartburn and irritation of the esophageal mucosa;
- Chronic inflammatory bowel disease – include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. They are characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestines and can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications;
- Irritable bowel syndrome – often seen in teenagers and can cause abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea;
- Hepatitis – liver disease caused by viruses or other factors;
- Allergies and food intolerances – children may be hypersensitive to certain foods, which can cause allergic reactions or intolerances.
The diagnosis of pediatric gastroenterology emphasizes symptoms, the child’s medical history, and family history. Various clinical investigations such as general blood tests, biochemical levels and fecal examinations are performed.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis and severity of the disease. In some cases, dietary changes and nutritional therapy may be sufficient, while in others, medications or procedures are prescribed.
Prevention of pediatric gastroenterological diseases includes proper nutrition and lifestyle, regular medical checkups and immunizations, and avoiding contact with infectious agents.
Parents’ awareness of a proper diet, commitment to a healthy lifestyle and timely referral to a specialist can provide optimal conditions for the healthy development of children and prevention of gastroenterological problems.
 Pediatric gastroenterology
Pediatric gastroenterology
Pediatric gastroenterology is an important area of pediatrics because GI health plays a key role in the overall development and well-being of children.The pediatric GI tract has its own characteristics that distinguish it from the system in adults.
Newborns and breastfed infants may have functional digestive disorders such as colic, dysbiosis, and reflux. Children also have different anatomical structures of the GI tract, which makes the diagnosis and treatment of some diseases in children more specific. Some of the most common diseases include:
- Gastritis and ulcers – inflammation of the gastric mucosa (gastritis) and ulcerative lesions can occur in children of all ages;
- Gastroesophageal reflux – a condition in which stomach contents rise into the esophagus, which can cause heartburn and irritation of the esophageal mucosa;
- Chronic inflammatory bowel disease – include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. They are characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestines and can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications;
- Irritable bowel syndrome – often seen in teenagers and can cause abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea;
- Hepatitis – liver disease caused by viruses or other factors;
- Allergies and food intolerances – children may be hypersensitive to certain foods, which can cause allergic reactions or intolerances.
The diagnosis of pediatric gastroenterology emphasizes symptoms, the child’s medical history, and family history. Various clinical investigations such as general blood tests, biochemical levels and fecal examinations are performed.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis and severity of the disease. In some cases, dietary changes and nutritional therapy may be sufficient, while in others, medications or procedures are prescribed.
Prevention of pediatric gastroenterological diseases includes proper nutrition and lifestyle, regular medical checkups and immunizations, and avoiding contact with infectious agents.
Parents’ awareness of a proper diet, commitment to a healthy lifestyle and timely referral to a specialist can provide optimal conditions for the healthy development of children and prevention of gastroenterological problems.
 Situational challenges for the hematologist
Situational challenges for the hematologist
Hematology refers to the field of medicine that deals with the study of blood, hematopoietic organs, and related diseases. Hematologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of anemia, hemophilia, leukemia, and many others. In their practice, hematologists are faced with a variety of situations and challenges that require quick and competent solutions.
Diagnosis and treatment of anemia
One of the main tasks of a hematologist is to diagnose and treat anemia. Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, which can lead to a decrease in oxygen supply to the tissues.
A specialized specialist should be able to correctly interpret the results of special tests to determine the cause of anemia and develop an appropriate plan of treatment measures, consisting of taking iron preparations, vitamins, medications.
Hemophilia therapy
Hemophilia refers to hereditary diseases characterized by blood clotting disorders. Patients with hemophilia have an increased tendency to bleed and require specialized treatment. Specialists should be able to diagnose the disease, monitor the level of clotting factors and prescribe treatment to normalize this condition.
Treatment of oncological diseases
Leukemia is one of the serious cancers characterized by abnormal development of blood cells. Physicians must be able to diagnose different types of leukemia, administer chemotherapy treatments, immunotherapy, and bone marrow transplants. They evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and monitor the patients’ condition.
The main goals of hematologists are
Specialists often encounter situations where patients need blood or blood components. They assess the need and indications for blood transfusion, select the appropriate blood component, monitor transfusion responses, and resolve problems that arise.
Hematologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of various disorders of the blood clotting system, such as thrombophilia or hemorrhagic disorders. They assess the risks and decide whether anticoagulant therapy or other measures are needed.
The situational challenges faced by hematologists require a wide range of knowledge, skills, and experience. They must be able to correctly diagnose various blood disorders, select appropriate treatments and provide proper therapy to patients. The work of a hematologist greatly improves the quality of life for patients with blood disorders.
 Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a special protein found in red blood cells (red blood cells) that performs an important function in the body – carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and back again. However, some people have problems with hemoglobin levels. In this situation, diagnosis and therapy is necessary.
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin consists of two parts: the globin (protein) part and the heme (iron) part. Genetic changes or mutations can lead to various forms of hemoglobin pathology, which impairs its function. Such a condition needs to be monitored and appropriate therapy provided.
Hemoglobin pathology
Hemoglobin abnormalities are often associated with genetic changes that affect its structure and function. One of the best known forms of hemoglobin abnormality is hemoglobinopathy, which can be inherited from parents. Some known hemoglobinopathies include:
- Spherocytosis: A genetic disorder in which red blood cells take on a spherical shape instead of the usual disc shape. This leads to increased red blood cell destruction and anemia.
- Hemoglobin C: This is a genetic change in hemoglobin that affects the structure of the globin chain. As a result of this change, red blood cells take on a sheared shape and have an increased tendency to clot and form blood clots.
- Hemoglobin E: This is another type of hemoglobin genetic alteration that is found in some regions of Southeast Asia. When hemoglobin E is present, hemoglobinopathies such as beta-thalassemia or a combination of hemoglobin E and thalassemia may develop.
Varieties of hemoglobin abnormalities
Hemoglobin pathology can be classified based on various parameters such as chain type, presence or absence of alpha or beta chain, and presence or absence of mutations. One of the most common variants is the classification based on globin chains, which includes the following forms of hemoglobin pathology:
- Alpha thalassemia – associated with a deficiency of the alpha globin chain. This can lead to a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin or a change in its structure, which can cause anemia.
- Beta-thalassemia – associated with a deficiency or alteration of the beta-globin chain. It can be divided into two main forms: beta thalassemia major (severe form) and beta thalassemia minor (mild form).
- Sickle anemia – results from the presence of a hemoglobin S mutation. This leads to the formation of abnormal forms of hemoglobin, which cause sickle-shaped deformation of red blood cells and the occurrence of various complications.
Diagnostic methods
Hemoglobin abnormalities can manifest with a variety of clinical signs including anemia, increased vulnerability to infections, chronic fatigue, jaundice, and others. Various diagnostic methods are used to make a diagnosis and determine the specific type of hemoglobin abnormality:
- Blood tests: Examination of hemoglobin, red blood cell count, iron levels and other indicators helps to identify the presence of anemia and suspected hemoglobin abnormalities;
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis: This method can separate the different forms of hemoglobin and determine the presence of abnormal hemoglobins;
- Genetic tests: Allows to detect the presence of mutations in the hemoglobin gene and determine the specific type of pathology.
Diagnosis of hemoglobin abnormalities includes blood tests, hemoglobin electrophoresis, and genetic tests. Understanding the pathology helps in providing early diagnosis and effective management of these diseases, which helps in improving the prognosis and quality of life of patients.
 Methods of treatment of gastroenterological diseases
Methods of treatment of gastroenterological diseases
Gastroenterologic diseases encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment of such diseases requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the patient’s characteristics and the type of disease.
Medication treatment is carried out with the help of appropriate medications. Antacids and proton pump inhibitors are used to reduce the acidity of gastric juice and treat canker sores.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used for inflammatory bowel disease. Probiotics and microbiome restoring drugs are used to treat dysbiosis and restore healthy microflora.
Endoscopy allows you to visualize the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract and perform diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Endoscopic mucosal resection is used to remove precancerous changes and small tumors.
Banding, sclerotherapy, and coagulation are used to stop bleeding from the esophagus and stomach. Surgery may be necessary for complicated ulcers, intestinal polyposis, cancer, and other conditions. Laparoscopic and minimally invasive techniques allow for a shorter rehabilitation period.
Biologic drugs such as antibodies to cytokines and receptors are used to treat chronic inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
These drugs have a targeted effect on immune processes and help reduce inflammation.
Microbiome transplantation is an innovative technique involves the transfer of healthy microflora from donor samples into the patient’s gut. It can be used to treat a number of conditions such as recurrent Clostridium difficile infection and other diseases associated with microflora imbalance.
The use of enzyme preparations helps to improve digestion in patients with insufficient pancreatic function. These medications contain digestive enzymes that help break down food and improve nutrient absorption.
Modern diagnostic techniques such as endoscopic ultrasonography and capsule endoscopy provide a more detailed view of the gastrointestinal tract. Genetic studies can identify predisposition to various gastroenterologic diseases.
Current treatments for gastroenterologic diseases continue to evolve with the latest medical advances and innovations. Individualized approach, comprehensive selection of methods and medications, as well as the use of advanced technologies in diagnosis and treatment, allow more effective management of a variety of GI conditions and improve the quality of life of patients.
 Diet number 1
Diet number 1
Diet #1 was designed to ease digestion and reduce the strain on the gastrointestinal tract. It is a complementary treatment for various diseases of the stomach and duodenum.
The diet may be prescribed to patients with various gastric and duodenal diseases such as acute and chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastroenteritis, and reflux esophagitis.
It is also used in the postoperative period after removal of part of the stomach or other surgical procedures.
One of the main goals is to reduce irritation of the gastric mucosa and decrease pain and discomfort in patients with gastritis and peptic ulcer disease.
The special menu is aimed at preventing exacerbations of chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum, as well as preventing complications after surgical interventions.
The diet is designed to provide the essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals the body needs to maintain optimal health and organ function.
The diet involves the exclusion from the diet of food that can irritate the gastric mucosa. This applies to spicy, fried, smoked, fatty foods, as well as chocolate, coffee and alcohol. The diet involves frequent meals in small portions.
The diet includes easily digestible foods, preferably boiled or stewed to simplify digestion. It is advisable to avoid coarsely ground foods and spicy carbohydrate porridge, and prefer puréed meals and liquid soups.
Diet is an effective means in the treatment and prevention of diseases of the stomach and duodenum. The prescription of the diet is carried out by a doctor-gastroenterologist, taking into account the diagnosis and condition of the patient. Proper adherence to it contributes to optimal treatment outcomes.
 Diet number 2
Diet number 2
Diet #2 is one of the medical diets designed to treat and maintain gastrointestinal (GI) health. It is used in gastroenterology to improve digestion and ease the GI tract.
Diet No. 2 is used to treat patients with various GI diseases such as acute gastroenteritis, dyspepsia, chronic gastritis, colitis, as well as for postoperative recovery after surgical interventions on the GI tract.
The main purpose of diet No. 2 is to facilitate digestion, reduce the load on the GI tract and prevent irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs.
Diet #2 involves the consumption of easily digestible foods such as porridge on water, broths, lean meat and poultry, soft fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products.
Spicy and fatty foods can irritate the mucous membrane of the GI tract, so they are excluded from the diet of diet No. 2.
Diet #2 recommends eating foods that minimally traumatize the walls of the GI tract. Thus, food should be boiled, stewed or pureed to aid digestion.
In some cases, in the presence of lactose intolerance or allergy to dairy products, the diet of diet No. 2 may exclude or limit their consumption.
Diet #2 can be prescribed to patients with various gastrointestinal diseases such as gastroenteritis, chronic gastritis, colitis, gastric or duodenal ulcers.
Also, diet No. 2 can be recommended to patients after GI surgery to facilitate the rehabilitation period and prevent complications.
Children with GI diseases may also be prescribed diet #2, taking into account their age and needs.
Diet is an effective tool in treating and restoring gastrointestinal health. Its basic principles include easy digestibility, gentle cooking, and the exclusion of spicy and fatty foods. The prescription of diet No. 2 is carried out by a doctor-gastroenterologist, taking into account the diagnosis and condition of the patient, and its proper observance contributes to optimal results in the treatment and maintenance of GI health.
 Diet number 3
Diet number 3
To improve digestion and maintain gastrointestinal health, gastroenterologists often prescribe diet #3. It is used to treat and prevent various intestinal diseases and improve the functioning of the GI tract.
The diet is designed for patients with various diseases of the large intestine and rectum such as chronic colitis, diverticulosis, irritable bowel syndrome and others.
Its main purpose is to facilitate digestion, reduce irritation of the intestinal mucosa and prevent exacerbations of diseases.
The diet is also used during post-operative recovery from bowel and rectum surgery.
The menu includes foods containing soluble and insoluble dietary fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, cereals, which help normalize digestion and improve intestinal peristalsis.
Spicy, fatty and fried foods can irritate the intestinal mucosa, so they are limited or eliminated from the diet. The diet involves eating food that does not traumatize the intestinal walls, so it is recommended to eat vegetables and fruits in boiled, stewed or pureed form.
In some cases, it is possible to avoid dairy products, especially in the presence of lactose intolerance or milk allergy. The diet may be recommended for patients after bowel or rectum surgery to ease the recovery period and prevent complications.
Children with diseases of the large intestine are prescribed it, taking into account the age characteristics. It is an effective tool in treating and maintaining the health of the large intestine and rectum. The basic principles of the diet include richness in dietary fiber, avoidance of spicy and fried foods, mechanical sparing, and moderate restriction of dairy products.
 Diet number 4
Diet number 4
Diet #4 is considered one of the most effective for the therapy of patients who have intestinal diseases. It is used to cure the disease as well as reduce the symptoms.
The diet shows high results in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and other diseases. It is necessary to reduce the inflammatory process and irritation of the mucous membrane.First of all get rid of diarrhea, bleeding.
The diet excludes or restricts certain foods. It is necessary to refuse spicy, fatty, smoked foods, as well as alcohol.
The menu consists of foods that do not traumatize the intestinal mucosa. The diet includes foods rich in soluble and insoluble dietary fiber. They are found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, cereals, which help to improve intestinal peristalsis and normalize digestion.
Children who have chronic inflammatory bowel disease may also be prescribed a diet individually.
Diet #4 is an effective tool in treating and maintaining health in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. The right menu for a short period of time will help to cope with the disease and return to a normal life regime.
The prescription of diet No. 4 is carried out by a doctor-gastroenterologist, taking into account the diagnosis and condition of the patient, and its proper observance contributes to achieving optimal results in the treatment and maintenance of GI health.
 Diet number 5
Diet number 5
Nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of gastroenterologic diseases. In exacerbation or chronic form, specialists prescribe diet No. 5 for the fastest recovery of body functions.
To whom diet No. 5 is prescribed
It can be prescribed to different groups of patients depending on their medical conditions:
- with chronic gastritis – to reduce irritation of the gastric mucosa, reduce pain;
- with gastric and duodenal ulcers – to reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid, heal ulcers and prevent exacerbations;
- with cholecystitis and gallstone disease – to improve the production and excretion of bile, prevent the formation of new stones and reduce the risk of biliary colic;
- after gallbladder removal – to adapt the body to the absence of the organ.
The diet helps to maintain an optimal state of the stomach, intestines and biliary tract, which helps to normalize digestion and prevent complications.
The menu helps unload the liver and improve its function, which is especially important for patients with gallstone disease and cholecystitis. The diet helps to reduce various symptoms such as abdominal pain, belching, heartburn, constipation or diarrhea.
Regular adherence to a healthy menu helps prevent exacerbations of chronic GI and biliary tract diseases, which reduces the risk of complications and improves disease prognosis.
One of the main features is to limit the intake of fats, especially of animal origin, which can impair the liver and biliary tract. That being said, the diet promotes the use of polyunsaturated fats such as olive oil and vegetable oils, which are beneficial to health.
Obligatory is the refusal of spicy seasonings and spices, as they can irritate the mucous membrane of the GI tract and aggravate the symptoms of diseases. It is recommended to refuse spicy and fatty dishes, replacing them with more gentle versions.
It involves eating regular meals in small portions. This helps digest food more efficiently and reduces the strain on the GI tract. It is recommended to eat 4-5 meals throughout the day with equal intervals between them.
Also limit salt intake, which helps to reduce fluid retention in the body and reduce the load on the kidneys and heart. You need to increase your intake of vegetables, fruits, greens and dairy products, which provides the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals to function properly.
Children suffering from GI or gallbladder disease may also be recommended this diet, taking into account their age and food preferences.
The diet aims to improve the digestive system, reduce symptoms and prevent exacerbations. The diet is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, taking into account the diagnosis and condition of the patient, and its proper adherence contributes to optimal results in treatment and health maintenance.
 Hematologist consultation
Hematologist consultation
Consultation with a hematologist is an important step in the diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders. The main purpose of consultation with a specialized specialist is to obtain expert opinion and recommendations on issues related to blood diseases.
Objectives of the consultation
Patients may see a hematologist for a variety of reasons. It may be associated with suspected anemia, thrombosis, hemophilia, hemoblastosis, and other hematopoietic disorders.
A hematologist performs a detailed examination, analyzes the patient’s medical history and performs the necessary tests to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the best treatment.
Prior to a consultation with a hematologist, it is recommended that the patient prepare to ensure the most effective and informative discussion of their condition.
It is important to gather all medical certificates, including previous blood tests, examination results and consultations with other specialists. It is also helpful to prepare a list of questions that the patient wants to discuss with the hematologist. This will make more efficient use of counseling time and allow you to get the information you need.
Hematologist consultation
The patient talks about his or her symptoms and their duration. It is also important to discuss your medical history, including previously diagnosed conditions and treatments received.
The hematologist will evaluate the blood test results provided, examinations and consultations with other specialists. He or she may request additional tests or repeat tests to get a more complete picture of the disease.
The hematologist will provide a diagnosis based on the data collected and the results of the tests. He or she will discuss treatment options with the patient, including drug therapy, surgery, blood transfusion, bone marrow transplantation, and other methods. Information will also be given about the prognosis of the disease and possible complications.
The hematologist will make recommendations for the care and management of the disease. These may include recommendations for lifestyle changes, taking medications, regular check-ups, and taking special precautions.
The hematologist can also offer follow-up and support afterward to help the patient cope with the disease.
A consultation with a hematologist provides patients with expert opinion, guidance and support regarding their disease. Being prepared for the consultation and openly discussing issues with the hematologist will help the patient get the most out of the consultation and ensure more successful treatment.
 Prevention of hepatologic diseases
Prevention of hepatologic diseases
Hepatologic diseases related to the liver are a serious health problem for many people. They can lead to chronic inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer. However, many hepatologic diseases can be prevented or their progression limited with effective prevention.
Immunization
Viral hepatitis (hepatitis A, B, C, D and E) is one of the most common causes of hepatologic disease. Vaccination against viral hepatitis is one of the key measures in prevention.
Hepatitis A and B vaccines are effective and safe, and are recommended for individuals at risk. Vaccination helps prevent infection with hepatitis viruses and reduce the risk of developing chronic hepatologic diseases.
Observing safety in contact with blood
Infection with hepatitis B and C viruses can occur through contact with contaminated blood or other infected fluids. To prevent hepatologic disease, it is important to follow safety precautions when handling blood.
Only disposable instruments should be used and the principles of medical sterility should be observed when administering injections. It is very important to make sure that the beauty salon or tattoo parlor adheres to safety and hygiene standards when using sharp instruments. Instruments used must be sterilized or disposable.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
A healthy diet and regular physical activity play an important role in preventing liver-related diseases. The diet should consist of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat proteins. You should also limit your intake of foods rich in fats, sugar and salt. Regular physical activity helps you maintain a healthy weight and overall fitness, which contributes to overall liver health.
Alcohol abuse is an important risk factor for the development of hepatologic diseases such as cirrhosis. To prevent such diseases, it is recommended to limit alcohol consumption or abstain from it completely.
Prevention of liver disease is an important aspect of a healthy lifestyle. Getting vaccinated against viral hepatitis, being safe when handling blood, limiting alcohol consumption, eating a healthy diet, and being physically active are all measures that can help reduce the risk of developing hepatitis-related diseases and keep your liver healthy.
 Diagnosis of gastroenterological diseases
Diagnosis of gastroenterological diseases
A physical examination is the first step in diagnosis. The gastroenterologist listens carefully to the patient’s complaints, asks questions about the nature of symptoms, their duration and associated factors. Particular attention is paid to the medical history as it may contain important information about previous illnesses, surgical procedures, and family history. Diagnosis consists of:
- general blood test – allows you to identify inflammatory processes and anemia, which often accompany gastroenterological diseases. Blood may also be analyzed for markers of hepatitis and other infections. Biochemical blood test provides information about the functional state of the liver, pancreas and other GI organs;
- endoscopy is a key method for diagnosing gastroenterologic diseases. A gastroenterologist uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) to examine the inside of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. This allows for the detection of ulcers, tumors, inflammation and other pathologies;
- colonoscopy – allows you to examine the large intestine area and detect polyps and other changes;
- ultrasound – used to evaluate the liver, gallbladder, pancreas and other organs;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging – used for additional evaluation of GI organs and surrounding tissues.
Some gastroenterologic diseases require functional tests to detect specific abnormalities. For example, the lactose test is used to detect lactose intolerance, and manometry is used to measure esophageal pressure and motility.
A biopsy provides tissue samples for laboratory analysis to help establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the nature of the pathology, including cancer cells.
To diagnose infectious diseases such as Helicobacter pylori (which causes stomach ulcers), gastroenterologists may use a variety of tests, including a breath test, blood or tissue samples.
Sometimes gastroenterologic symptoms can be related to allergies or intolerances to certain foods. In this case, specialized tests are performed to identify the allergens or food components causing the reaction.
Each patient requires an individual approach, and the gastroenterologist, based on the collected data, determines the most appropriate methods of diagnosis. Early detection and proper identification of gastroenterologic diseases allow you to timely start treatment and prevent the development of complications. Regular preventive checkups and following a healthy lifestyle also play an important role in maintaining a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
 Clinical guidelines in gastroenterology
Clinical guidelines in gastroenterology
Clinical guidelines in gastroenterology are a key tool to ensure high quality medical practice. They are a set of recommendations and protocols developed based on the best scientific evidence and experience in the field of gastroenterology.
Clinical guidelines are systematized approaches to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of patients with various gastroenterological diseases.
They are based on scientific research, randomized clinical trials and practitioner experience. Clinical guidelines provide specific protocols for the diagnosis of various diseases such as peptic ulcer disease, gastritis, Crohn’s disease, and others.
They describe not only the necessary diagnostic methods, but also identify signs and symptoms on the basis of which additional investigations should be initiated.
Clinical guidelines define optimal treatments for various gastroenterologic conditions. These may include pharmacologic therapies, surgical techniques, nutritional therapy, rehabilitation, and next steps in patient monitoring.
An important feature of clinical guidelines is the consideration of individual patient characteristics and disease specificity. The guidelines provide individualized treatment planning to allow for a variety of factors including age, gender, comorbidities, and risk.
Clinical guidelines are a valuable tool in gastroenterology, providing a standardized and effective approach to the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
They help professionals make informed decisions based on scientific evidence and the experience of colleagues and contribute to improving the quality of care for patients with gastroenterologic diseases.
Clinical guidelines in gastroenterology are the basis for optimal management of patients with various gastrointestinal diseases.
They provide standards of diagnosis and treatment, taking into account scientific evidence, experience and the individual characteristics of each patient. Applying current guidelines and discussing them with patients together are key to achieving the best outcomes in gastroenterology practice.
 Pediatric hematology
Pediatric hematology
Pediatric hematology is a branch of medicine that specializes in the study of blood, hematopoietic organs, and related diseases in children. Pediatric hematology has its own peculiarities, as children may have differences in blood physiology and pathology compared to adults.
Anemia in children
Anemia is one of the most common diseases in pediatric hematology. It is characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, which can lead to a decrease in oxygen supply to the tissues.
In children, anemia can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as iron deficiency, vitamin deficiencies (such as vitamin B12 or folic acid), genetic disorders, chronic diseases, or nutritional disorders.
Pediatric hematologists diagnose anemia in children, determine the cause, and prescribe appropriate treatment, which may include taking iron preparations, vitamins, or other medications.
Hemophilia in children
Hemophilia is a rare inherited disorder characterized by a blood clotting disorder. Children with hemophilia have an increased tendency to bleed, both internally and externally.
Pediatric hematology deals with the diagnosis of hemophilia in children, monitors the level of clotting factors and prescribes appropriate replacement therapy with clotting factor preparations. Teaching parents and children how to self-manage and prevent bleeding is also an important aspect.
Hemolytic anemia in children
Hemolytic anemias are a group of diseases in which the destruction of red blood cells occurs earlier than usual. In children, hemolytic anemias can be congenital or acquired. They can be caused by genetic disorders, immunologic reactions, infections, or other factors.
Pediatric hematology is to diagnose hemolytic anemias in children, determines the cause and extent of red blood cell destruction. Specialists prescribe appropriate treatment, which may include taking medications to help reduce the destruction of red blood cells, blood transfusion or bone marrow transplantation.
Hemoblastosis in children
Hemoblastoses are a group of malignant diseases affecting hematopoietic cells. This is true for leukemia (cancer of the blood) and lymphoma (cancer of the lymphatic system). In children, hemoblastoses are more common than in adults and require a special approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Pediatric Hematology performs extensive laboratory tests to diagnose hemoblastosis in children, including blood tests, molecular and genetic tests. Treatment in children may consist of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and bone marrow transplantation.
Thrombosis in children
Thrombosis is the formation of blood clots (blood clots) in blood vessels that lead to impaired blood flow and tissue damage. In children, thrombosis can be caused by hereditary disorders, clotting disorders, immunologic reactions, trauma, or other factors.
Pediatric Hematology provides diagnosis of thrombosis in children, including laboratory tests, vascular ultrasound and other techniques. Treatment of thrombosis in children may include taking anticoagulants, regulating the activity of clotting factors, and other methods.
Pediatric hematology plays an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of various blood disorders in children. Early diagnosis and timely treatment can improve the prognosis of the disease and the quality of life of children.
 Preventive recommendations for gastritis and ulcers
Preventive recommendations for gastritis and ulcers
Gastritis and gastric and duodenal ulcers are common gastroenterologic findings. Proper preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of disease.
Alcohol and nicotine affect the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the risk of gastritis and ulcers. The best solution is to give up bad habits.
Limit your intake of foods that can irritate the gastric mucosa. Preference should be given to low-fat dairy products, store-bought fish, lean meat.
Include vegetables, fruits, and grains in your diet that are rich in fiber. This helps to improve digestion and maintain a healthy GI tract. Your diet should include many different foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains (buckwheat, oatmeal), dairy products, store-bought fish, seafood, low-fat meats (chicken, turkey), nuts, seeds, and try to keep your diet full of vitamins and minerals.
Too much salt can retain fluid and cause discomfort. Watch your salt intake, use spices to flavor your dishes.
Stress can be a catalyst for the development of gastritis and ulcers. Mastering relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing helps reduce stress levels that affect the GI tract. Ensure you get enough time to sleep. Lack of sleep can reduce symptoms and increase the risk of gastritis and ulcers.
Pay attention to the quality and freshness of the food. Avoid consuming expired foods, especially seafood. Wash your hands before eating to catch a dangerous virus. Try to eat your meals at the same time each day. Snacking between main meals will help reduce the strain on your stomach.
If you are diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori infection, follow your doctor’s recommendations for this infection to prevent the development of gastritis and ulcers.
Excessive caffeine consumption can be safe. Coffee is drunk in limited quantities to reduce the risk of unpleasant symptoms.
Preventive advice for gastritis and ulcers is an important component of a healthy lifestyle. Following a proper diet, managing stress, avoiding bad habits will prevent the development of gastrointestinal diseases.
 Hospitalization in gastroenterology
Hospitalization in gastroenterology
Hospitalization in gastroenterology is an important step in the management and treatment of various gastrointestinal diseases. It provides the opportunity for detailed diagnosis, effective treatment and monitoring of patients with serious gastroenterologic conditions.
Hospitalization allows the medical staff to assess the patient’s condition in more detail, perform the necessary diagnostic tests and observation. This provides intensive therapy and monitoring.
Hospitalization provides the opportunity for immediate adjustment for complications and rapid change of therapy. Severe stages of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis need intensive treatment and monitoring.
Complications of peptic ulcer disease, bleeding, ulcers with perforation, require urgent intervention. Suspicion of cancer, tumors of the esophagus, stomach or intestines, are also indications for hospitalization.
Next, the patient’s condition is assessed. The doctor performs a detailed history, physical examination and necessary diagnostic tests. Based on the diagnostic results, an individualized therapy and monitoring regimen is developed.
Patients are supervised by trained staff who monitor the condition. Gastroenterologists watch for possible complications and respond immediately.
When a stable condition is achieved, the patient is prepared for discharge with instructions for home care and continued treatment.
Hospitalization in gastroenterology plays an important role in the effective management and treatment of various GI diseases. It allows for a more detailed assessment of the patient’s condition, to provide the necessary treatment, and to ensure that the patient’s health is monitored.
 Hematology in pregnancy
Hematology in pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life when there are strong changes in the environment. Hematology is the science that studies blood and its changes. Through diagnosis and timely treatment, it is possible to maintain maternal health and normal fetal development.
Hematologic diseases in pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period in which a woman experiences an increase in blood volume and a change in blood composition. Hematology in pregnancy is necessary because changes in the blood can be associated with various abnormalities in the health of the mother and child.
Anemia, characterized by low hemoglobin levels in the blood, is one of the most common problems found in pregnant women. The disease may be caused by a deficiency of iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12. The hematologist will perform blood tests and, if necessary, prescribe the patient to take iron or vitamin complexes.
Pregnancy may come with an increased risk of thromboembolic complications such as venous thrombosis or embolism. A hematologist can assess a patient’s individual risk and recommend preventive measures such as anticoagulant therapy or the use of compression stockings to reduce the risk of clotting.
Result-conflict occurs when the mother and baby do not have the same Rhesus conflict. This can lead to antibody formation and health risks to the fetus. A hematologist will perform the necessary tests and monitoring to determine if there is a Rh conflict and take steps to prevent or treat side effects.
Some women may have a decrease in the number of platelets in their blood during pregnancy. This causes the blood to clot and there can be a problem with blood clots. The hematologist will monitor the platelet count and take steps to adjust the platelet count if necessary.
In pregnancy, there is a risk of bleeding, especially with complications such as placenta previa or placental abruption. In this case, it is important to have regular consultations with a hematologist, especially for previously diagnosed hematologic conditions or the discovery of new blood problems. Regular monitoring will ensure the safety of the mother’s health during pregnancy.
 Gastroenterology – when to refer
Gastroenterology – when to refer
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract plays an important role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Unpleasant GI symptoms can affect a person’s overall health and quality of life.
The most common gastrointestinal problem can be called abdominal pain. Pain sensations can vary in intensity, manifest in different parts of the abdomen and be accompanied by different sensations: dull, stabbing, spasmodic pain or burning. The pain may occur after eating, with certain movements, or at bedtime.
Frequent constipation or diarrhea can be a sign of GI disorders. Constipation may be related to a lack of dietary fiber, lack of fluids, or low physical activity. Diarrhea can be caused by infections, food poisoning, stress, or intolerance to certain foods.
A constant feeling of hunger or, conversely, apathy to food may indicate problems with the GI tract. In children, this may manifest as food refusal or selective eating.
A constant sensation of burning mucus in the esophagus and regurgitation are signs of possible gastroesophageal reflux, when stomach contents rise into the esophagus.
Constant belching or a feeling of bitterness in the mouth after eating can be the result of an insufficient sphincter between the esophagus and stomach. Changes in taste preferences and the occurrence of strange desires to eat unusual foods may be due to deficiencies in certain nutrients or minerals.
A constant feeling of fatigue, even with little exercise, as well as unexplained weight loss may be the result of chronic GI conditions such as inflammatory diseases.
With such problems, it is very important to see a gastroenterologist in time for diagnosis and treatment. However, it should be remembered that many of the above symptoms may be characteristic of other diseases, so an accurate diagnosis can be made only after undergoing the necessary laboratory tests.
 Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is an important diagnostic tool in gastroenterology, allowing direct visualization of the internal structures of the digestive system. This method has a great role in detecting various diseases and pathologic changes in the stomach and esophagus.
Gastroscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible endoscope (gastroscope) is inserted through the patient’s mouth to visualize the internal structures of the stomach and esophagus. The gastroscope is equipped with a camera on the end that transmits the image to a monitor, allowing the doctor to examine the mucous membranes in detail.
Gastroscopy allows visualization of ulcers on the mucosa of the stomach or duodenum. It also allows you to detect inflammation and irritation of the esophagus due to backflow of gastric contents.
Gastroscopy allows visualization of tumors, polyps, and other unusual masses. Gastroscopy with biopsy can detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria associated with the development of peptic ulcer disease.
The procedure allows you to assess the degree of inflammation of the mucosa. During a gastroscopy, tissue samples (biopsy) may be taken for further analysis. A biopsy can determine the nature of the pathologic changes, including determining the presence of cancer cells.
Gastroscopy can be used to screen high-risk groups of people, such as early detection of gastric cancer in those with a hereditary predisposition.
Gastroscopy plays a central role in the diagnosis of gastroenterologic diseases. This method allows not only to visualize changes in internal structures, but also to perform biopsies for further analysis. Gastroscopy helps provide more accurate and earlier diagnosis, which is the basis for effective treatment and management of patients with GI diseases.
 Hepatology and the liver
Hepatology and the liver
Hepatology occupies a special place in medicine. This is because the liver is one of the main organs in the human body, performing many important functions. Hepatology plays a key role in the diagnosis, therapy and prevention of liver disease as well as in research.
Diagnosis of hepatologic diseases
Hepatologists have many kits to evaluate liver function and detect pathologic changes. They use various methods of investigation – biochemical blood tests, liver ultrasound, CT and MRI, liver puncture biopsy and others to make an accurate diagnosis and degree of liver damage.
Treatment methods for hepatologic diseases
Every day, hepatologists develop treatment plans based on the type and stage of the disease. They may prescribe medications, perform procedures, or recommend surgery, including liver transplantation. Hepatologists also track the effectiveness of treatment and monitor patients to prevent disease progression.
Hepatology plays an important role in research and development in the field of liver diseases. Hepatologists conduct research for new ways to diagnose, treat and prevent liver disease.
Specialists examine the mechanisms of disease development, identify new markers and risk factors, and develop innovative therapeutic approaches. This allows for continuous improvement in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with liver exams.
Hepatology emphasizes the diagnosis, management, and prevention of liver disease. Advances in hepatology and research greatly increase the chances of successful treatment and prevention of liver disease, improving the quality of life of patients and the health of society.
 Modern drugs in gastroenterology
Modern drugs in gastroenterology
Modern medicine provides a wide arsenal of pharmacological agents to cure gastroenterological diseases. Modern medicines can relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, accelerate healing of mucous membranes and prevent relapses.
Omeprazole, esomeprazole, and pantoprazole reduce stomach acid production. PPIs are widely used to treat gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, reflux esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Antacid preparations (e.g., aluminum, magnesium, calcium) help neutralize stomach acid and fight heartburn and dyspepsia. Often used for symptomatic control in gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Drugs such as histamine blockers (e.g., cimetidine, famotidine) and histamine-2 receptor inhibitors (e.g., raglan) reduce stomach acid production and can be used for peptic ulcers and gastritis.
In Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs such as sulfasalazine, mesalazine and biologic drugs aimed at suppressing the immune response is mandatory.
Probiotics, such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, may be helpful in maintaining a healthy gut flora and reducing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.
Drugs aimed at relieving intestinal smooth muscle spasms (antispasmodics), such as Drotaverine (No-shpa), may be useful for relieving pain discomfort in irritable bowel syndrome and other functional GI disorders.
In recent years, biologic drugs have become an important element in the treatment of some gastroenterologic diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis, when conservative therapy is ineffective. These drugs can modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Combinations of antibiotics (usually amoxicillin, clarithromycin) with proton pump inhibitors are used to treat Helicobacter pylori infection associated with the development of peptic ulcers and gastritis.
Modern drugs in gastroenterology provide an opportunity for precise and targeted treatment of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the choice of drug should be made by the physician based on a thorough diagnosis and evaluation of the patient’s history. An optimal treatment approach, consideration of individual factors and regular monitoring allow for the best results in the management of gastroenterological diseases.
 Gastroenterological diseases
Gastroenterological diseases
Many people are diagnosed with gastroenterologic diseases every year. They have different causes and symptomatology. However, timely detection is very important to keep your gastrointestinal tract healthy.
Functional disorders of the GI tract are characterized by changes in organ function that are not accompanied by structural changes. This includes irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) with its characteristic symptoms such as abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea, as well as functional dyspepsia, which manifests as digestive disorders.
The inflammatory process affects different parts of the gastrointestinal tract. This applies to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and enteritis. These conditions can cause pain, bleeding, and digestive disorders.
This group includes fatty hepatosis, hepatitis (viral and alcoholic), cirrhosis, cholestasis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, gallstone disease and others. These diseases can lead to liver dysfunction, gallstones and other complications.
Inflammatory processes such as acute and chronic pancreatitis, as well as cysts and tumors of the pancreas, are included in this group of diseases. The pancreas plays an important role in the digestive process, and its disorder can cause serious problems.
Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), achalasia, reflux (including gastroesophageal reflux – GERD) and other esophageal pathologies are also part of gastroenterologic diseases. It is a chronic condition in which the acidic contents of the stomach back up into the esophagus, causing irritation. GERD provokes esophagitis, esophageal ulcers, and other complications.
Cancers are also included in this group. They require comprehensive treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities.
Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the stomach or duodenum, contributing to the appearance of bleeding and other complications.
Some conditions may be mild and require only dietary therapy or medication, while others may be serious and require surgery or long-term therapy. It is important to see a qualified gastroenterologist for proper diagnosis, treatment, and disease management to promote GI health and overall well-being.
 A hematologist is who and what he treats.
A hematologist is who and what he treats.
Hematology is considered to be one of the most promising and basic fields in medicine. Hematologists diagnose and successfully treat many diseases in this area each year.
Who’s a hematologist
A hematologist is a physician who specializes in the field of hematology, which studies the functions and changes in blood composition. Hematology is a serious field of internal medicine, and specialists are involved in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the blood and bone marrow.
The help of a specialist is very important for patients with hematologic diseases. Hematologists specialize in various aspects of science, including the study of blood and hematopoietic organs, detection and treatment of blood disorders, transfusion procedures, and management of hemostasis.
Studies in hematology
Hematologists detect various blood disorders using laboratory tests. They analyze blood composition, blood cell count and composition, clotting function, the presence of anticoagulants and other parameters to determine the presence and type of disease.
Hematologic studies include:
- general blood work;
- molecular genetic analysis;
- cytogenetic studies;
- bone marrow biopsy.
Hematologic diseases
Hematologists treat a wide range of blood disorders, including:
- anemia: hematologists determine the cause of anemia (iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency or genetic disorders) and prescribe iron preparations or vitamin complexes;
- hemophilia: doctors specialize in diagnosis and screening, looking for a genetic disorder characterized by low levels of blood clotting traits. Treatment may have an intermittent infusion;
- Leukemia: this is a type of blood cancer that occurs in the hematopoietic system. Specialists diagnose and treat the disease using chemotherapy, radiation therapy and bone marrow transplants;
- Myelodysplastic syndrome: this is a group of hematopoietic communities that can progress to leukemia. Hematologists prescribe treatment based on the extent of the course and the patient’s symptoms;
- Thrombophilia: followed by treatment of thrombophilia and disorders that lead to recurrent blood clots. Treatment may be with anticoagulants and other drugs.
Hematologists also prescribe transfusion procedures, including transfusions of blood and blood components. They manage blood banks, check blood is safe and appropriate before transfusion, and deal with complications.
Hematology is closely related to oncologic, immunologic diseases, as many hematologic diseases are systemic in nature and can cause various organ dysfunctions and malfunctions in the body.
Hematologists are involved in the diagnosis, detection, and identification of blood disorders. Their work helps patients with hematologic conditions receive medical care and improve their quality of life.
 Hepatology as a science
Hepatology as a science
Hepatology is the branch of medicine dedicated to the study and treatment of liver disease. The liver is one of the most important organs in the human body, performing many functions including synthesizing important proteins, neutralizing toxins, and more. Liver disease can have serious consequences and requires a specialized approach.
What diseases does hepatology study
Hepatology studies various aspects of liver diseases, their causes, mechanisms of development, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Hepatologists are engaged in research on pathological processes occurring in the liver, and develop new methods of diagnosis and treatment of diseases of this organ. The main subjects of study in hepatology are:
- Viral Hepatitis: Hepatologists study the different types of viral hepatitis, such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. They study how the viruses are transmitted and develop therapies for these diseases. They investigate how viruses are transmitted and develop therapies for these diseases.
- Fatty liver disease: Accumulation of fat in the liver that leads to inflammation and cirrhosis. Hepatologists study the mechanisms of fatty liver disease and develop therapies to prevent the progression of the disease.
- ABP: develops due to excessive alcohol consumption and can cause organ damage. Hepatologists study the effect of alcohol on the liver, mechanisms of disease development and develop therapeutic techniques, rehabilitation measures.
- Development of cirrhosis and liver failure: A condition in which the organ is unable to function fully. Cirrhosis refers to the last stage of many chronic liver diseases. In this case, healthy liver tissue is changed to scar tissue. Hepatologists study the causes and mechanisms of this disease and develop techniques and strategies for therapy of these conditions.
Treatment of hepatologic diseases
Given the diagnosis, hepatologists develop individualized treatment plans. They may consist of:
- Drug therapy: The use of various drugs that reduce inflammation, improve liver function, destroy infections and maintain the general condition of patients;
- Nutritional therapy: Nutritional recommendations to improve liver function and reduce the burden on the liver. It is a mandatory restriction of fats, sugar, alcohol or salt;
- procedures or surgical treatment: This includes surgical interventions such as liver transplants, tumor removal, or abscess drainage.
Hepatology as a science studies diseases of the liver. The specialty supports liver health, prevents the development of complications, and improves patients’ quality of life. Modern methods developed by hepatologists contribute to early detection and effective therapy of liver diseases, thus improving treatment outcomes.
 Gastroenteric allergy
Gastroenteric allergy
Gastroenteric allergy is a form of allergic reaction that is manifested by exposure of the gastrointestinal tract to allergens. It is a complex disease that can affect the digestive system, causing a variety of symptoms.
Gastroenteric allergies are related to the body’s immune response to certain food allergens. It can affect different parts of the GI tract, including the stomach, intestines, and mucous membranes. Symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the type of allergy.
Common symptoms include colic, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and food refusal. In children, gastroenteric allergies can cause underweight and stunting.
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination and analysis of the patient’s medical history. Allergy skin and blood tests are performed to identify allergens. Exclusion diets can be used to identify food allergens.
Eliminating allergens from the diet is the mainstay of treatment. When breastfeeding, mothers can follow a hypoallergenic diet. Special hypoallergenic mixtures can be used for artificially fed babies.
Anti-allergy medications may be used if necessary. Management of gastroenteric allergies includes adherence to dietary restrictions. It is important to read food labels carefully and avoid contact with known allergens.
Gastroenteric allergies can have a serious impact on the quality of life of patients, especially children. Diagnosis and proper management are key to wellbeing. Timely identification of allergies, adherence to dietary recommendations, and use of medication if necessary can help control symptoms and minimize the negative impact of gastroenteric allergies on the patient.
 Hepatologic diseases
Hepatologic diseases
Hepatologic diseases are a broad group of pathologies that are associated with liver dysfunctions. The liver performs many important functions in the body. Because of this, it is very important to monitor the condition of the liver and consult a hepatologist if unusual symptoms occur.
Fatty liver disease
This disease is a disorder of lipid metabolism in which fat accumulates in the liver cells. It can be a result of obesity, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism.
There are two types of fatty liver disease: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). If fatty liver disease is not controlled, it can progress to more serious conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and cirrhosis.
Features of viral hepatitis
It is a group of infectious diseases caused by different hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E). They lead to inflammation of the liver and can cause varying degrees of damage.
Viral hepatitis A and E are transmitted through contact with contaminated food and water, while viral hepatitis B, C and D are transmitted through blood and other infected fluids. Uncontrolled infection with viral hepatitis can lead to chronic viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular cancer.
Features of liver cirrhosis
It is a chronic and progressive disease in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. In cirrhosis, the liver loses its normal structure and functionality. It is caused by alcoholic disease, presence of viral hepatitis, fatty organ disease and autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of the disease can include the appearance of fatigue, jaundice, digestive problems, the formation of ascites (fluid accumulation). The disease can lead to various complications, which is fraught with serious consequences.
Features of hepatocellular cancer
It is a malignant tumor that develops in the liver tissue. A type of cancer usually develops in patients who have chronic cirrhosis or viral hepatitis.
The disease may be asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to diagnose.
Treatment for hepatocellular cancer may consist of surgical removal of the tumor, liver transplantation, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or the use of molecularly targeted drugs.
Hepatologic diseases bring serious health problems because the organ performs many vital functions. Early diagnosis and adequate treatment are important aspects in the management of these diseases.
 Hematology is one of the most important fields in medicine.
Hematology is one of the most important fields in medicine.
Science is related to the circulatory system and plays a vital role in the human body.
Referral to a hematologist occurs in case of various symptoms indicating malfunctions in the circulatory system. Thanks to a timely visit to a specialized specialist, serious health consequences can be avoided.
A hematologist is a specialist in the science that studies the tissues, functions, and disorders of the blood. Hematology plays an important role in the diagnosis, examination, and dissemination of blood and bone marrow diseases.
What are the symptoms for which a hematologist should be consulted?
If you experience prolonged weakness, fatigue, pale skin, dizziness and other symptoms that can occur with low hemoglobin levels in the blood, it is worth seeing a doctor. The hematologist will perform clinical tests to determine the cause of the anemia and develop a treatment plan. In this case, the doctor confirms or rules out anemia.
If you are detected bleeding, frequent bruising, a long time stops blood or on the contrary, blood clots are formed, it is obligatory to consult a hematologist. He will perform tests that will establish the causes of hemostasis and prescribe treatment.
See your doctor if you have enlarged inflammatory nodes, persistent or unexplained fever, weight loss, swelling or lumps in the cranial, axillary or inguinal nodes. He will perform an examination and, if necessary, may recommend a biopsy for signs of inflammation or manifestation in conjunction with bloodstream inflammation.
Hereditary blood disorders such as hemophilia, thrombophilia, or hereditary anemias are managed by hematologists to perform genetic analysis and develop an individualized surveillance and treatment plan.
If leukemia, lymphoma, or other tumors of the hematopoietic organs are suspected, the doctor performs tests including blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and masses.
In the presence of any unusual symptoms, changes in the blood, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialized specialist. He has specialized knowledge and experience in the field of hematology. If diseases are detected, the hematologist will prescribe all necessary tests, establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
 Hepatology – clinical guidelines
Hepatology – clinical guidelines
Hepatology is the medical field that deals with the study and treatment of liver disease. An important aspect of hepatology is the clinical guidelines that are developed for optimal diagnosis, treatment and management of patients with hepatologic diseases.
Diagnosis of hepatologic diseases
Correct diagnosis of liver disease is the first step in determining the patient’s condition and selecting appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis begins with :
- history and physical examination: the physician reviews the patient’s medical history, paying attention to symptoms, duration, risk factors, and comorbidities. A physical exam can help detect signs of liver disease, such as increased liver size or splenomegaly;
- Laboratory tests: blood tests such as measuring liver enzyme levels (e.g., alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase), bilirubin, albumin, and blood coagulation can help assess liver function and detect the presence of abnormalities. Other laboratory tests may include tests for viral markers such as antigens and antibodies to hepatitis viruses, or determination of iron, copper, or other levels;
- instrumental investigations: ultrasound, CT scan, MRI or liver biopsy to determine the structure, size and extent of liver damage.
Methods of therapy of hepatologic diseases
Treatment of hepatologic diseases is based on modern clinical recommendations, which are developed on the basis of scientific research and expert opinion of specialists. The therapy consists of:
- treatment of the underlying disease – aimed at eliminating or reducing the activity of the underlying disease. This may include antivirals for viral hepatitis, drugs to reduce inflammation, or immunomodulators for autoimmune diseases;
- symptom and complication management: symptom relief and complication management are very important. In this case, medications are prescribed to relieve pain, improve digestion, or lower blood ammonia levels in liver failure;
- Lifestyle changes: avoiding alcohol, following a fat- and sugar-restricted diet, being physically active, and avoiding risk factors such as infection with hepatitis viruses;
- Liver transplantation: This is a backup treatment that may be recommended in case of liver failure or ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
Clinical guidelines play an important role in hepatology by providing guidance on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of patients with these diseases. Correct diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease will improve the patients’ condition.
 Hepatology and gastroenterology
Hepatology and gastroenterology
Hepatology and gastroenterology are closely related in the field of medicine. Although these sciences have their own characteristics and specific aspects, they often interact in the diagnosis and examination of patients.
Anatomical links between hepatology and gastroenterology
Hepatology and gastroenterology have an anatomical connection because the liver, biliary tract and gastrointestinal tract interact with each other. The liver plays an important role in the digestive tract, producing bile, which is necessary for the breakdown and inflammation of fats.
The biliary tract, including the biliary vesicles and bile ducts, increase the transfer of bile to the intestines to participate in digestion. Thus, liver and biliary tract diseases are often related to gastroenterologic problems and vice versa.
Hepatology and gastroenterology have similar disease symptoms. Certain diseases such as cirrhosis, chronic viral hepatitis, gallstone disease and hepatitis can affect digestive system function and cause stomach, intestinal or digestive malfunctions.
For example, patients with cirrhosis may have problems with digestion, appetite, stool irregularities, and ascites. Such symptoms require comprehensive follow-up by both hepatologists and gastroenterologists.
Therapies
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases arising with the digestive system often require the participation of specialized specialists in both areas.
For example, if liver disease is suspected, a patient may be referred to a hepatologist for diagnostic tests such as biochemical blood tests, ultrasound or liver biopsy.
Once a diagnosis is identified, a hepatologist can suggest appropriate treatment, which may involve the use of specific medications or surgical interventions.
Doctors recommend prevention of hepatopathologic diseases in the form of vaccination against viral hepatitis, refusal of alcohol and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In addition, the collaborative work of hepatology and gastroenterology specialists allows for the integrated development of a therapeutic action plan that takes into account both the liver and the digestive system.
Hepatology and gastroenterology are closely related and very important in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the digestive system. Anatomical relationships, common diseases and symptoms, and shared diagnostic and treatment approaches necessitate the development of effective interventions for patients’ early recovery.
 Hematology– blood work
Hematology– blood work
Blood testing is one of the main techniques used in hematology to diagnose and evaluate the condition of the blood and hematopoietic system. The qualitative analysis provides insight into the stage of hematologic disease. After that, the hematologist prescribes the necessary therapy.
Evaluation of blood tests
Blood tests show the levels of various blood components such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. The following studies are conducted during the analysis:
- total blood count (TBC): to measure the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, white blood cells, platelets and other parameters, to study the shape and size of blood cells (morphology), and to count reticulocytes (young red blood cells). OAC is the primary test for detecting anemia, inflammation, infections, and other conditions;
- Advanced blood work: using additional tests such as measuring hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, total white blood cell count, differential white blood cell count, platelet count, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). It may also include measuring levels of various plasma constituents such as total protein, electrolytes, and functional enzymes;
- Bone marrow: if necessary, a bone marrow puncture may be performed to examine the cells of the hematopoietic system, determine their condition and detect the presence of certain diseases.
Blood tests provide information on various parameters that are key to assessing blood conditions and detecting pathologies. They show the condition:
- hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells and responsible for transporting oxygen in the body. Its level is a major indicator of anemia and other conditions;
- red blood cells, red blood cells. Their number reflects the level of hematocrit. A low red blood cell count is a marker of anemia;
- white blood cells – white blood cells that play a role in the immune system and fighting infections. An elevated white blood cell count may indicate inflammation or infection;
- platelets, the cells responsible for blood clotting. Low platelet levels increase the risk of bleeding, and high levels lead to blood clots.
Blood tests are an integral part of hematologic diagnosis and monitoring of patients with blood disorders. It allows you to assess blood conditions, detect abnormalities and help in making a diagnosis. Blood tests can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and monitor the health status of patients.
